| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
- 1. 8AddressesAndPointers-ObjectiveC
- 2. To understand the way pointers operate, you first must understand the concept of indirection.
- 3. This unary operator, known as the address operator, makes a pointer to a variable in Objective-C.
- 4. Addresses
- 5. console output Addresses
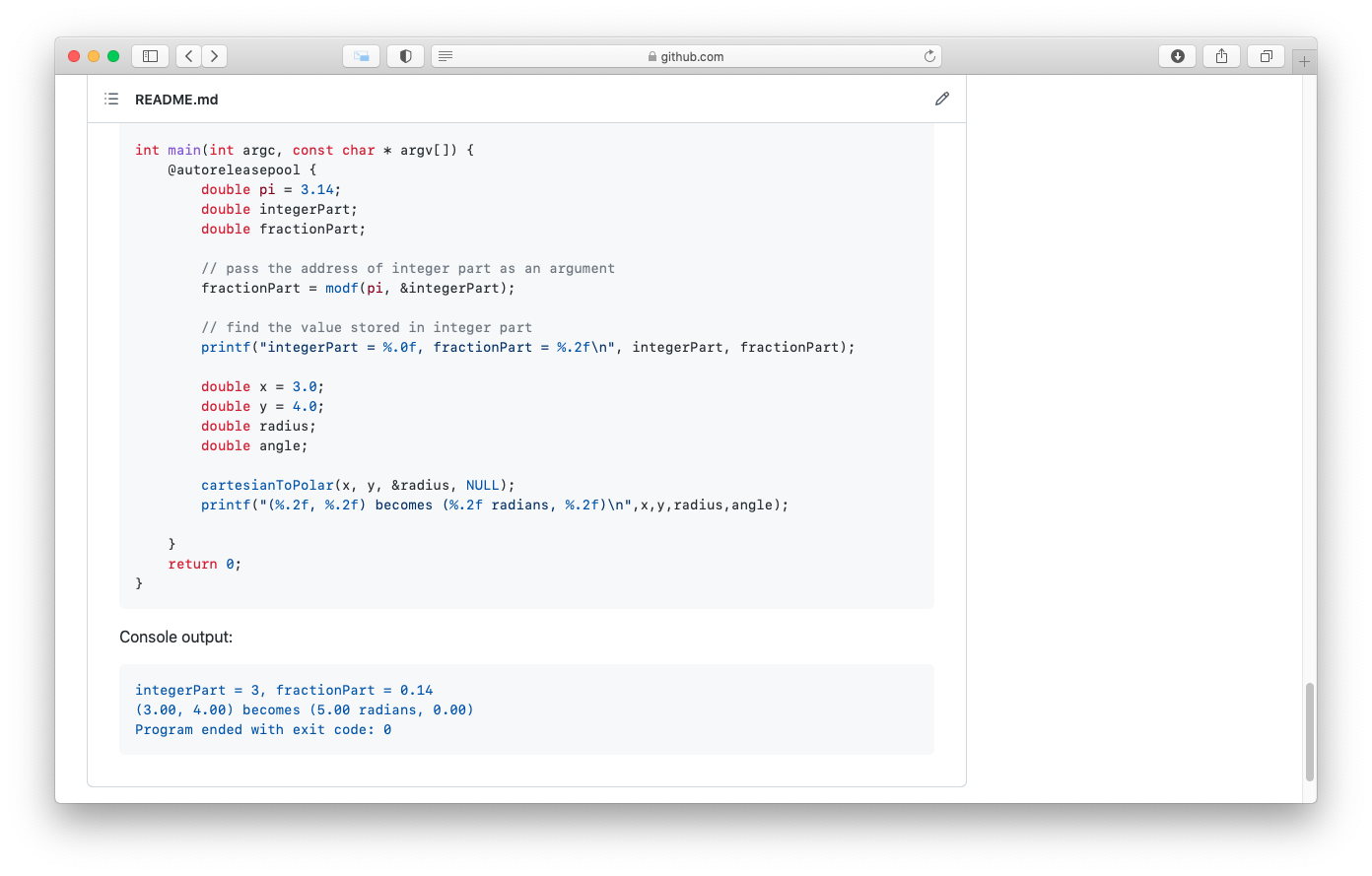
- 6. In a computer, everything is stored in memory, and thus everything has an address.
- 7. Console output
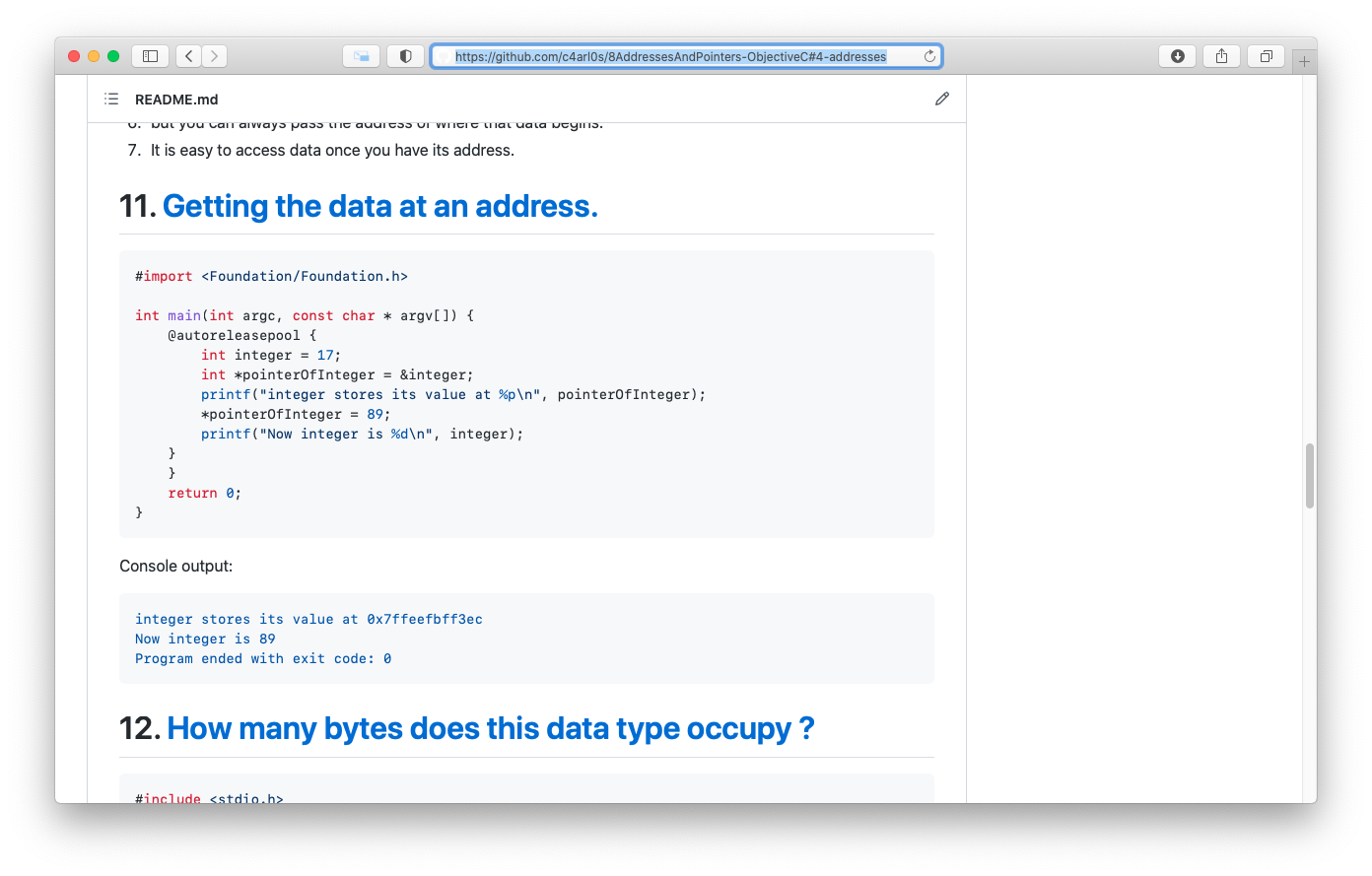
- 8. Getting addresses.
- 9. Use the * operator on the left-hand side of an assignment to store data at a particular address:
- 10. Storing addresses in pointers.
- 11. Getting the data at an address.
- 12. How many bytes does this data type occupy ?
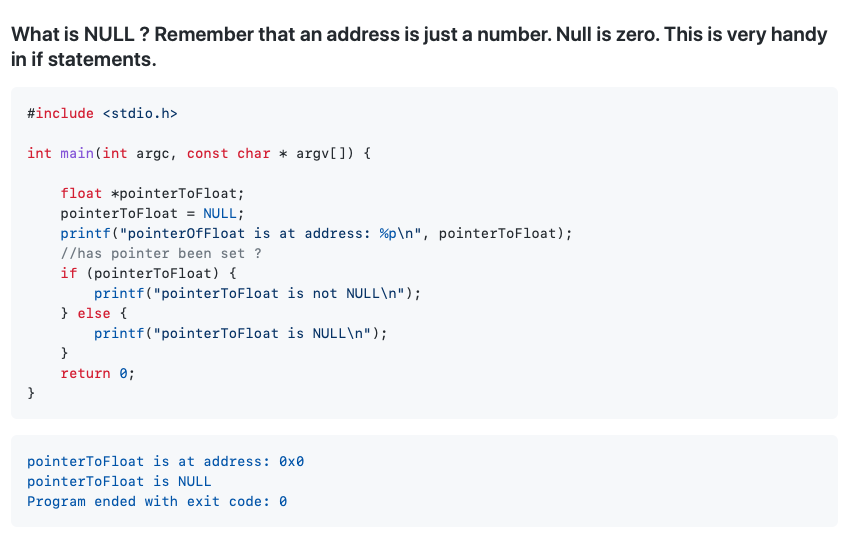
- 13. NULL
- 14. another example
- 15. Stylish pointer declarations.
- 16. A function is not able to change the actual parameters value.
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
- 1. A typedef defines an alias for a type declaration and allow us to use it more like the usual data types.
- 2. Now pass a Person structure to another function.
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
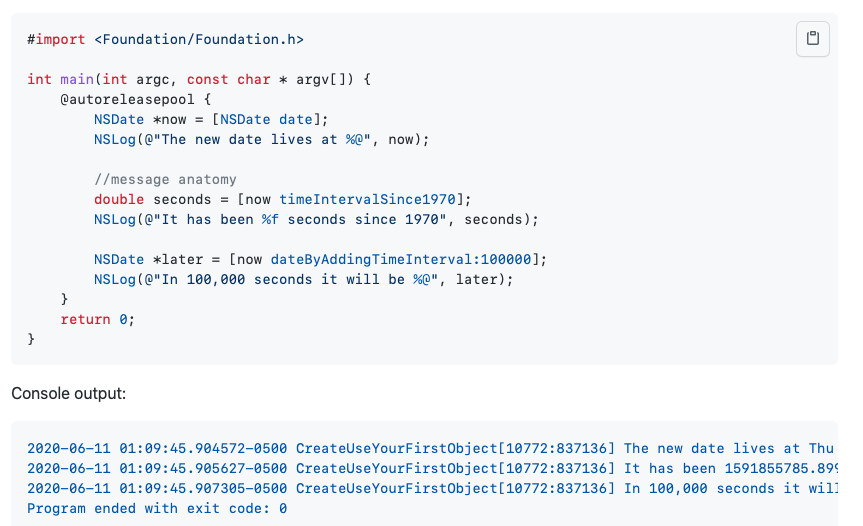
- 1. 11TheHeap
- 2. So far, your programs have only used memory that has been in frames on the stack.
- 3. Programmers often use the word buffer to mean a long line of bytes of memory.
- 4. You claim a buffer of memory using the function malloc().
- 5. When you’re done using the buffer, you call the function free()
- 6. We need a chunk of memory big enough to hold 1,000 floats.
- 7. You can also use malloc() to claim space for a struct on the heap.
