Python lectures and codes for the National Workshop on Python in Scientific Computing, taught at the University Science Instrumentation Centre (USIC), The University of Burdwan
A repository of all my codes, tutorial lectures and simulations used to teach Computational Physics in Python to students at the USIC in The University of Burdwan
The simulations are written in the Python programming language.
-
For a quick introduction to the Python programming language, as well as Numerical Python, Scientific Python and Matplotlib, see this tutorial
-
For a more detailed introduction to the abovementioned topics, see Robert Johansson's Scientific Python Lectures.
You can run these python codes by installing the requisite software in your computer, or online through Google Colab.
-
Suggested: If you can't install Python locally, you can run the codes through Google Colab by clicking on the links to the jupyter notebooks below and then hitting "Open in Colab" at the top. This works on any computer, smartphone, or tablet with internet connectivity and a web browser like Chrome, Edge, Firefox, etc. These scripts will execute on colab servers, not your machine. Although servers may be slow, this is usually not a problem.
-
In order to run these programs locally in your computer (instead of Google Colab), perform the following steps.
-
Then, on the dropdown menu, click on "Download ZIP". Once downloaded, uncompress the zip file anywhere. Now, you have a local copy of this repository, together with all data files, slides and notebooks.
-
Anaconda (https://www.anaconda.com/) should be downloaded and installed last. Jupyter notebooks or the Spyder IDE can be used to design and run Python code in Anaconda. See this blog post for anaconda installation instructions.
-
Optionally, if you need to install any additional packages like, for example, the SfePy package for Finite Element Method (FEM) computations, you'll want to install them manually.
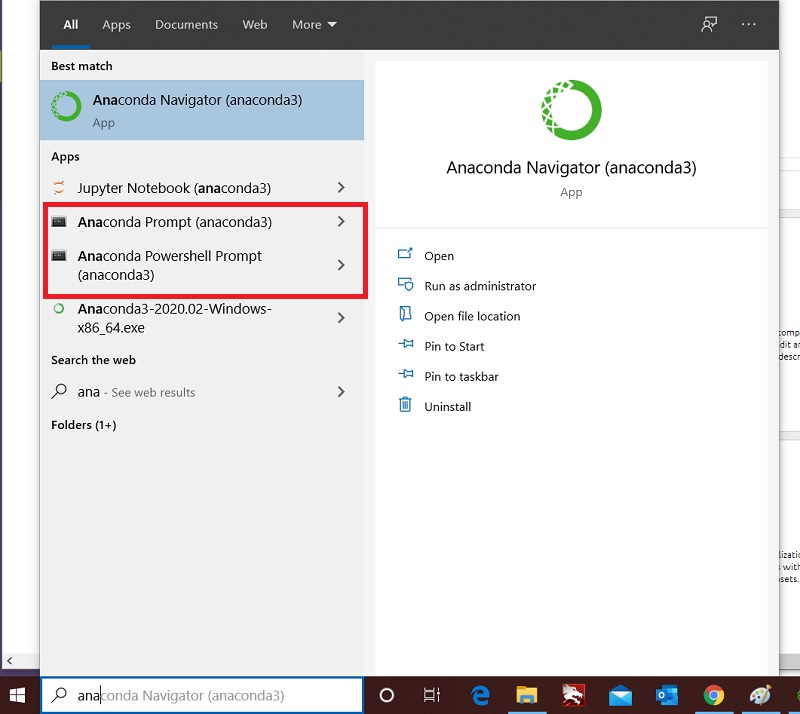
In order to do this, first load a shell with the anaconda base environment activated. On Windows, this can be done by opening the "Anaconda PowerShell Prompt" from "Start Menu". See the image below for details.
On Linux, simply start a terminal emulator like gnome-terminal and activate anaconda with the shell command
console $ conda activate baseOnce the shell with the base environment is loaded, run the commands given below (replace 'sfepy' with whatever package that you need) in order to configure the 'conda-forge' package repository and have the conda package manager download and install the package of choice:
(base) PS C:\Users~1> conda config --add channels conda-forge (base) PS C:\Users~1> conda install sfepy
Note that you might want to install complex packages like sfepy in a fresh conda environment that is different from the 'base' environment that anaconda provides. See this link for details.
-
Recommended: The default version of python in anaconda can be a little old. I would suggest that you update the python to at least version 3.11 in a fresh conda environment. To check if the default version is older than 3.11, open the Anaconda PowerShell Prompt as described above and run the following command
(base) PS C:\Users~1> python --versionIf the version is older than 3.11, then run the following commands to create an environment (named 'exercises') with python version 3.11 inside it, then install all necessary packages and activate the environment for use.
(base) PS C:\Users~1> conda config --add channels conda-forge (base) PS C:\Users~1> conda create -n exercises python=3.11 numpy scipy matplotlib qutip (base) PS C:\Users~1> conda activate exercises
-
If you're having problems with Git, and do not want to use Google Colab, you can simply copy-paste the codes individually into your local python setup:
-
Click on the "Copy raw contents" button on the top-right corner of the github page of a particular code (to the right of the 'Blame' button).
-
Then, paste it into a text editor or a running python IDE like Spyder or IDLE in order to execute it.
-
However, this only works for normal Python, not Jupyter notebooks. You can run them in Google Colab or copy-paste each code cell from the jupyter notebook to a local Python file on your device. In standard Python, IPython magics won't work, so delete or rewrite them.
-
Use the following links:
-
Examples of Partial Differential Equations using Finite Difference Method
-
Extra: Estimate the value of pi by Monte Carlo Method (in parallel)
-
Scientific Python Tutorials (including numpy and matplotlib)
-
SfePy: Simple Finite Elements in Python, including extensive documentation and theoretical background.
This work is licensed under a MIT License
Analabha Roy
Assistant Professor,
Department of Physics,
The University of Burdwan
Bardhaman, India 713104
Webpage: https://www.ph.utexas.edu/~daneel