SPROUT is a lightweight segmentation toolkit for fine-grained and multi-part segmentation of grayscale 2D/3D images.
👉 Quickstart: Quickstart with Demo Data
Video demo — Getting started with GUI-supported SPROUT using napari:
Click here for the playlist of all SPROUT videos (mainly focus on GUI-based SPROUT in napari). See Usage section for command-line usage.
SPROUT (Semi-automated Parcellation of Region Outputs Using Thresholding and Transformation)
SPROUT is an interpretable workflow for semi-automated, multi-class segmentation of volumetric images (e.g., CT, MRI). It requires no training data and is designed for researchers facing challenging segmentation tasks, such as structures with fine details or weak boundaries, where data for deep learning is scarce.
Y. He, M. Camaiti, L.E. Roberts, J.M. Mulqueeney, E. Ioannou, M. Didziokas, A. Goswami. 2024.
SPROUT: A User-friendly, Scalable Toolkit for Multi-class Segmentation of Volumetric Images
**Install Python and environment manager**: To manage Python environments, we recommend using a lightweight and open alternative to Anaconda, such as:
- **Miniforge**: minimal `conda` installer with `conda-forge` as default
https://conda-forge.org/download/
After installing your preferred environment manager, you can create the environment using the prompt/terminal
- SPROUT supports Python 3.10. Required libraries and versions are:
NumPy: 1.26.4 Pandas: 2.2.1 Scikit-image: 0.22.0 Tifffile: 2024.2.12 imagecodecs: 2025.3.30 Pyyaml: 6.0.1 Trimesh: 4.3.1 Matplotlib: 3.8.3 open3d: 0.18.0 - Steps to create the environment:
- Create the environment:
conda create -n sprout python=3.10
- Activate the environment:
conda activate sprout
- Install dependencies:
This shows pip installation; alternatively, you can use conda.
pip install numpy==1.26.4 pandas==2.2.1 scikit-image==0.22.0 tifffile==2024.2.12 pyyaml==6.0.1 trimesh==4.3.1 matplotlib==3.8.3 open3d==0.18.0 imagecodecs==2025.3.30
- Create the environment:
SproutSAM is an optional module that enables prompt-based segmentation using foundation models like SAM and SAM2. If you wish to use SproutSAM, please install the following additional dependencies:
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio
pip install opencv-python-headless
https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/
You also need to install the SAM and/or SAM2 libraries:
-
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/segment-anything.git cd segment-anything pip install -e .
-
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/sam2.git cd sam2 pip install -e .
Napari is an open-source image viewer designed for 2D and 3D visualisation and interactive manipulation.
We developed napari-sprout, the SPROUT plugin for Napari, which enables users to interactively visualise, edit, and refine seeds, segmentation results, and other image-derived layers.
napari-sprout has been tested with napari==0.6.1.
To install Napari, you can use either pip or conda:
pip install napari==0.6.1or
conda install -c conda-forge napari=0.6.1 pyqtAfter installation, you can launch Napari from the command line:
napariIf you encounter the following error message:
napari requires either PyQt5 (default), PyQt6 or PySide2 to be installed in the environment.
it means a Qt GUI is missing.
You can fix this by installing one of the following:
-
With pip:
pip install "napari[all]" # or a specific Qt backend: pip install "napari[pyqt5]" pip install "napari[pyqt6]" pip install "napari[pyside2]"
-
With conda:
conda install -c conda-forge pyqt # or conda install -c conda-forge pyside2
After installing napari, you can proceed to install the SPROUT plugin.
cd ./napari_sprout
pip install -e .- More on using napari-sprout: see View & Edit (napari)
- Full napari docs: https://napari.org/
SPROUT follows a two-step workflow for multi-class segmentation:
-
Seed Generation
The goal of this step is to reduce the regions of the image by breaking it into multiple distinct components (splits). There are two strategies:- Vanilla seed generation: generate multiple seeds by varying configurations such as thresholds and erosion steps.
- Adaptive seed generation: automatically combine information across seeds from different configurations to produce a often better and final seed.
-
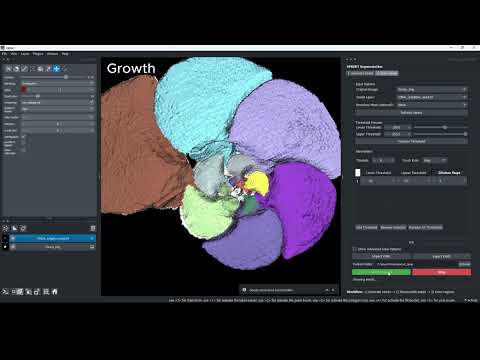
Seed Growth
- Threshold-based growth: grows a seed by expanding the reduced components back toward their full target shapes. Growth is guided by image intensity and connectivity.
- SproutSAM: seeds are converted into prompts for a segmentation foundation model such as SAM, which then predicts the segmentation. These slice-wise predictions are then fused into a final 3D output.
🧪 Interactive Inspection & Editing
In practice, both seed and grow results often require visualisation, quality checking, or manual editing, depending on your segmentation goals.