- 8. Notice the operator ->
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
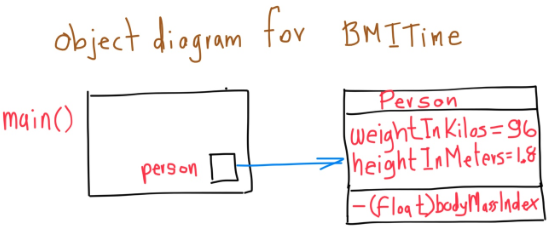
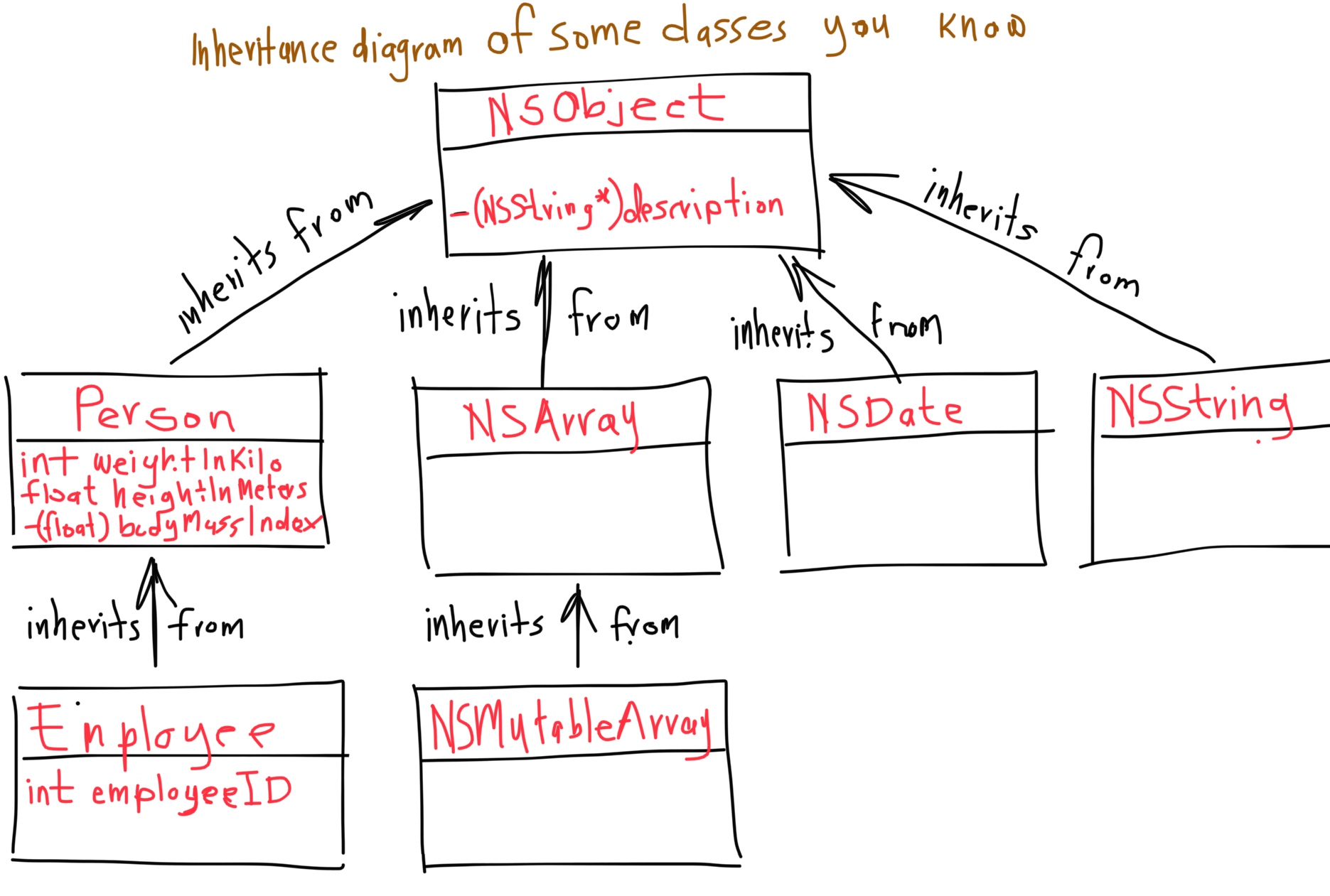
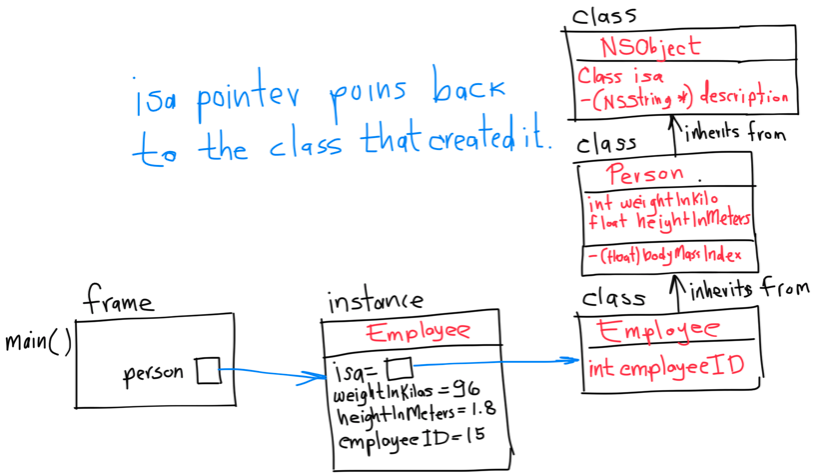
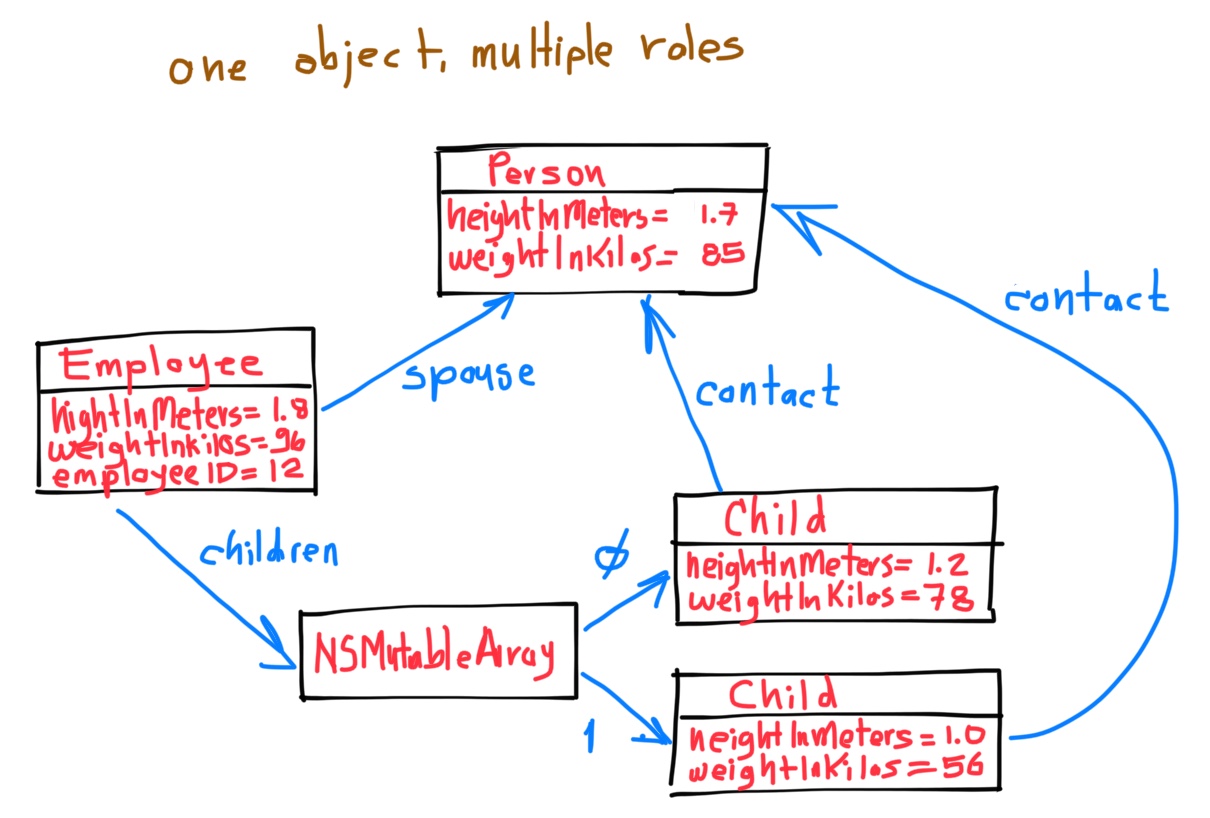
- 1. Your First Class
- 2. Accessor methods
- 3. Dot notation
- 4. Properties
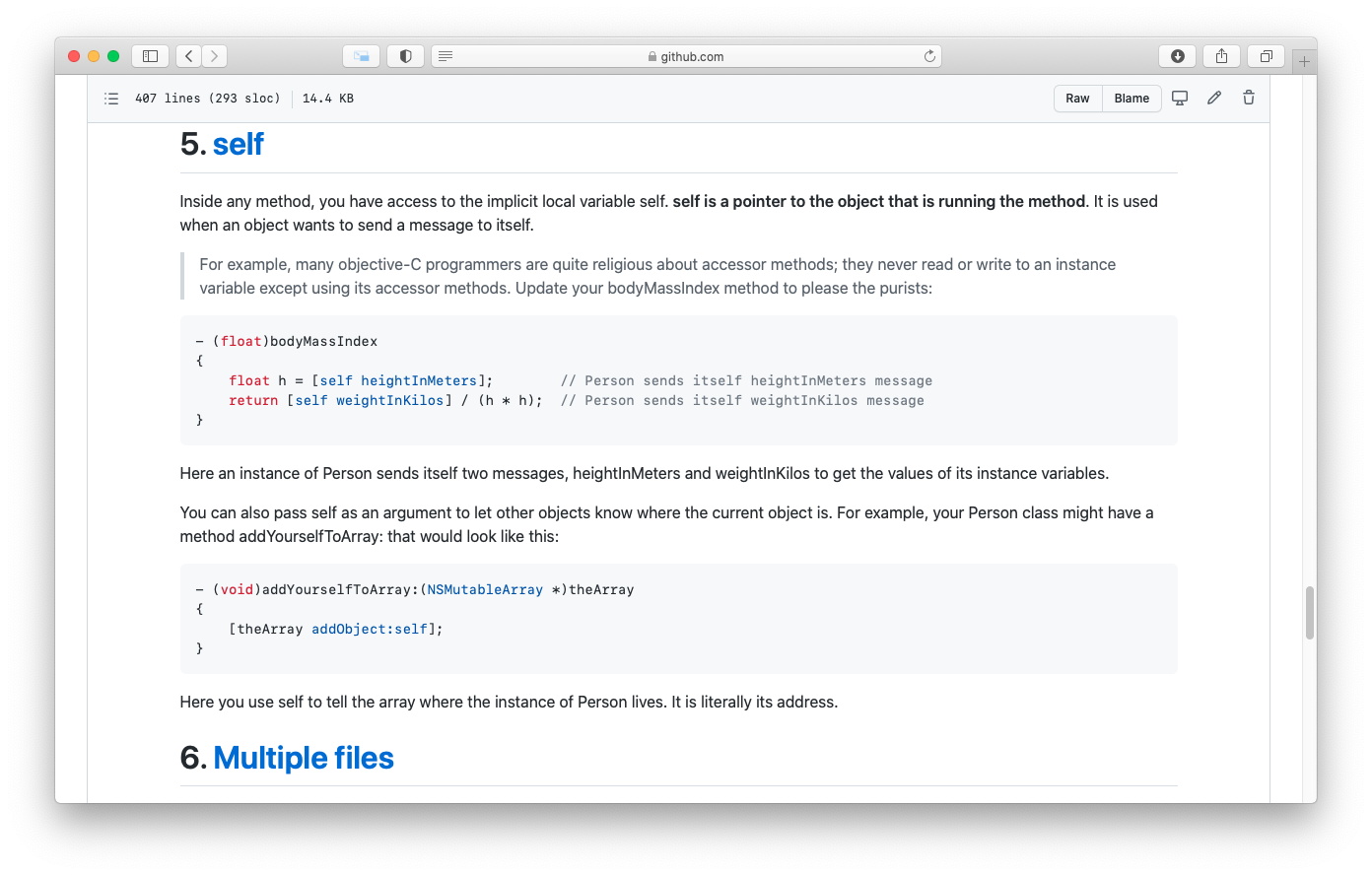
- 5. self
- 6. Multiple files
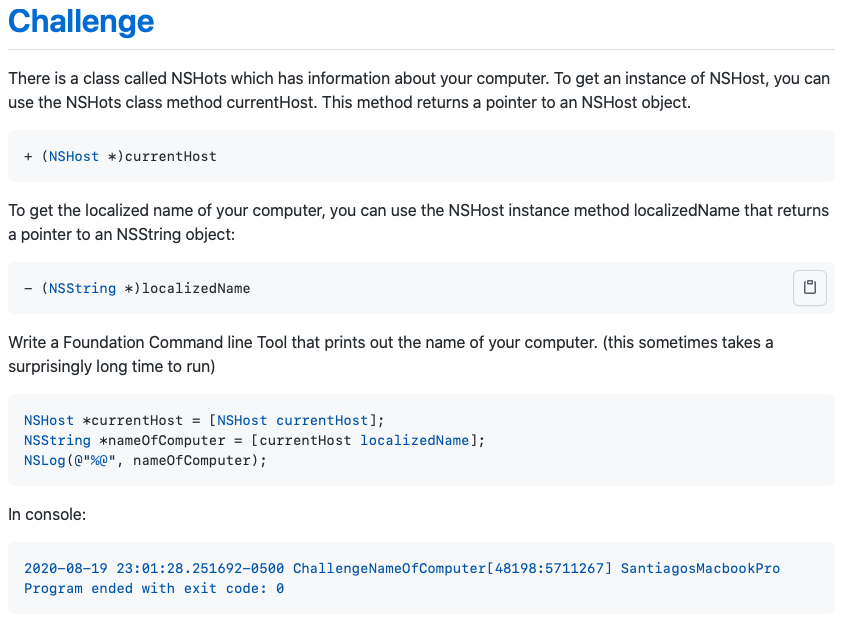
- 7. Challenge
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| At a glance: Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
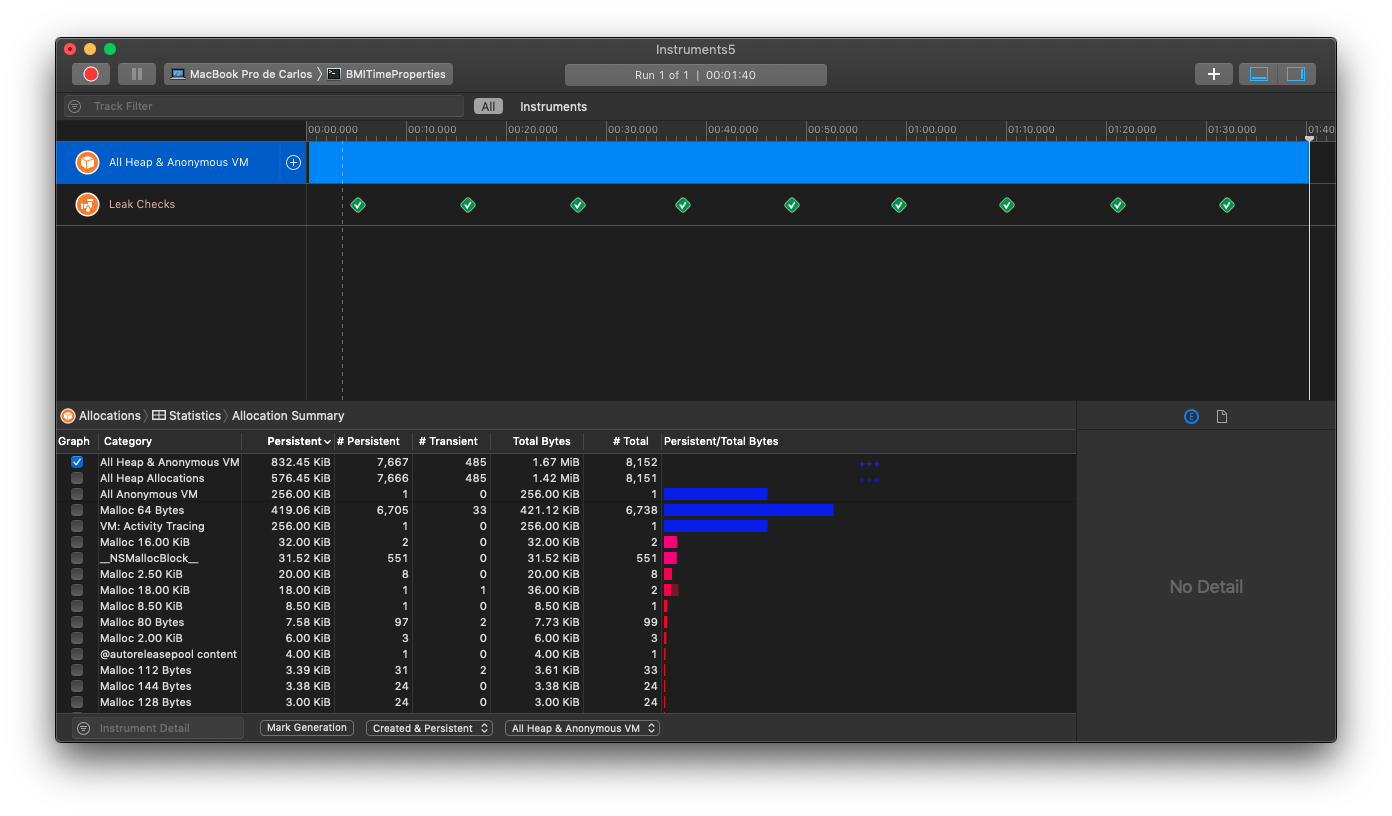 |
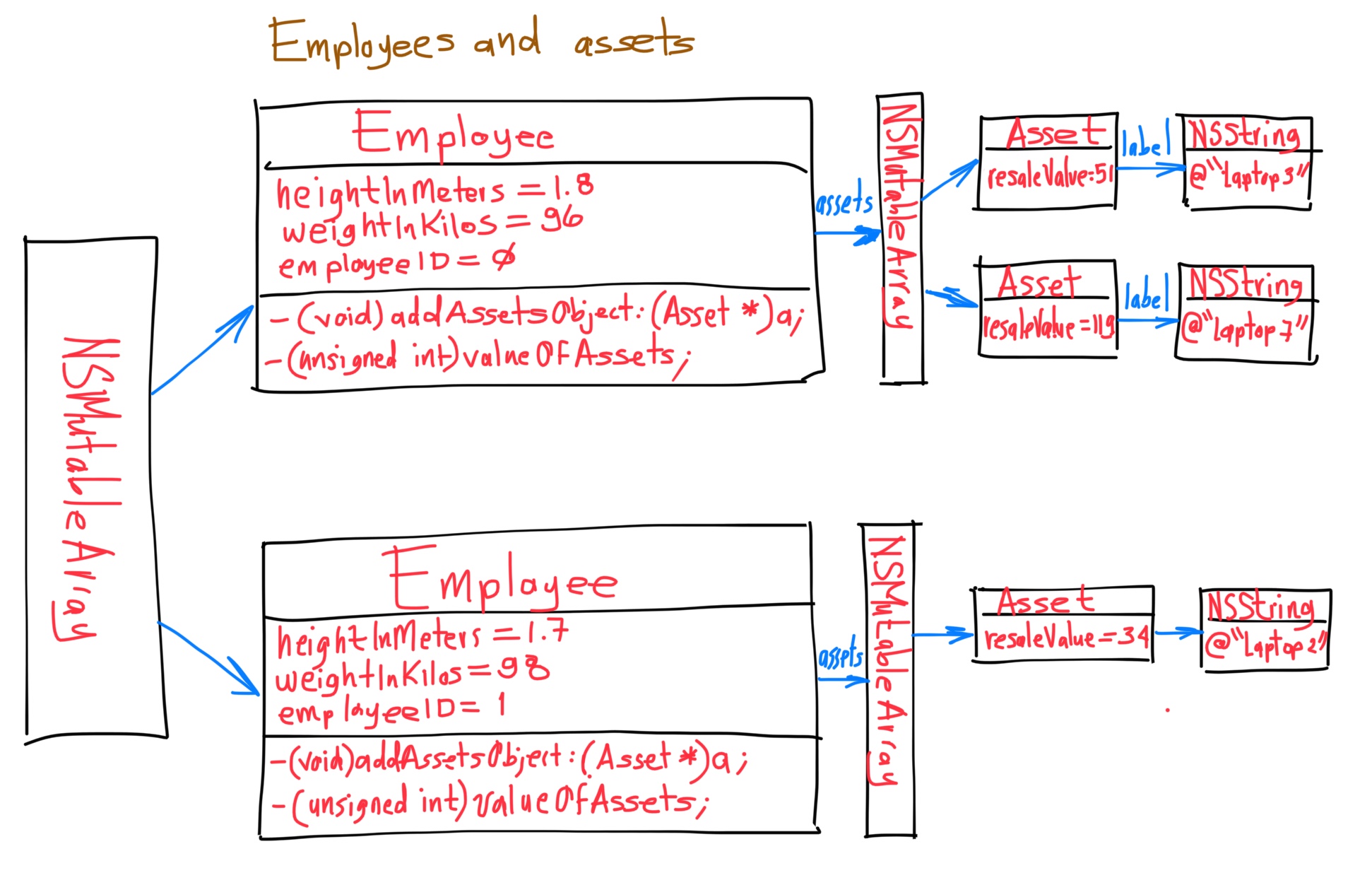
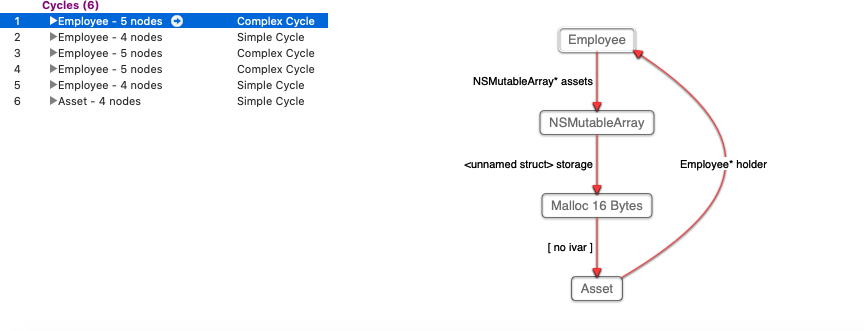
- 1. Retain Cycles
- 2. Weak References
- 3. Zeroing of Weak references
- 4. Manual Reference Counting and ARC History
- 5. New basic example of Retain Cycles
- 6. Retain count rules
