This basic code illustrate the use of 'Process' Class to parallelize the gradient descent algorithm. The logistic regression algorithm is used to investigate the gradient descent. Parallel and sequential implementation are coded. In parallel computation, the model is shared between the workers, while the data is randomly divided equally. The ultimate goal is to experience the difference between sequential and parallel computation, and the performance of the classification machine is not investigated (test data were not used).
The multiprocessing module that is installed by python is used to parallelize the GD. Class process is used explicitly in beginning before moving to more advanced classes (e.g. Pool.map and Pool.Apply). The model is put on shared memory so all workers can access it. The Shared model assigned a free lock to allow asynchronous updates. The synchronization can be done easily by placing lock() module before and after the model update (however it’s not listed in results).
The sequential batch GD is first implanted with 10,000 iterations.
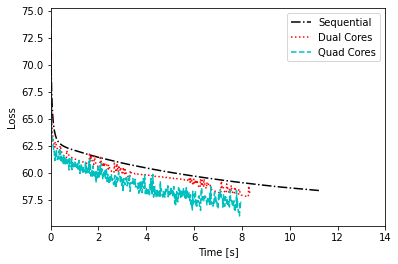
The high number of iterations is mandatory to show advantage the parallelism (otherwise, sequential is faster).
Each sample of the 300 samples of the training data has 21 feature.
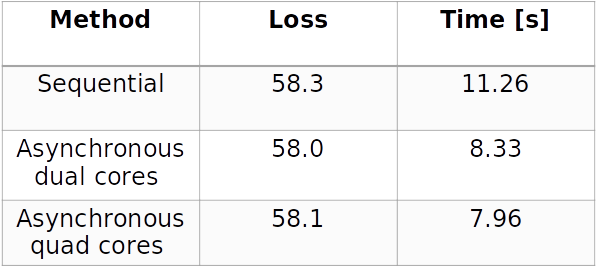
The True Predictions of the classifier are similar in all scenarios (sequential and parallel).
The time is clearly faster in parallel with more cores as shown in next and last slide.