To write a program to predict the profit of a city using the linear regression model with gradient descent.
- Hardware – PCs
- Anaconda – Python 3.7 Installation / Jupyter notebook
- Import the required library and read the dataframe.
- Write a function computeCost to generate the cost function.
- Perform iterations og gradient steps with learning rate.
- Plot the Cost function using Gradient Descent and generate the required graph.
/*
Program to implement the linear regression using gradient descent.
Developed by:Karthik R
RegisterNumber: 212221040074
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data=pd.read_csv("ex1.txt",header=None)
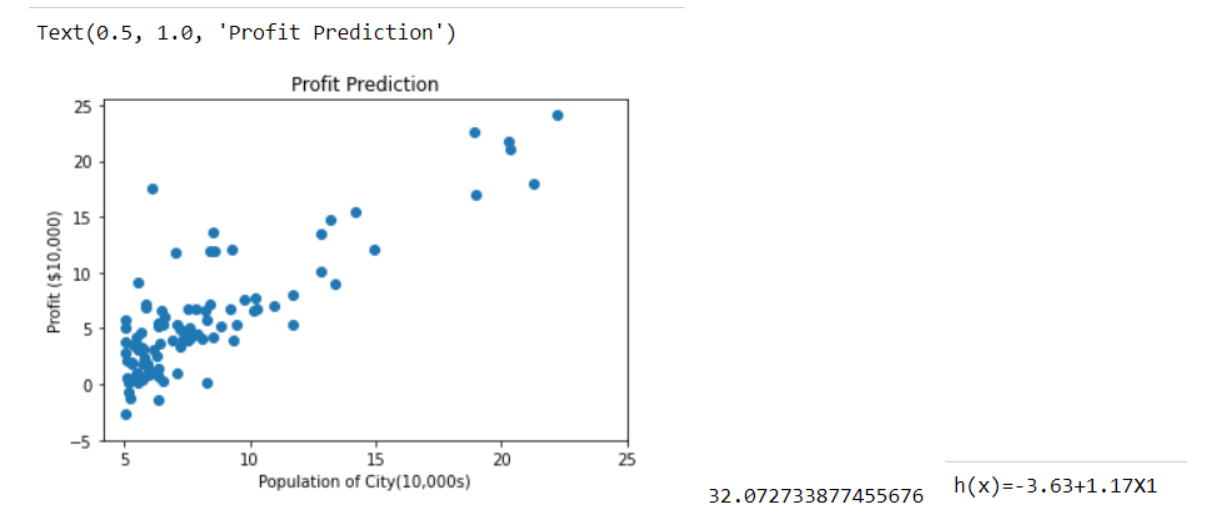
plt.scatter(data[0],data[1])
plt.xticks(np.arange(5,30,step=5))
plt.yticks(np.arange(-5,30,step=5))
plt.xlabel("Population of City(10,000s)")
plt.ylabel("Profit ($10,000)")
plt.title("Profit Prediction")
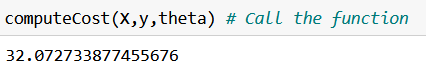
def computeCost(X,y,theta):
""""
Take in a numpy array X,y,theta and generate the cost function of using theta as a parameter in a linera regression tool
"""
m=len(y)
h=X.dot(theta)
square_err=(h-y)**2
return 1/(2*m)*np.sum(square_err)
data_n=data.values
m=data_n[:,0].size
X=np.append(np.ones((m,1)),data_n[:,0].reshape(m,1),axis=1)
y=data_n[:,1].reshape(m,1)
theta=np.zeros((2,1))
computeCost(X,y,theta)
def gradientDescent(X,y,theta,alpha,num_iters):
""""
Take in numpy array X,y and theta and update theta by taking num_iters gradient steps with learning rate of alpha
return theta and the list of the cost of the theta during each iteration
"""
m=len(y)
J_history=[] #empty list
for i in range(num_iters):
predictions=X.dot(theta)
error=np.dot(X.transpose(),(predictions-y))
descent=alpha*(1/m)*error
theta-=descent
J_history.append(computeCost(X,y,theta))
return theta,J_history
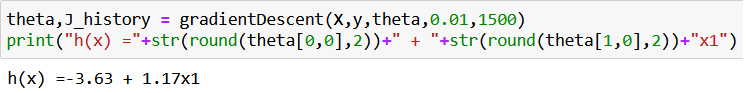
theta,J_history = gradientDescent(X,y,theta,0.01,1500)
print("h(x) ="+str(round(theta[0,0],2))+" + "+str(round(theta[1,0],2))+"x1")
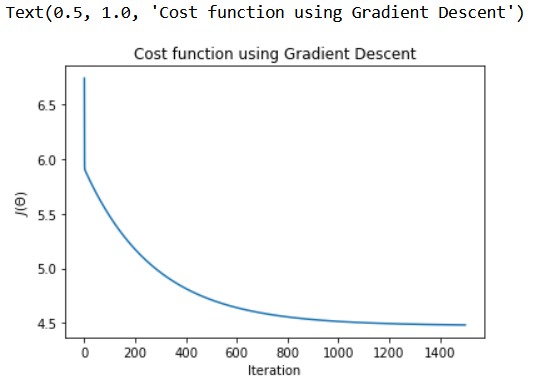
plt.plot(J_history)
plt.xlabel("Iteration")
plt.ylabel("$J(\Theta)$")
plt.title("Cost function using Gradient Descent")
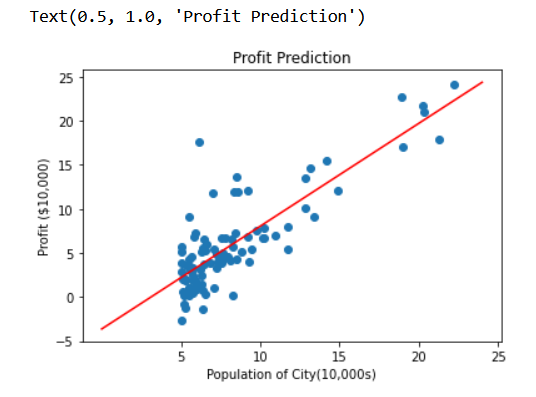
plt.scatter(data[0],data[1])
x_value=[x for x in range(25)]
y_value=[y*theta[1]+theta[0] for y in x_value]
plt.plot(x_value,y_value,color="r")
plt.xticks(np.arange(5,30,step=5))
plt.yticks(np.arange(-5,30,step=5))
plt.xlabel("Population of City(10,000s)")
plt.ylabel("Profit ($10,000)")
plt.title("Profit Prediction")
def predict(x,theta):
""""
Takes in numpy array of x and theta and return the predicted valude of y based on theta
"""
predictions=np.dot(theta.transpose(),x)
return predictions[0]
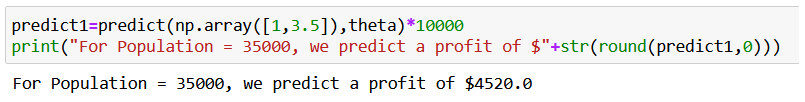
predict1=predict(np.array([1,3.5]),theta)*10000
print("For Population = 35000, we predict a profit of $"+str(round(predict1,0)))
predict2=predict(np.array([1,7]),theta)*10000
print("For Population = 70000, we predict a profit of $"+str(round(predict2,0)))
*/
Thus the program to implement the linear regression using gradient descent is written and verified using python programming.