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
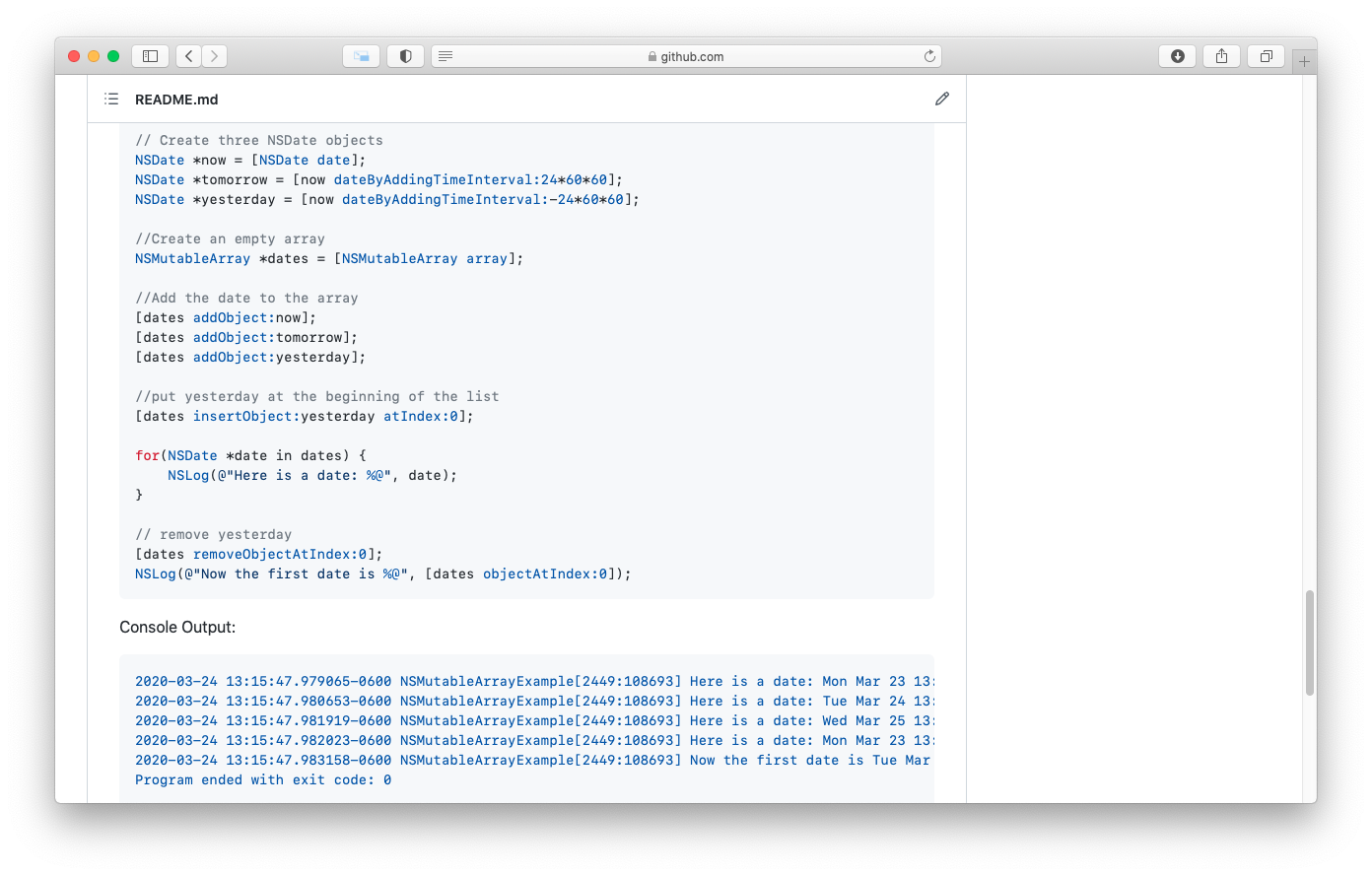
- 1. NSArray / NSMutableArray
- 2. Immutable objects
- 3. Sorting
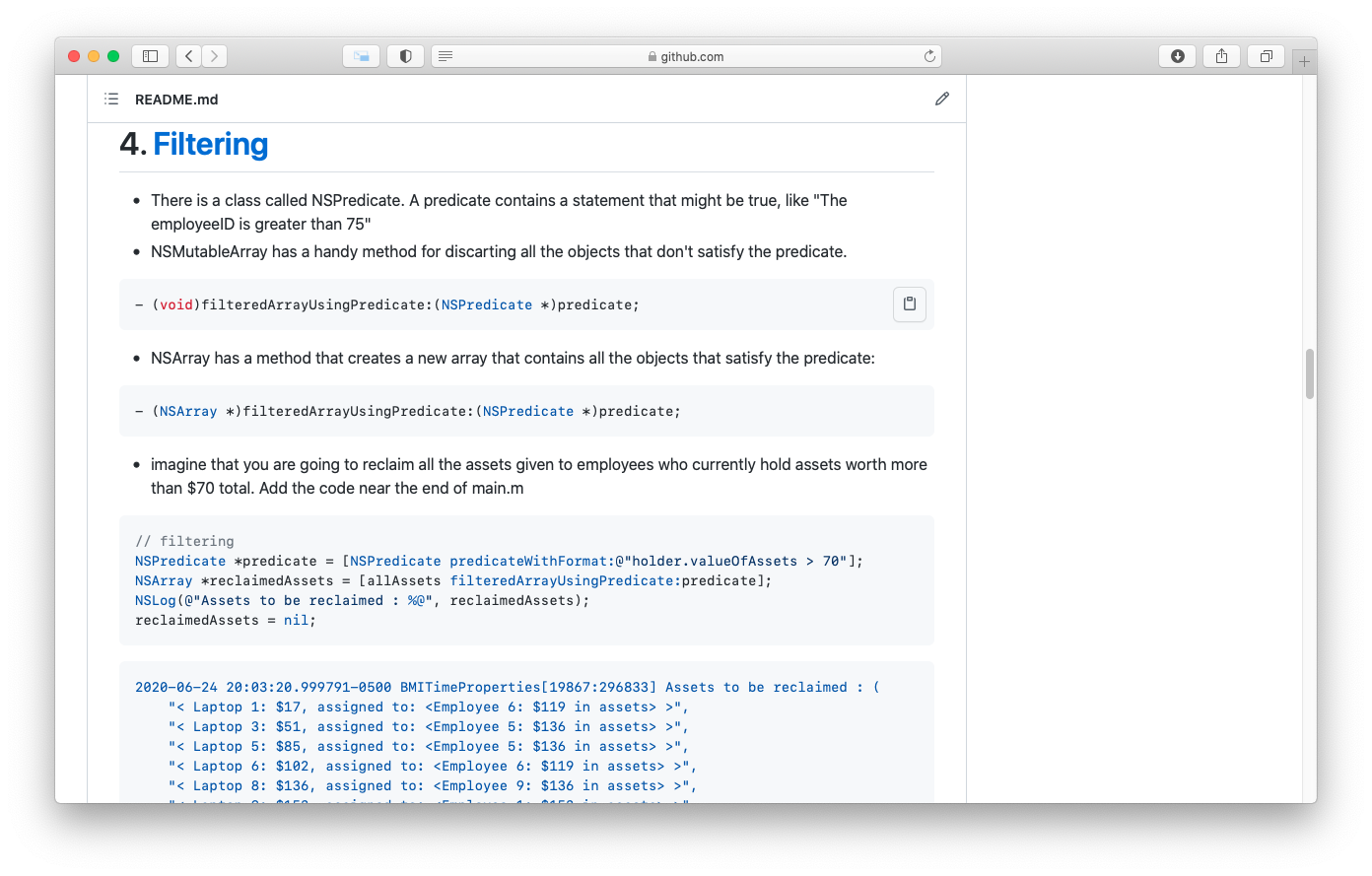
- 4. Filtering
- 5. NSSet/NSMutableSet
- 6. NSDictionary/NSMutableDictionary
- 7. C primitive types
- 8. Collections and nil
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
- 1. Preprocessor directives
- 2. #include and #import
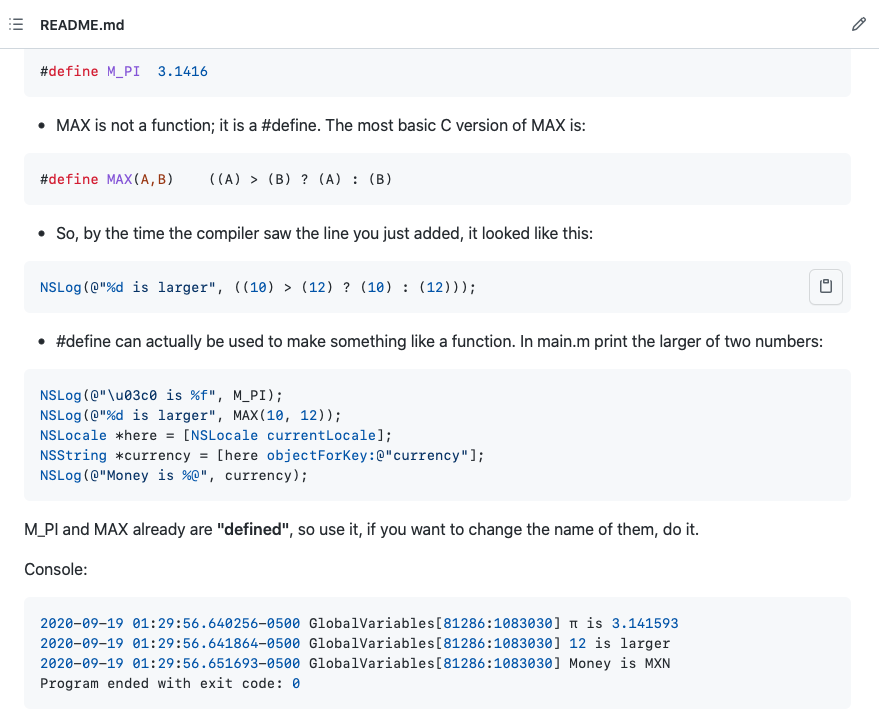
- 3. #define
- 4. Global Variables
- 5. enum
- 6. #define vs global variables
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
- 1. Writing an NSString to a file
- 2. NSError
- 3. Reading files with NSString
- 4. Writing an NSData object to a file
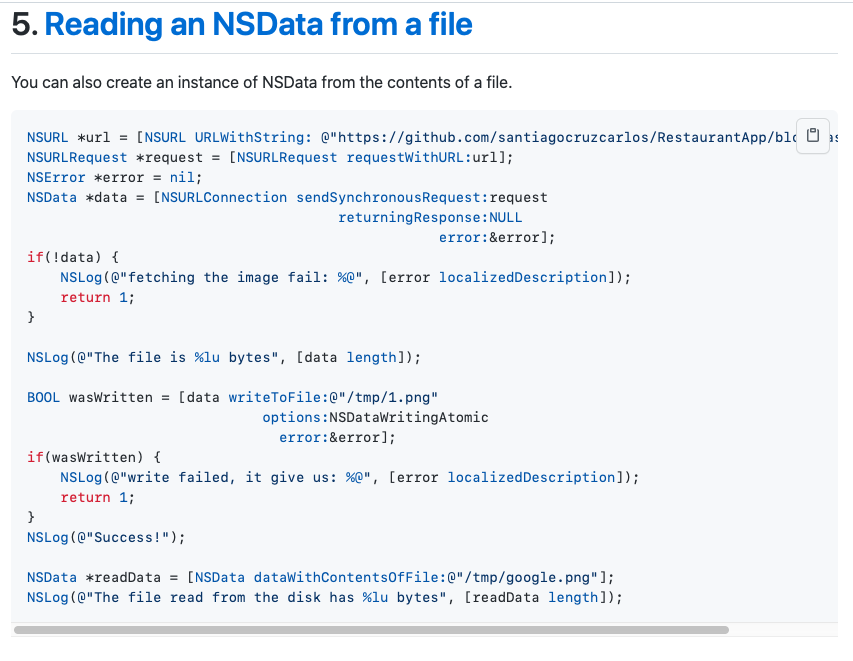
- 5. Reading an NSData from a file
| At a glance: Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
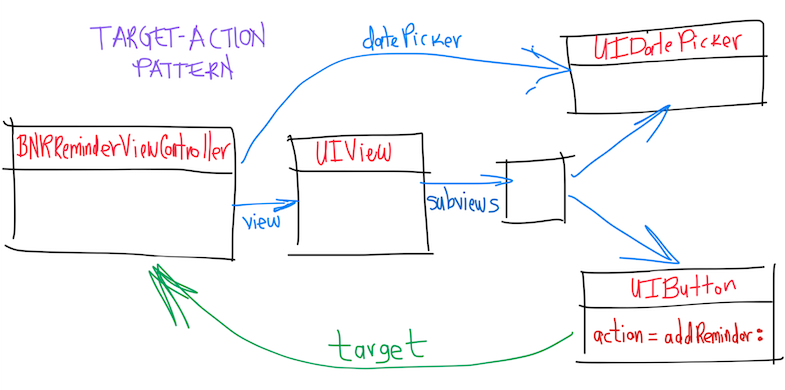