To support this, SPROUT is fully integrated into the Napari ecosystem as a plugin, please see napari-sprout.
SPROUT processes 2D and 3D grayscale images stored in TIFF (.tif, .tiff) format.
- Supported file types:
.tif,.tiff - Image Type: 2D or 3D grayscale images
- Bit Depth: 8-bit, 16-bit, or 32-bit (floating point)
- File Structure:
- 2D images:
(Height, Width) - 3D images:
(Depth, Height, Width)
- 2D images:
Unsupported inputs: Color images.
See Demo Data and Basic Usage for a quick start.
See Scenarios for advance usage in a Q&A style.
./demo_data includes a dog skeleton dog_img.tif, a foraminifera chamber segmentation foram_img.tif and a 2D cell microscopy image 2d_cell.tif. Their corresponding seed images are also provided in the same directory.
Additional demo data can be found here.
on a single image
python sprout.py --seeds --config path/to/seed_config.yamlin batch mode
python sprout.py --seeds --batch --config path/to/batch_seed.yamlA video explain batch mode: link
For full details on YAML parameters and other configs see:
For example, see the YAML configuration files in ./template/.
on a single image
python sprout.py --adaptive_seed --config path/to/adaptive_seed_config.yamlin batch mode
python sprout.py --adaptive_seed --batch --config path/to/batch_adaptive_seed.yamlFor full details on YAML parameters and other configs see:
For example, see the YAML configuration files in ./template/.
on a single image
python sprout.py --grow --config path/to/grow_config.yamlin batch mode
python sprout.py --grow --batch --config path/to/batch_grow.yamlFor full details on YAML parameters and other configs see:
For example, see the YAML configuration files in ./template/.
on a single image or a folder of images
python sprout.py --sam --config path/to/config.yamlin batch mode
python sprout.py --sam --batch --config path/to/batch_config.yamlFor full details on YAML parameters and other configs see:
For example, see the YAML configuration files in ./template/.
sprout.py can run tasks in parallel using Python’s threading. Just set num_threads in your config to speed up processing, especially for large datasets.
🎥 Tutorial Video — Editing Segmentation Results in napari-SPROUT
To launch napari-sprout:
- Start napari by running
napariin a terminal or command prompt. - Open the
napari-sproutplugin from the napari menu: Plugins → SPROUT.
From here, you can use a set of tools to load, view, and edit your data.
-
SPROUT_main
GUI for running seed generation, adaptive seed generation, and growth.
Parameters match those used in the command-line scripts. -
SPROUT_load
Batch loader for multiple images or segmentations. -
SPROUT_edit
Interactive editing of segmentation results such as:-
Click to keep or remove regions
-
Re-assign class numbers (e.g. merge
i → j, deletei → 0) -
Split disconnected regions
-
-
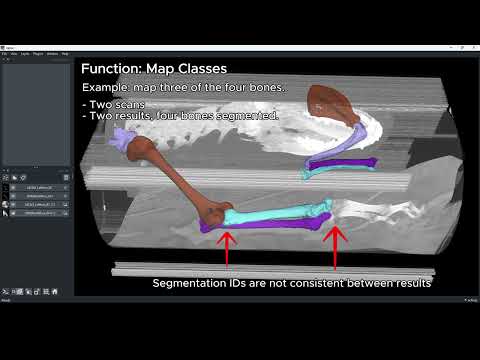
SPROUT_map
Map regions to a semantic class scheme, e.g.1 → bone_1,2 → bone_2. -
SPROUT_tools
Miscellaneous tools, including:-
Inspect reference shapes (e.g. show a ball of radius 10 pixels)
-
Generate batch-processing CSVs, can provide per-image adaptive thresholds (e.g. Otsu)
-
-
SPROUT_info
Inspect information (e.g., resolutions, how many segmentation classes) of images or segmentations.
In addition to napari-sprout, napari also provides powerful editing options (e.g. Brush to add regions, Erase to remove).
You can also visualize, inspect, and edit seeds or results using 3D image processing tools such as 3D Slicer, DragonFly, and AVIZO. Alternatively, you can generate meshes and view or edit them in mesh-based tools like MeshLab. See Extra section
Batch processing results of segmenting dog bones in CT scans with varying anatomy and postures.

Batch processing results of segmenting foram binary segmentation (supports segmentation masks as input too) with variable numbers of chambers

Gallery of other results
Note: All results underwent manual post-processing primarily to verify and correct segmentation errors.
You can use other tools to visualize and edit SPROUT's segmentation results, see Optional Tools for details.
In napari-sprout and plugins, we provided GUI version of editing results. You can also find the script-version in Helper Functions.
SPROUT was inspired by BounTI, a boundary-preserving threshold iteration approach:
M. Didziokas, E. Pauws, L. Kölby, R. H. Khonsari, M. Moazen. 2024.
BounTI: A user-friendly tool for automatic hard tissue segmentation. Journal of Anatomy 245, 829–841.
The script ./BounTI/run_bounti_mp.py is designed to run BounTI and BounTI Flood using a multithreaded approach. It efficiently processes a list of initial thresholds in parallel, leveraging multiple threads for improved performance.