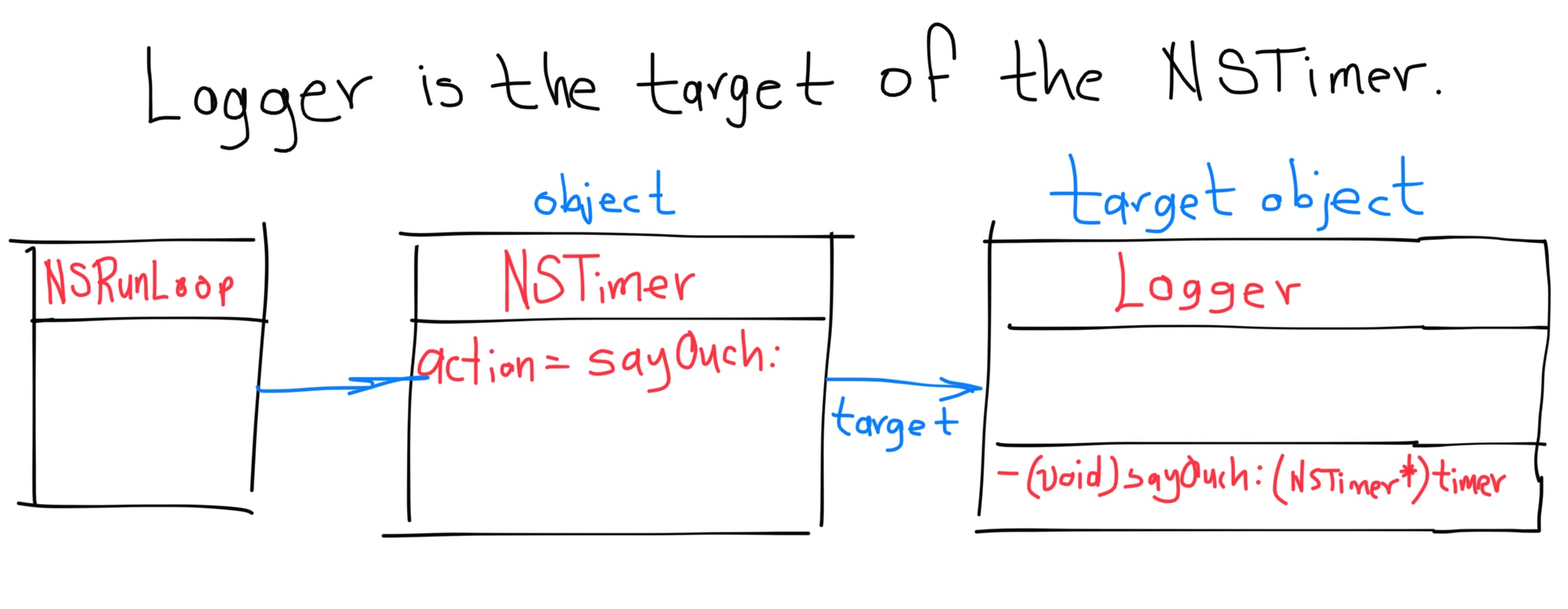
- 1. Target-Action
- 2. Helper Objects
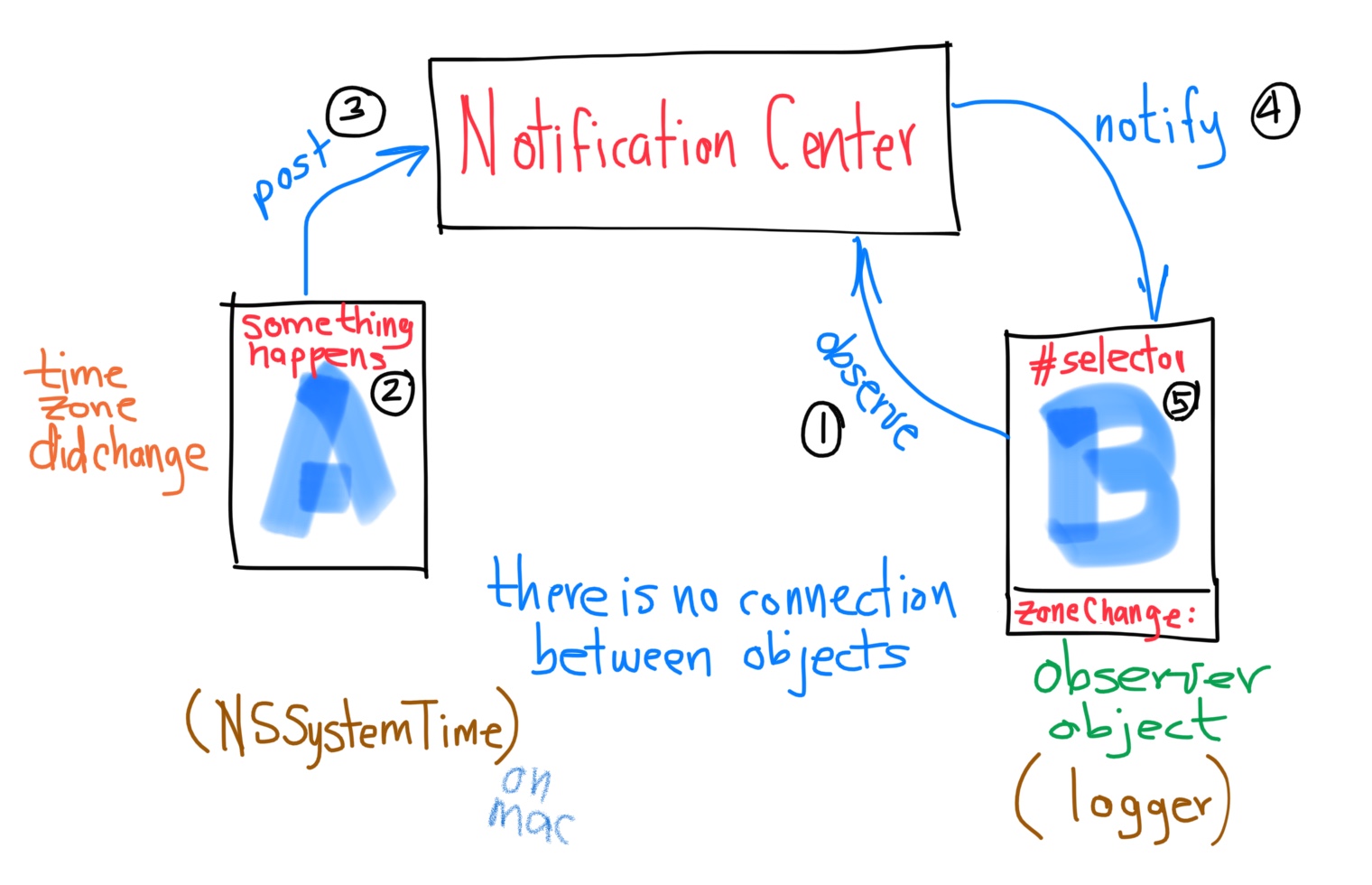
- 3. Notifications
- 4. Which to use
- 5. Callbacks and object ownership
| At a glance: Notes |
|---|
 |
- 1. 25Protocols-ObjectiveC
- 2. It is importan to remember that who you are is different from what you do
- 3. The class of an object is different from its role in a working system.
- 4. We’ve talked about how to specify a class. Is it possible to specify a role?
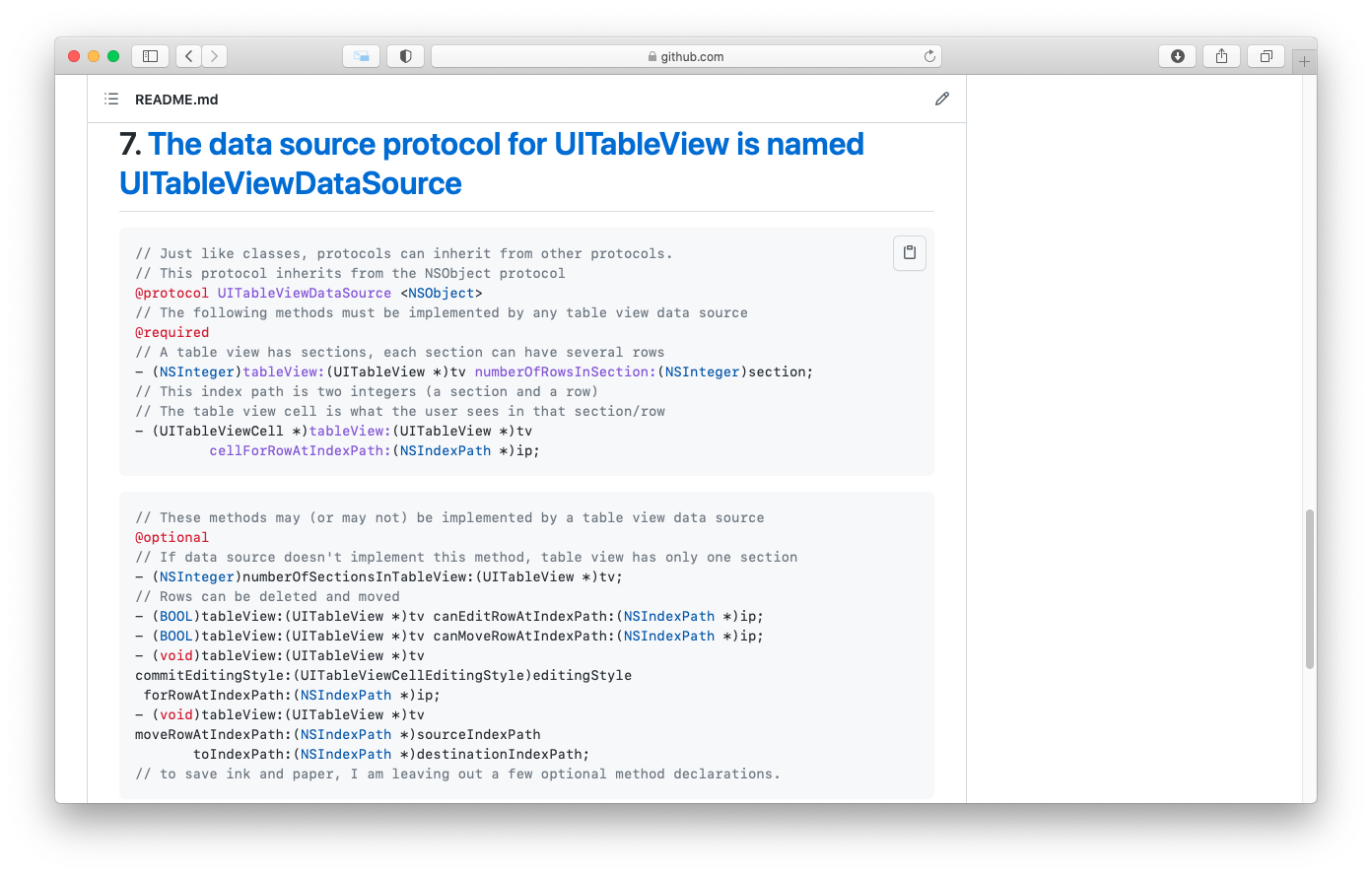
- 5. How did the developer who created the UITableView class specify the role of UITableView’s data source? He created a protocol.
- 6. A protocol is a list of method declarations.
- 7. The data source protocol for UITableView is named UITableViewDataSource
- 8. Do you remember an instance of Logger the delegate of an NSURLConnection object ?
| At a glance: Notes |
|---|
 |
I created a basic app by code (XIB files or storyboards are not used)
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
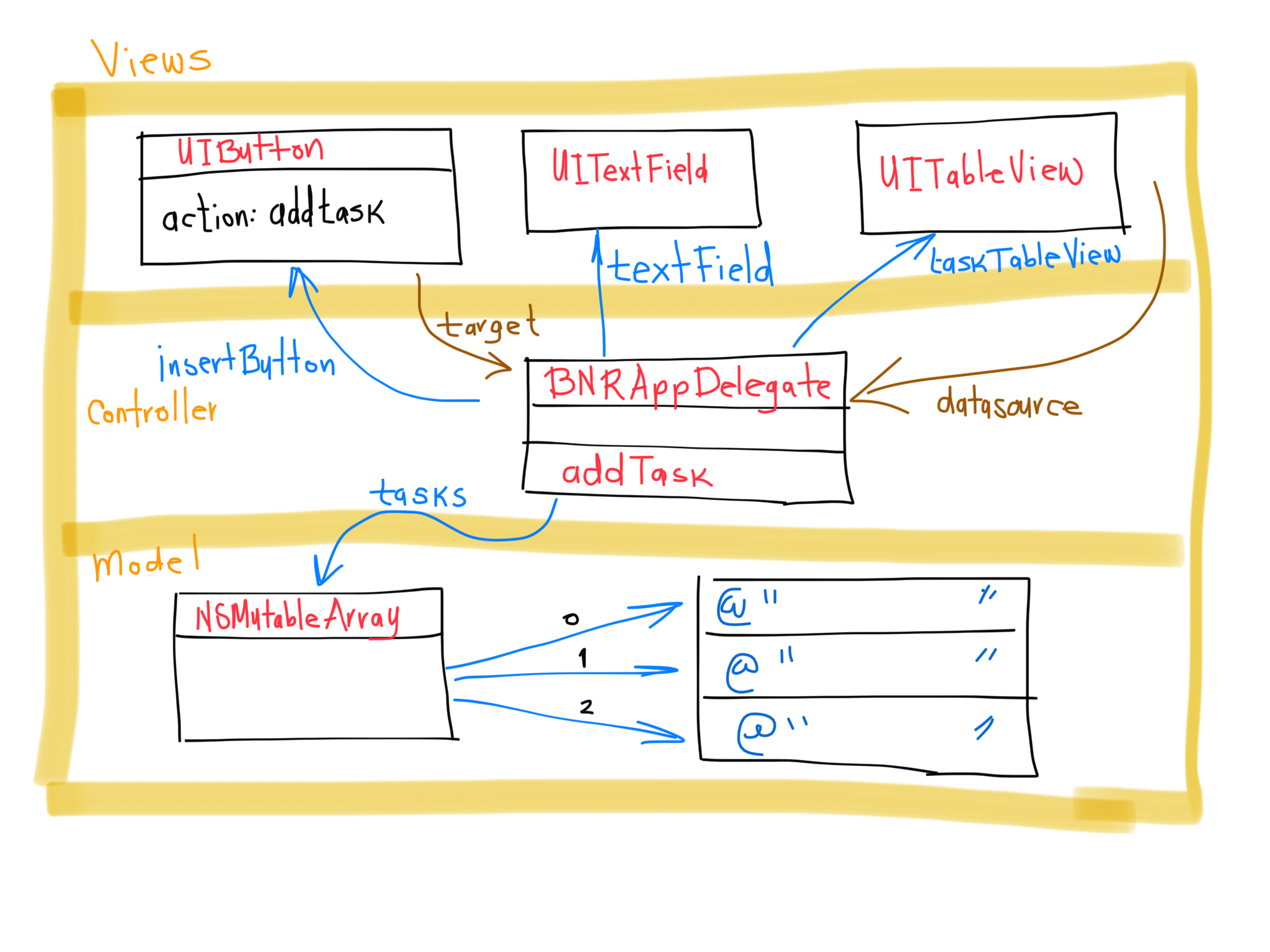
- 1. 27YourFirstiOSApplication
- 2. The run loop waits for events
- 3. Model View Controller
- 4. The UIApplication Object
- 5. The application delegate
- 6. Watch out about this after continue with the project
- 7. AppDelegate.h
- 8. AppDelegate.m
- 9. pragma mark - Application Delegate callbacks
- 10. iOS Documentation: Responding to Notifications and Events
- 11. Setting up the Views
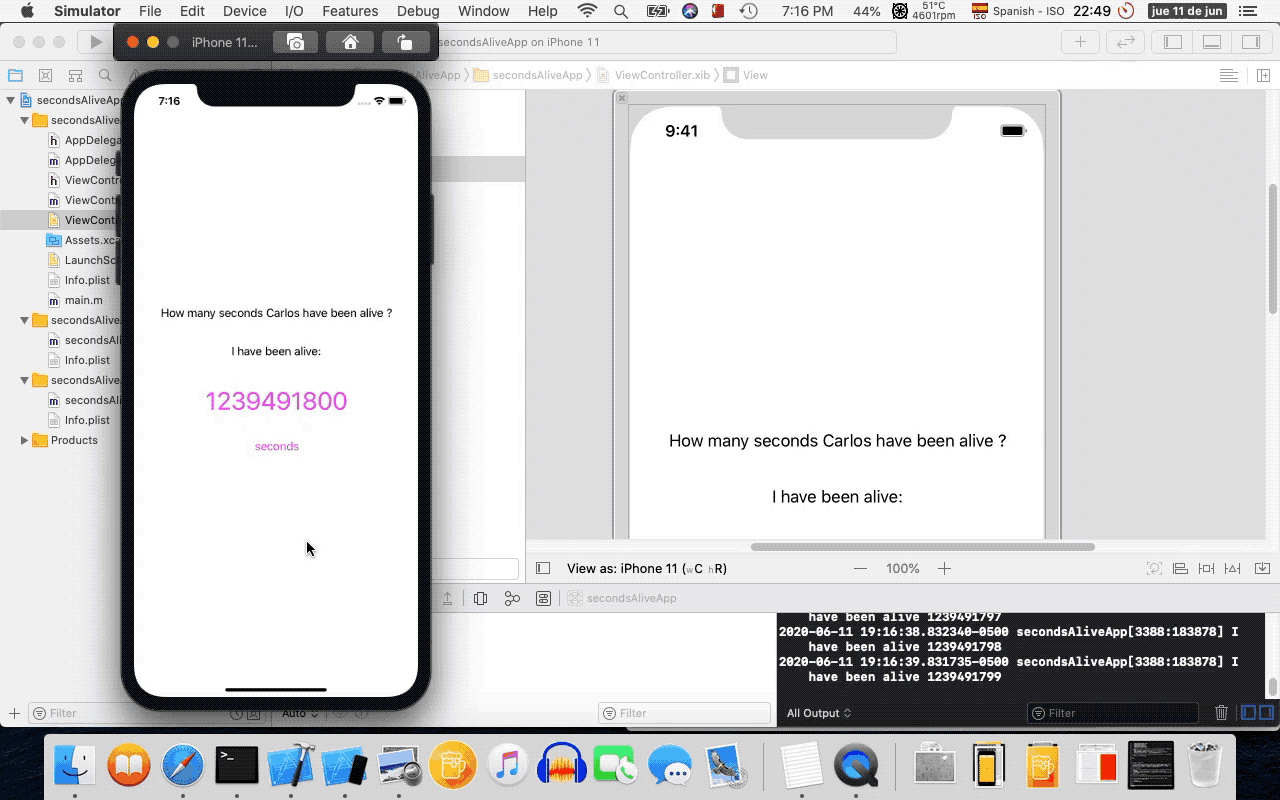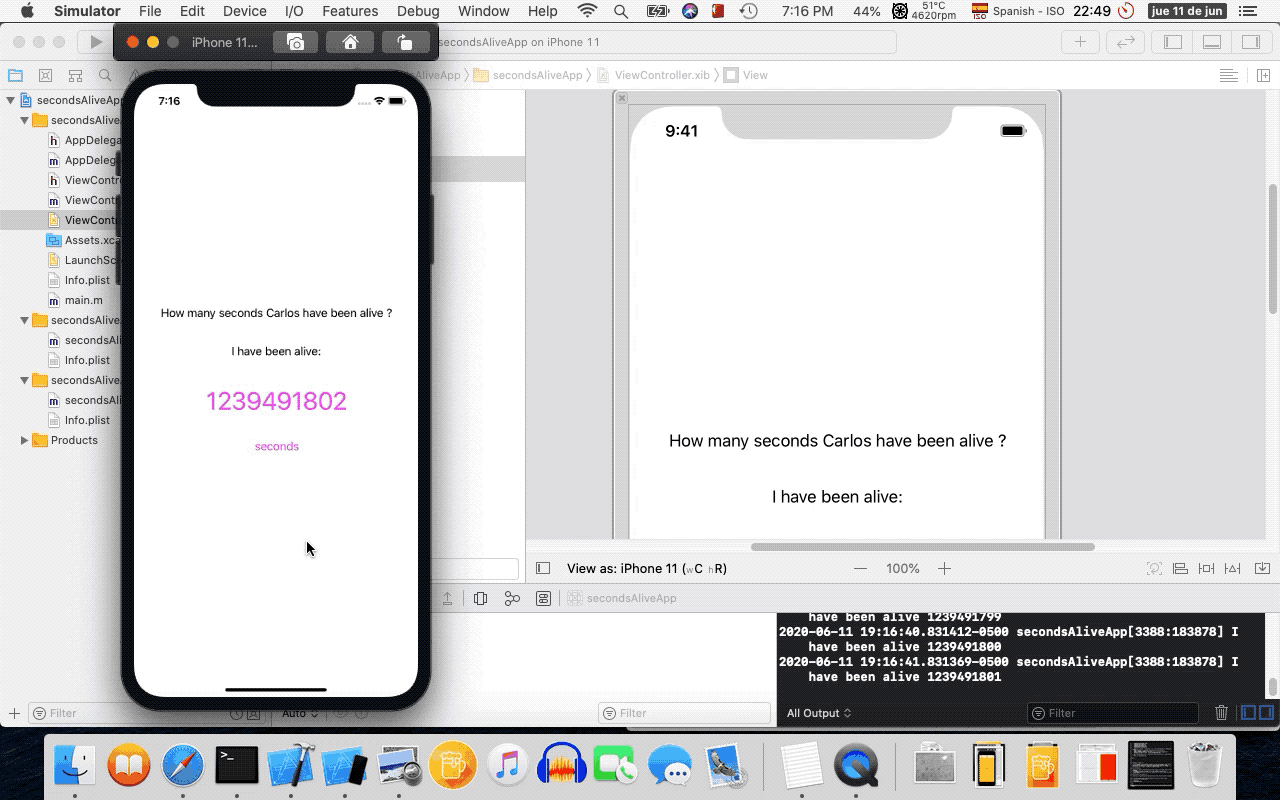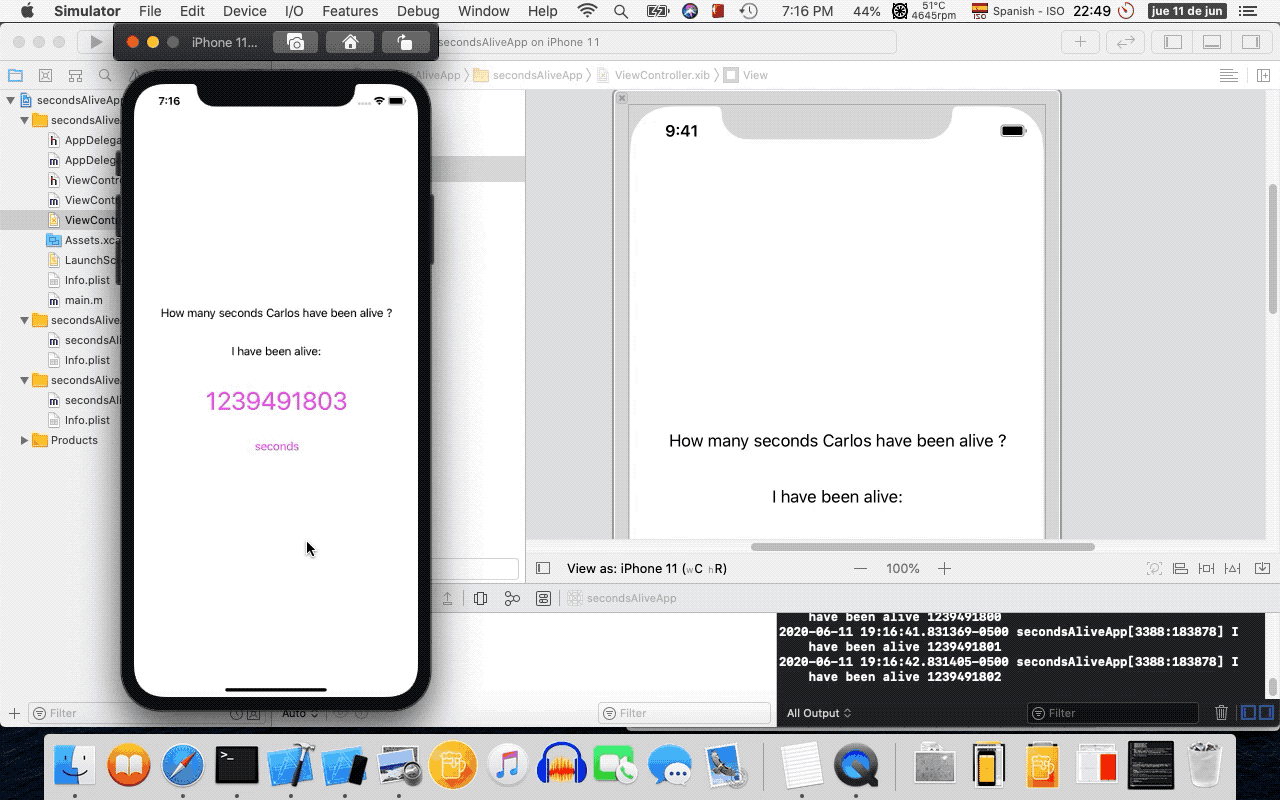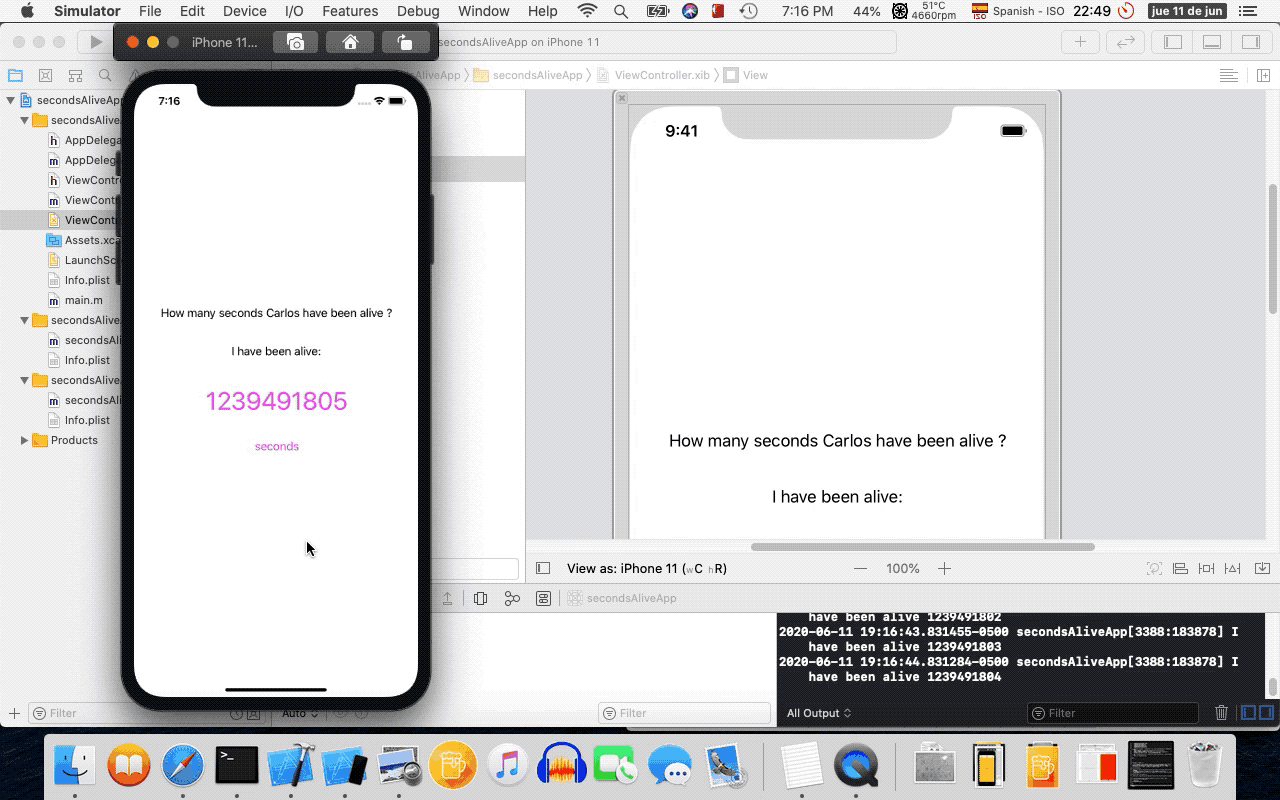
- 12. Running on the iOS Simulator
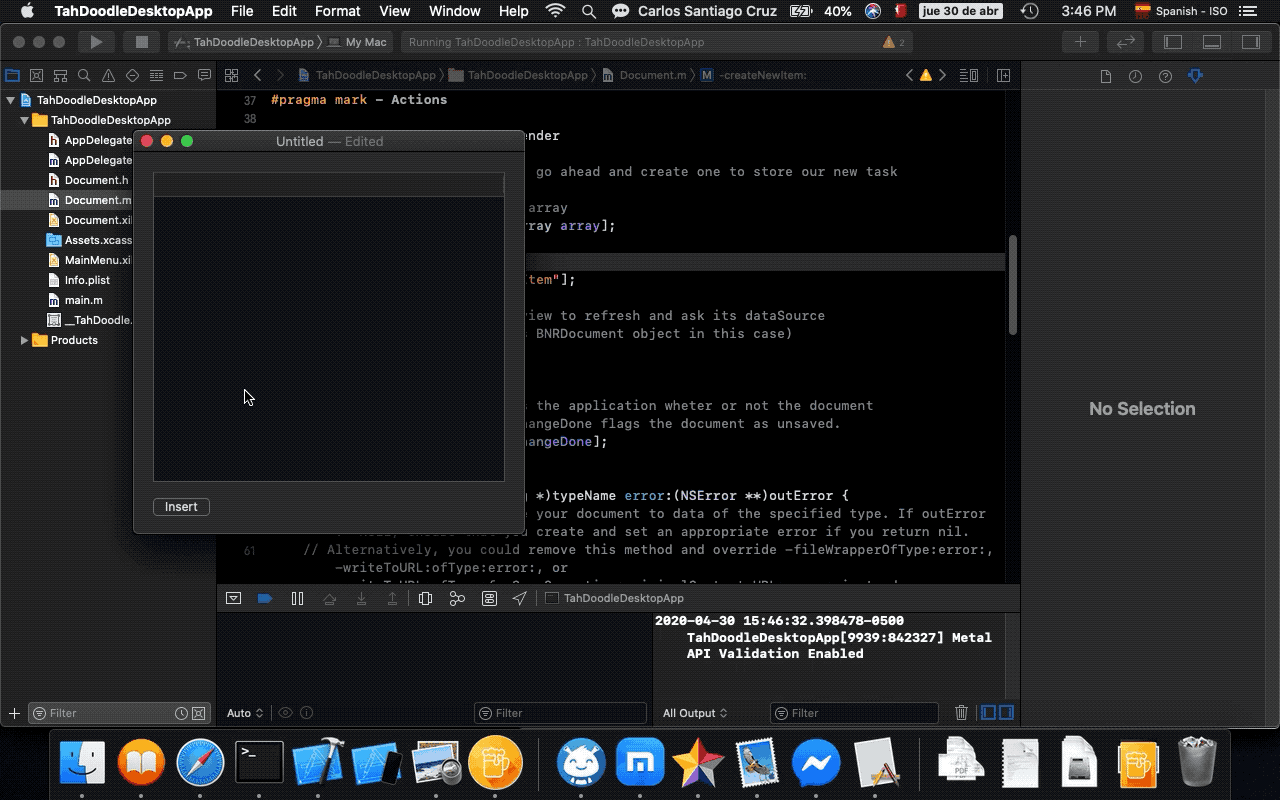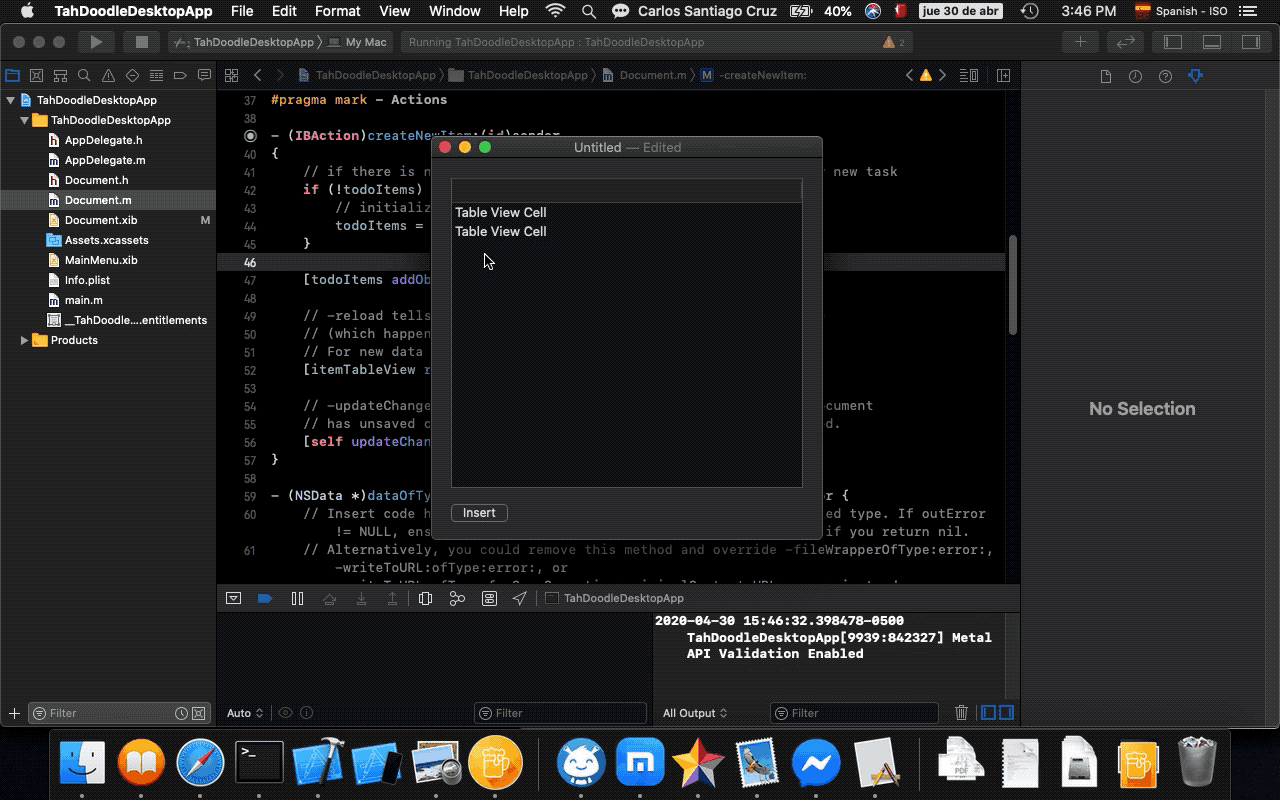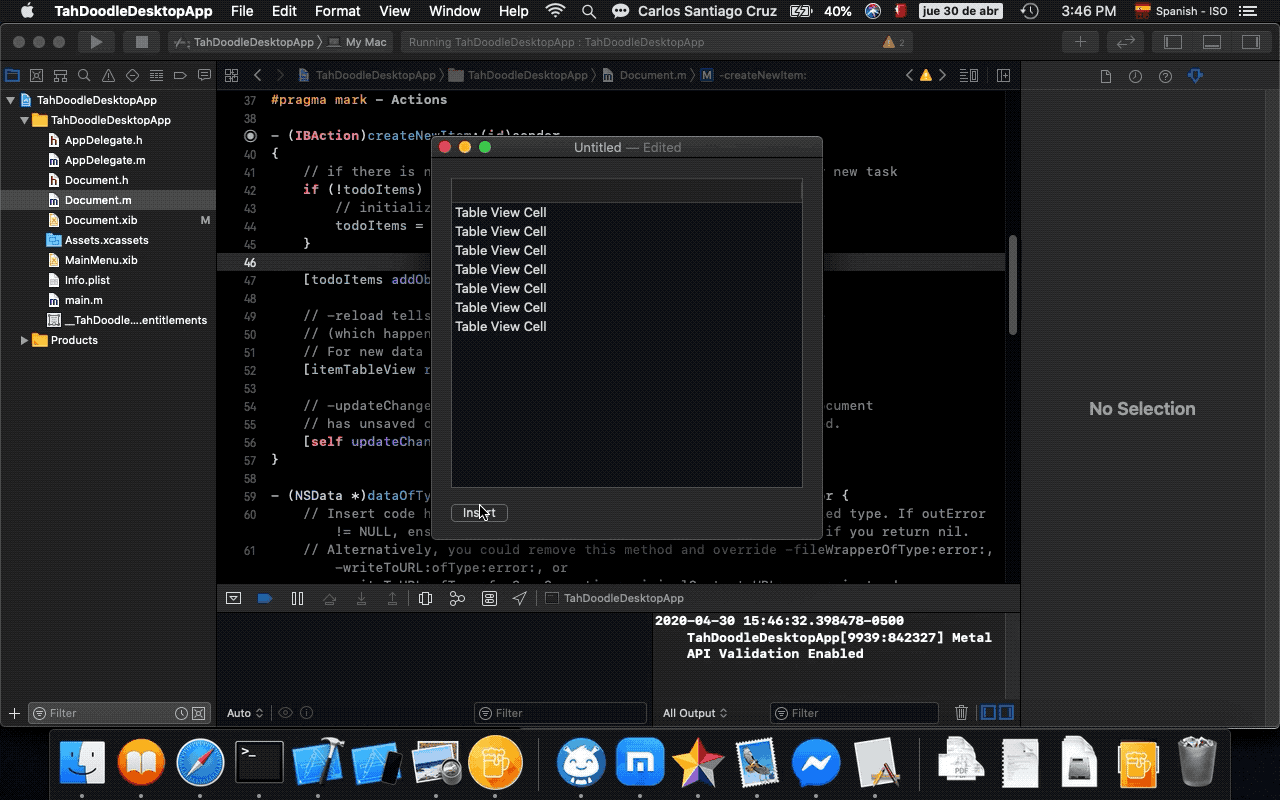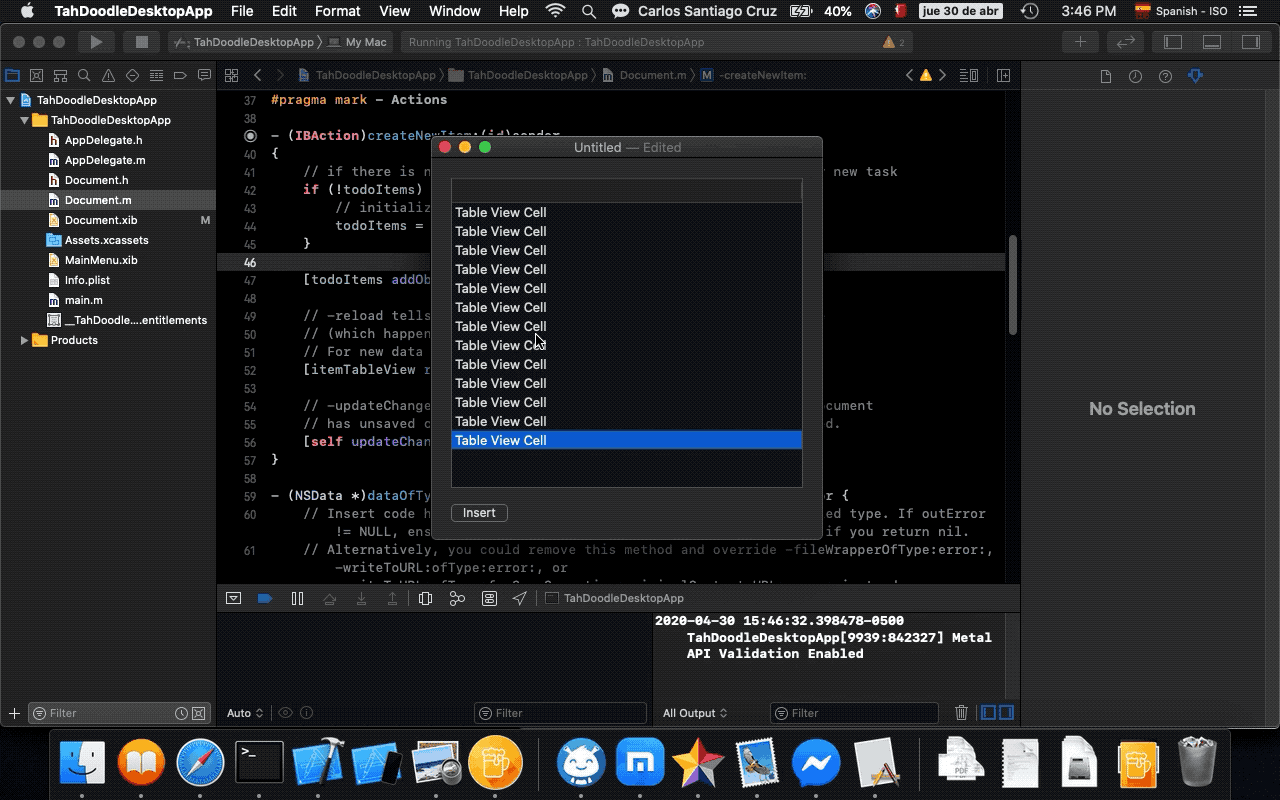
- 13. Adding new tasks
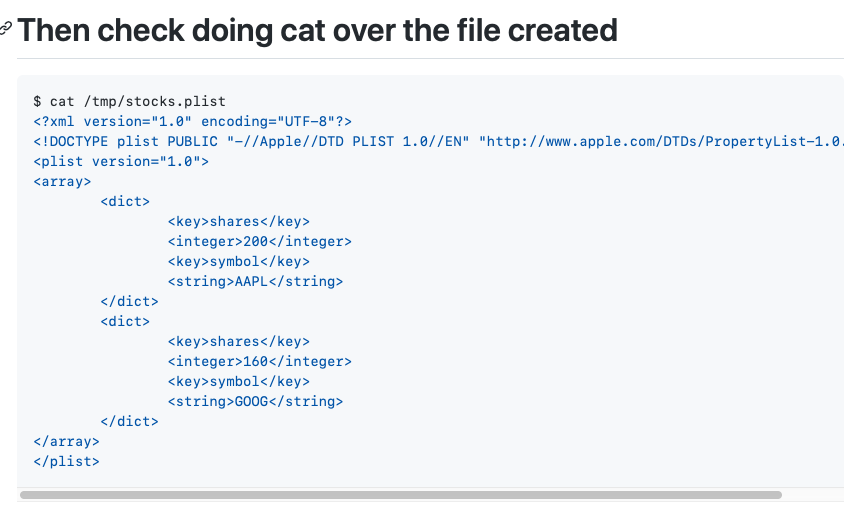
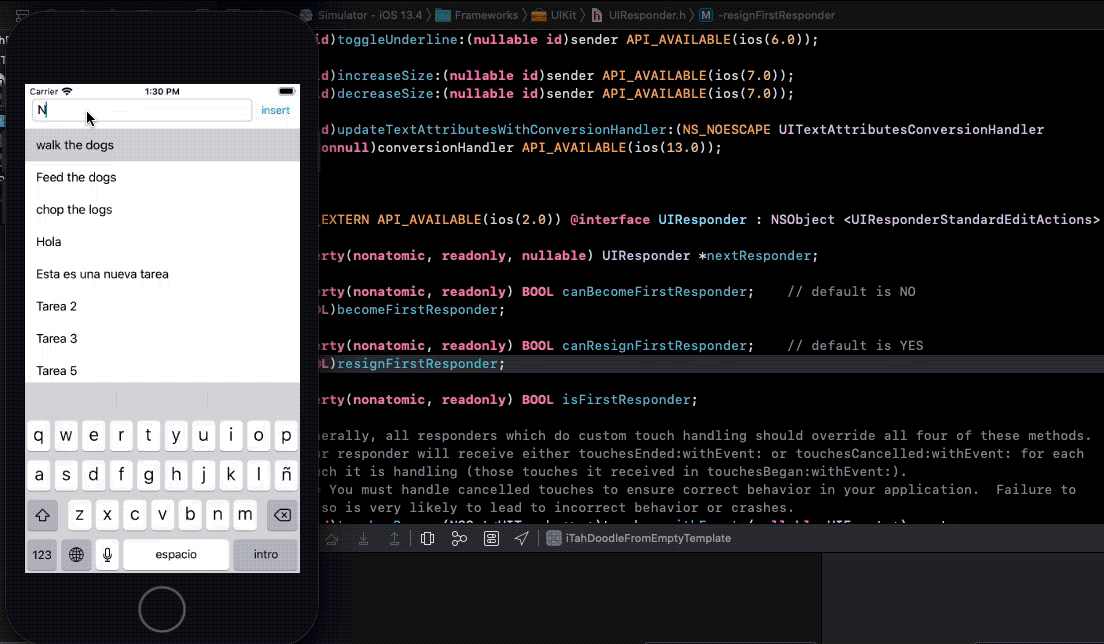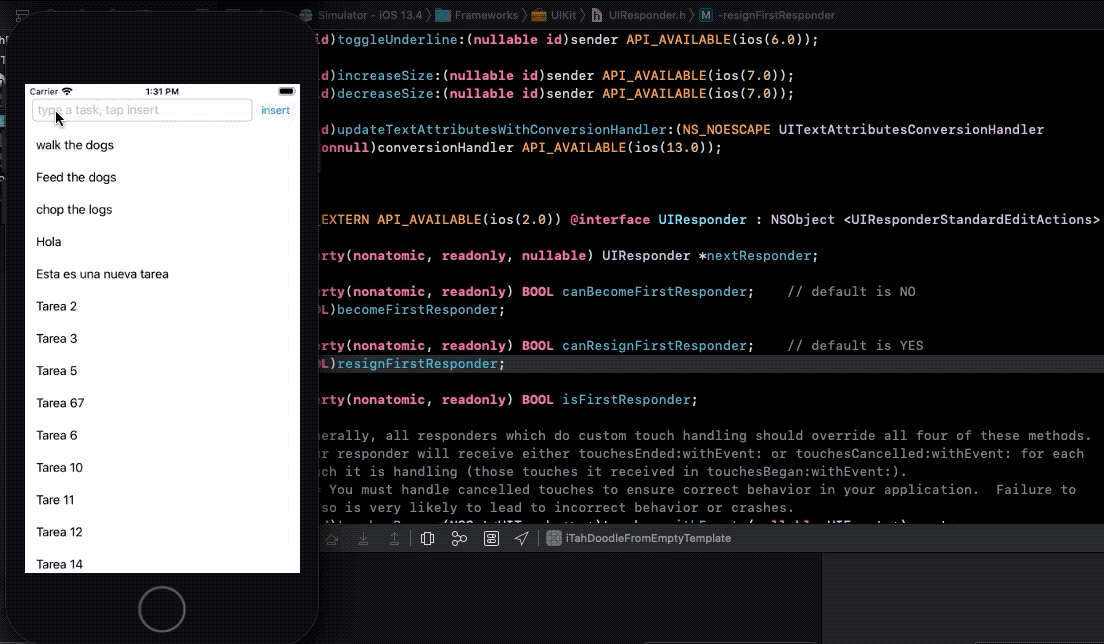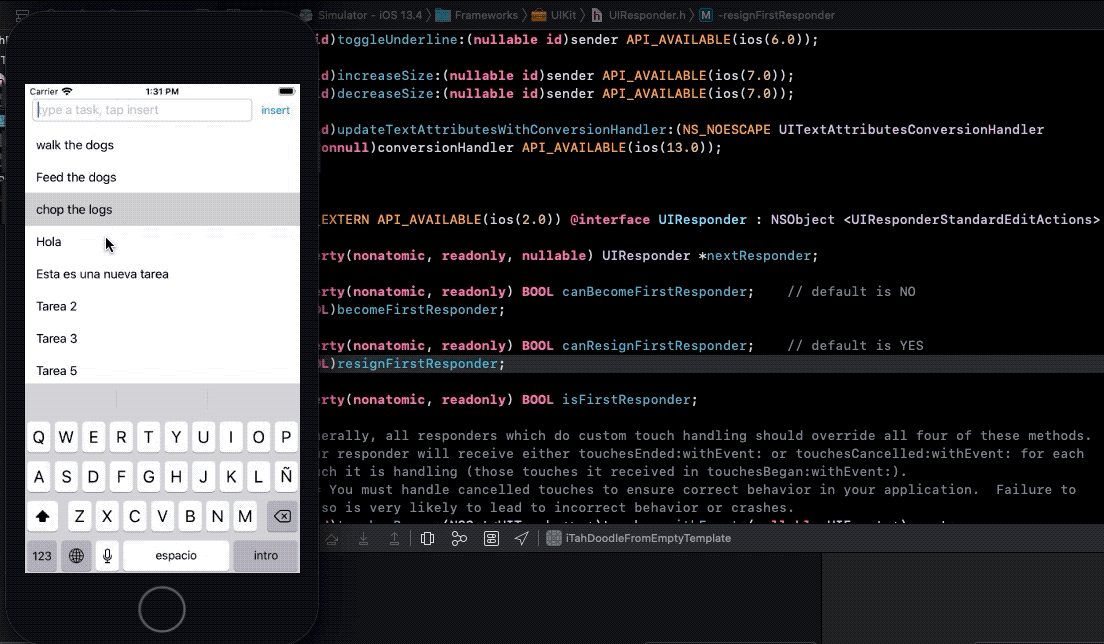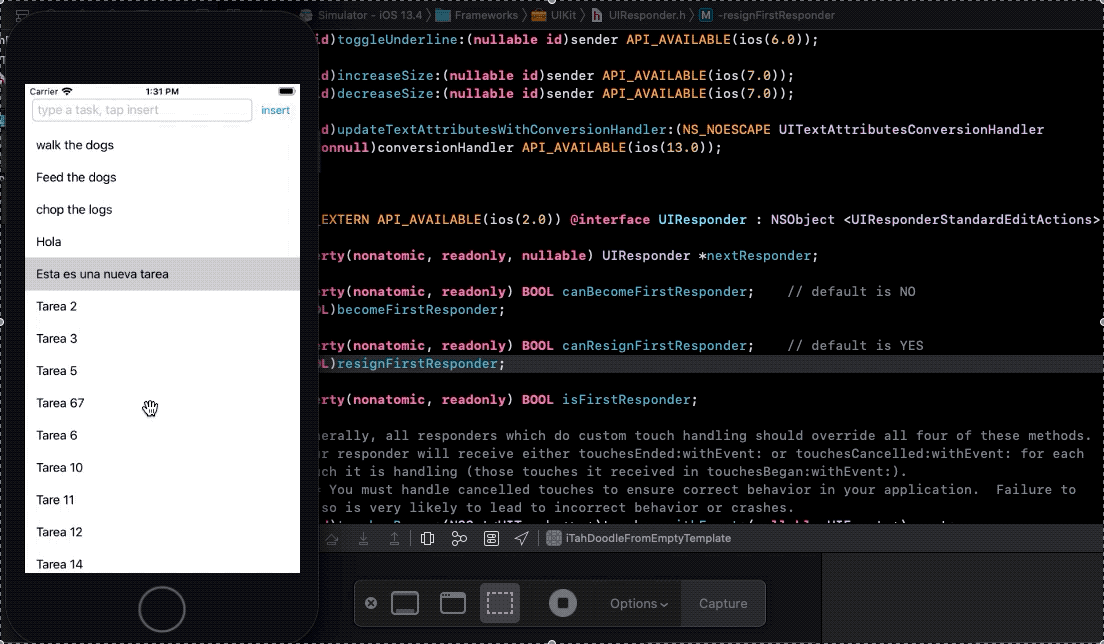
- 14. Saving task data
- 15. What is the first responder bussines ?
- 16. Fix object sizes
- 17. When you tap a cell, hide keyboard
- 18. Disable insert button when taskTextField is empty and present an alert momentary
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
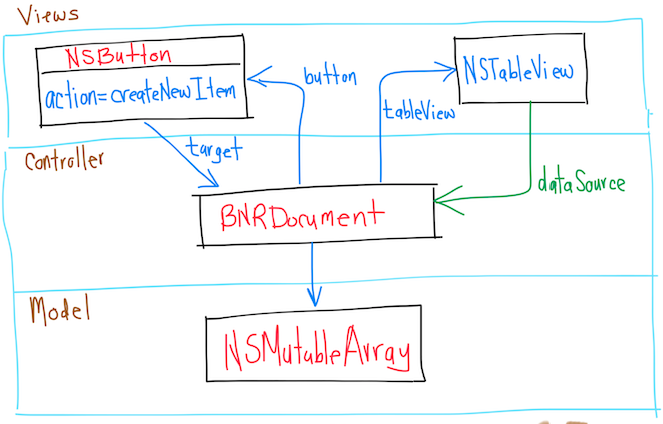
- 1. Edit BNRDocument.h
- 2. A look at Interface Builder
- 3. Edit BNRDocument.xib
- 4. Setting the autosizing mask
- 5. Making connections
- 6. Revisiting MVC
- 7. Edit BNRDocument.m
- 8. Challenges
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
- 1. Writing init methods
- 2. A basic init method
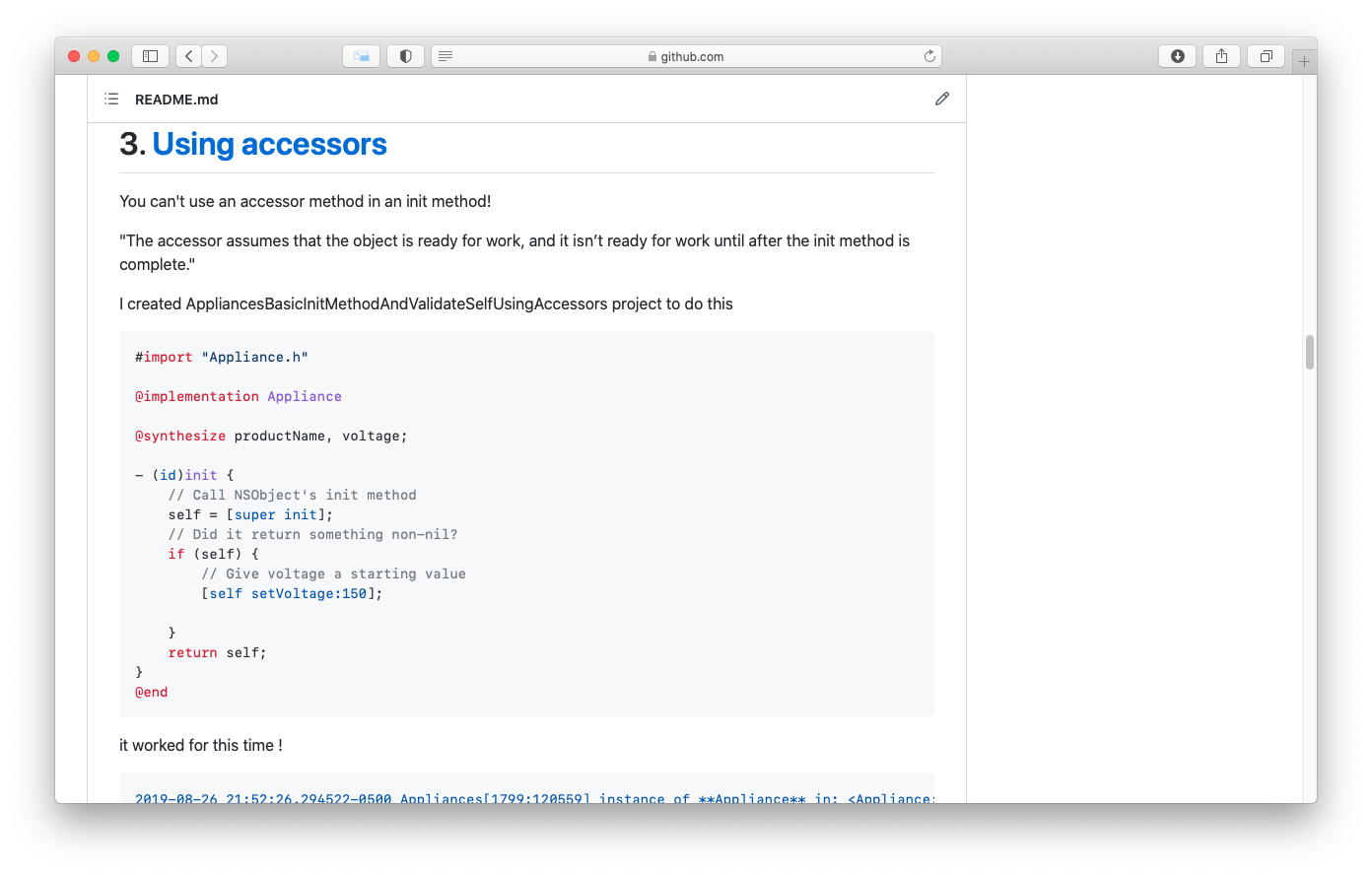
- 3. Using accessors
- 4. init methods that take arguments
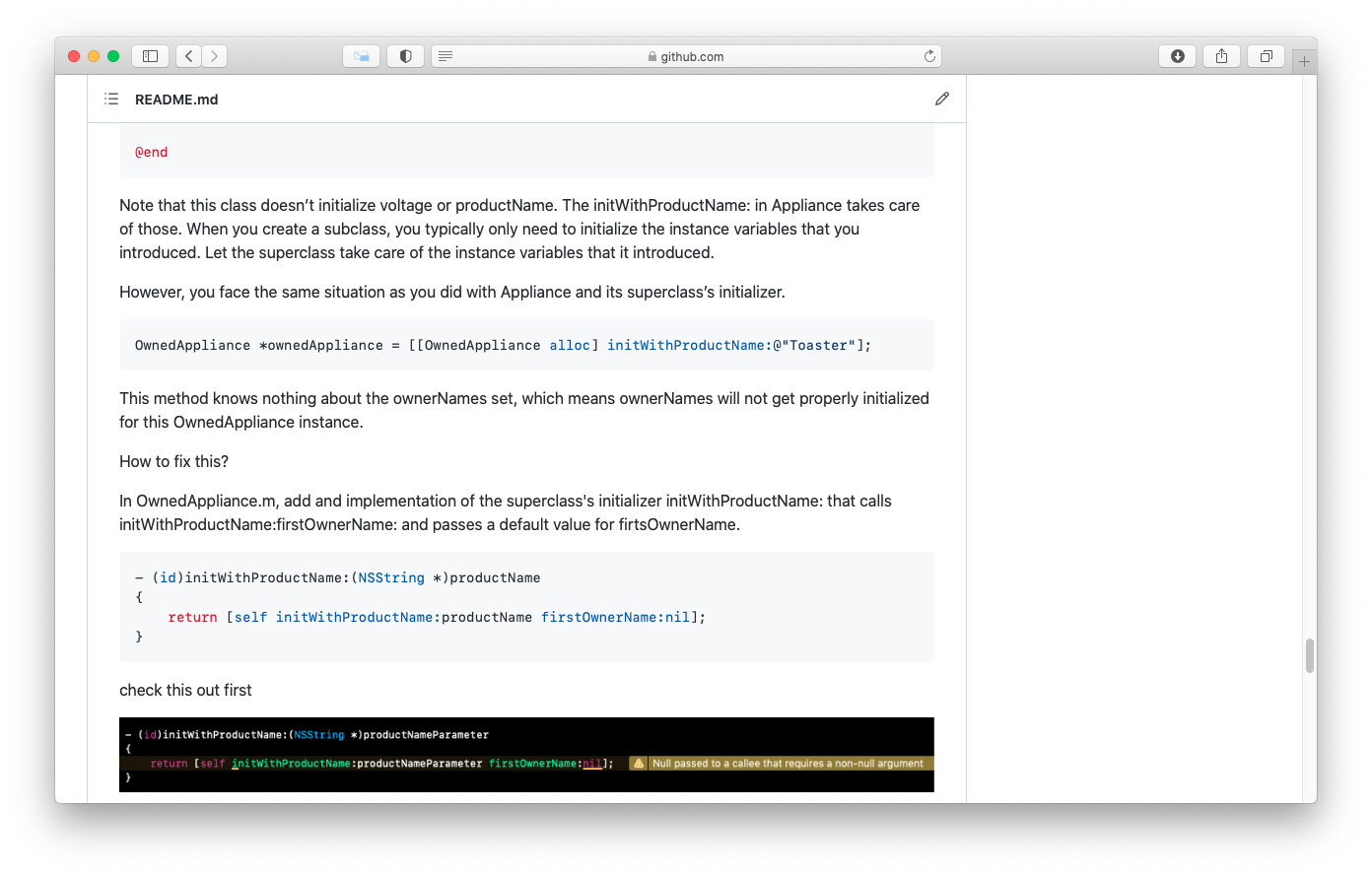
- 5. Deadly init methods
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
- 1. Property attributes
- 2. Mutability
- 3. Lifetime specifiers
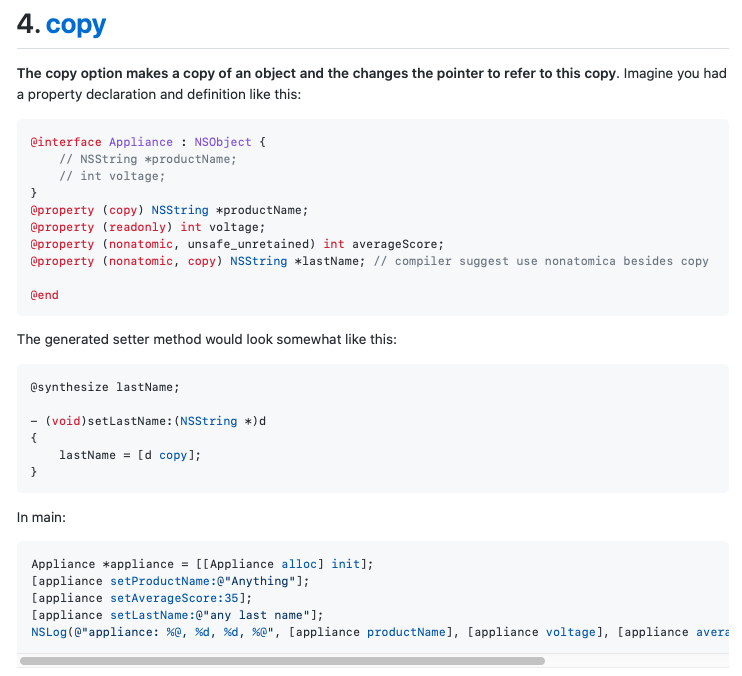
- 4. copy
- 5. More about copying
- 6. Advice on atomic vs. nonatomic
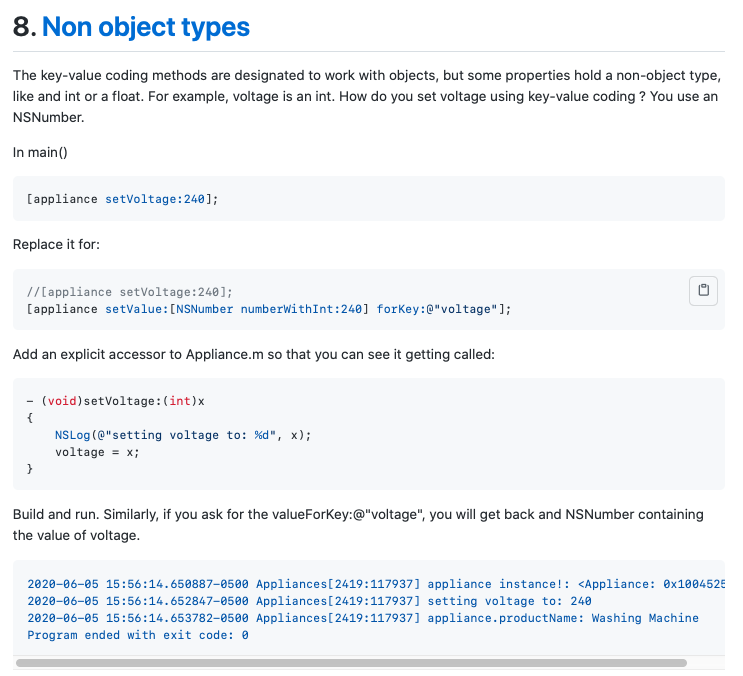
- 7. Key-value coding
- 8. Non object types
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
- 1. Blocks
- 2. Defining blocks
- 3. Using blocks
- 4. Declaring a block variable
- 5. Assigning a block
- 6. Passing in a block
- 7. typedef
- 8. Return values
- 9. Memory management
- 10. The block-based future
- 11. Challenges - Anonymous block
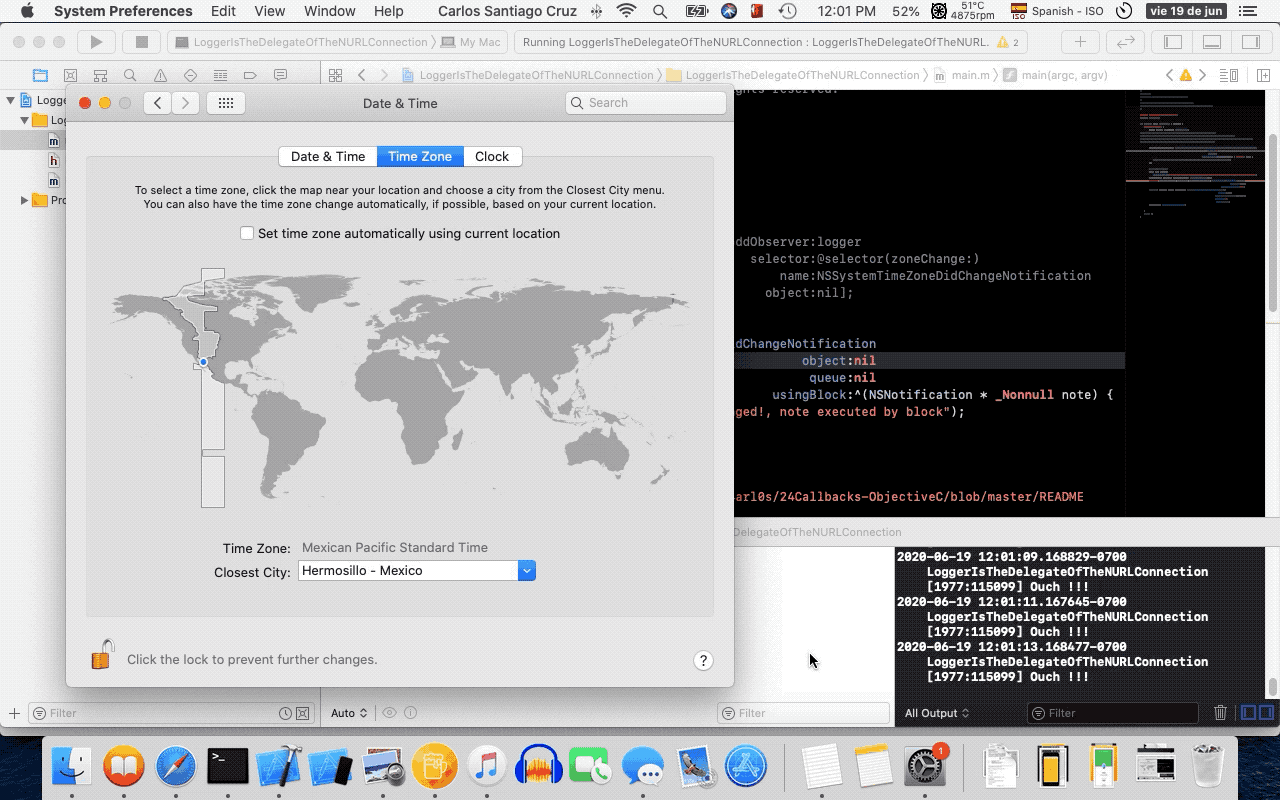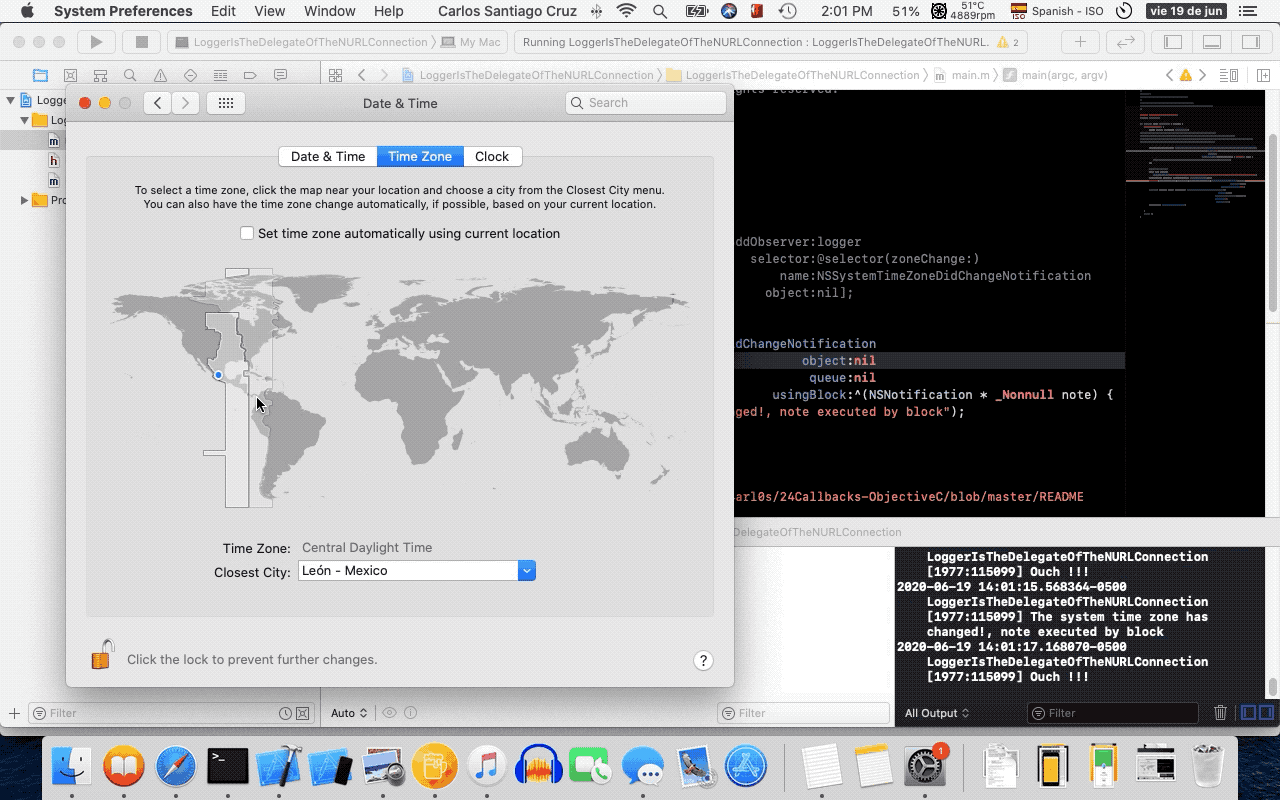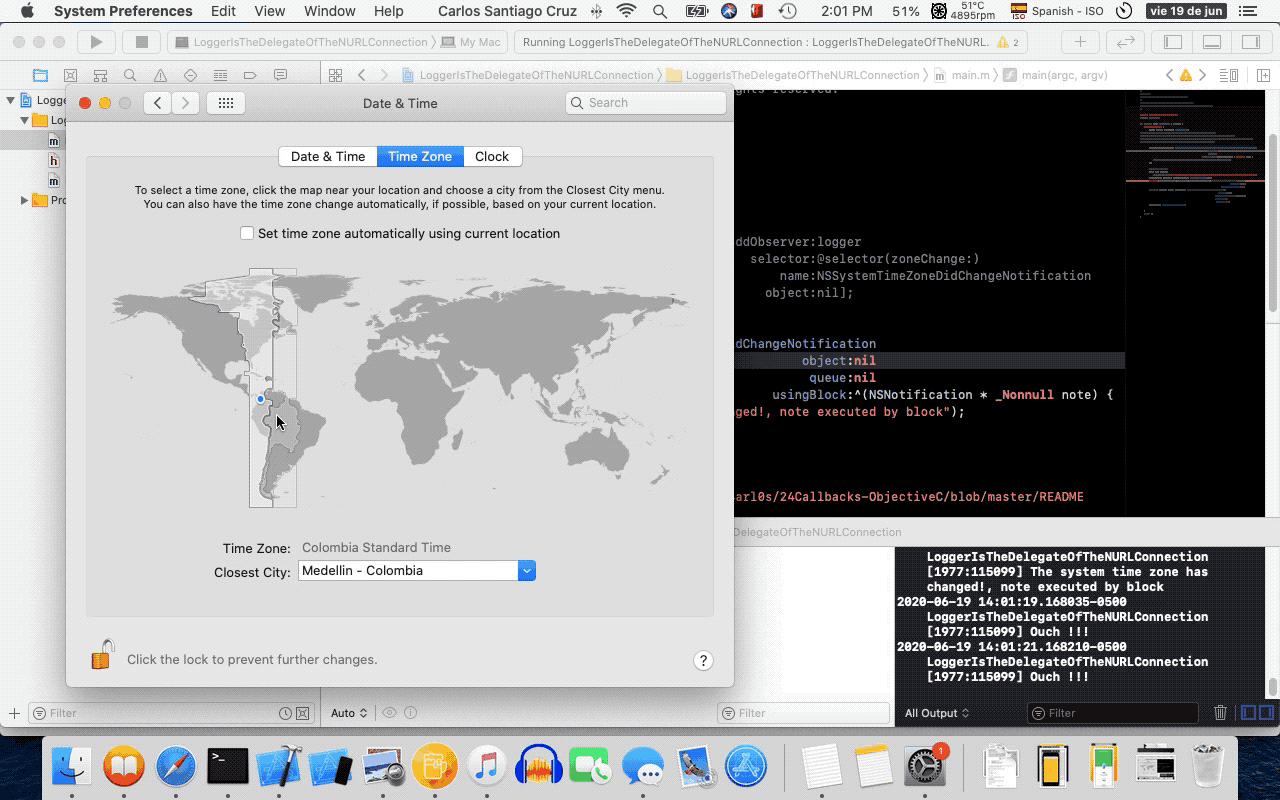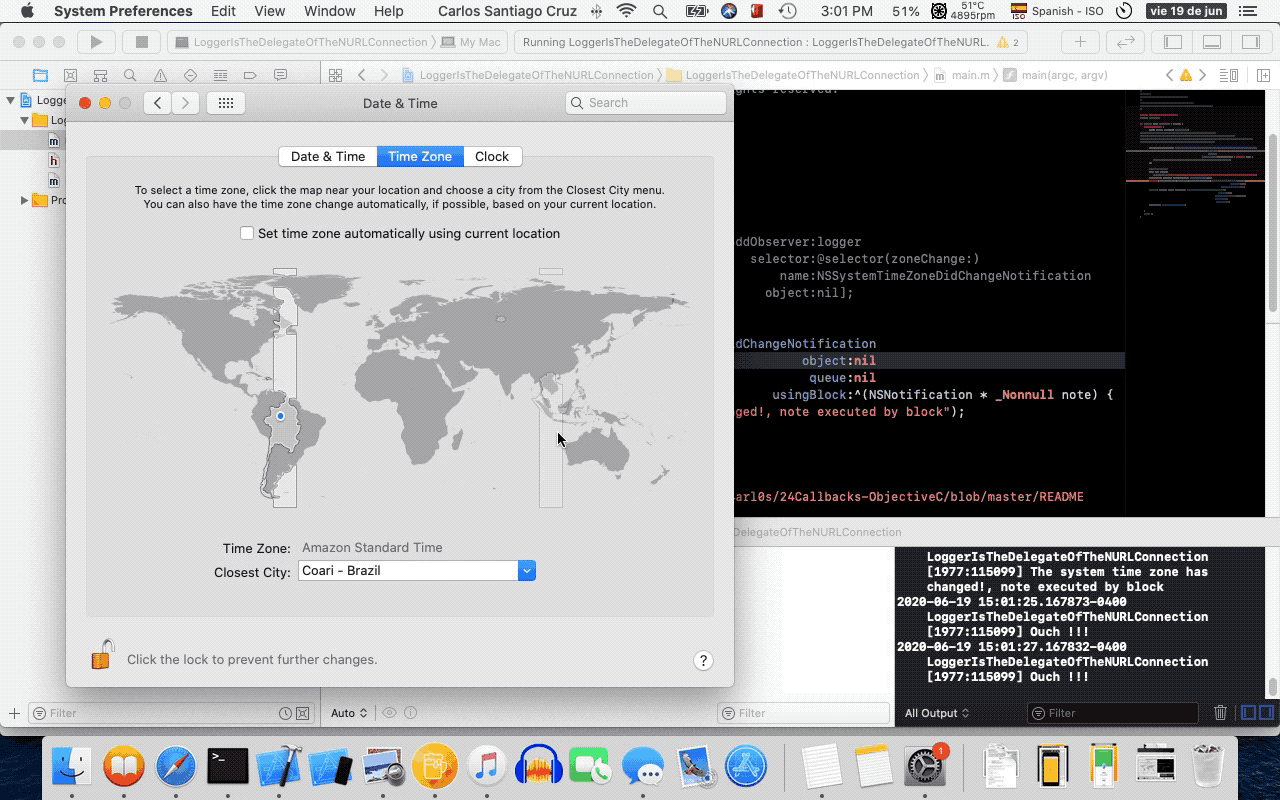
- 12. NSNotificationCenter
- 13. Retain Cycles and Blocks
| At a glance: Notes | |
|---|---|
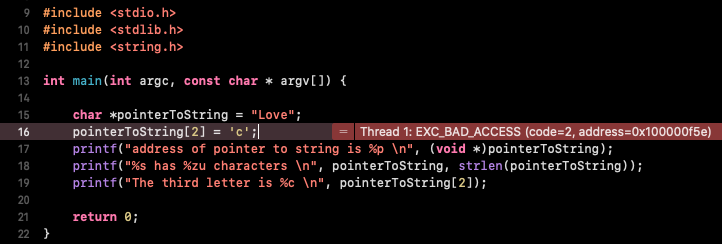 |
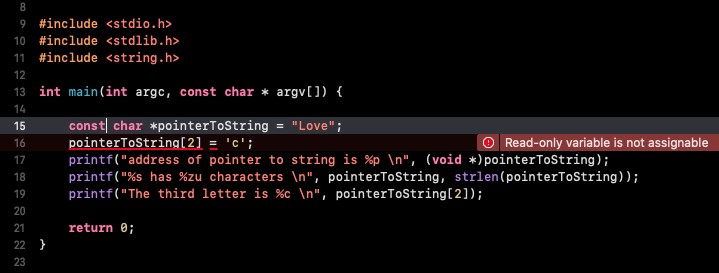 |