An extensible Django app that displays system version information in the Django admin interface.
- 📊 Version Display: Shows versions of Django, Python, PostgreSQL, Celery, and Redis
- 🔍 Git Information: Displays git commit hash, deployment date, and repository URL
- 📦 Third Party Apps: Automatically detects and displays Django apps and Python integrations
- 📈 Cache Statistics: View Redis cache statistics (read-only, no clearing)
- 🎨 Clean Admin Integration: Seamlessly integrates with Django's admin interface
- ⚙️ Highly Configurable: Customize what information is shown
- 🔌 Optional Dependencies: Gracefully handles missing Celery or Redis
- 🛠️ Extensible: Add custom information sections
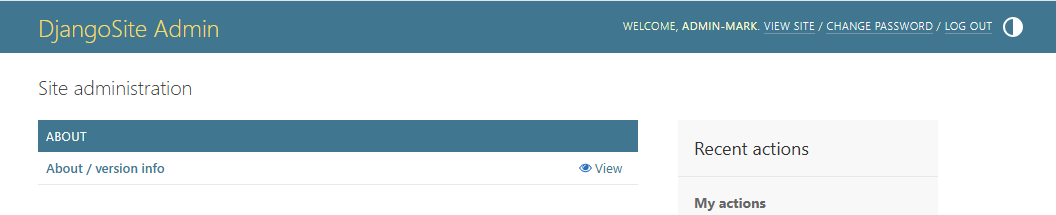
The About dashboard integrates seamlessly with Django's admin interface, providing a clean and organized view of your system information.
Shows the page_title and page_intro customizable sections in use and default version of "show_dashboard_description": True,. Also shows the Code Information Section (shows git commit hash and deployment date) and Software Version Information (Displays major software versions with links to documentation)
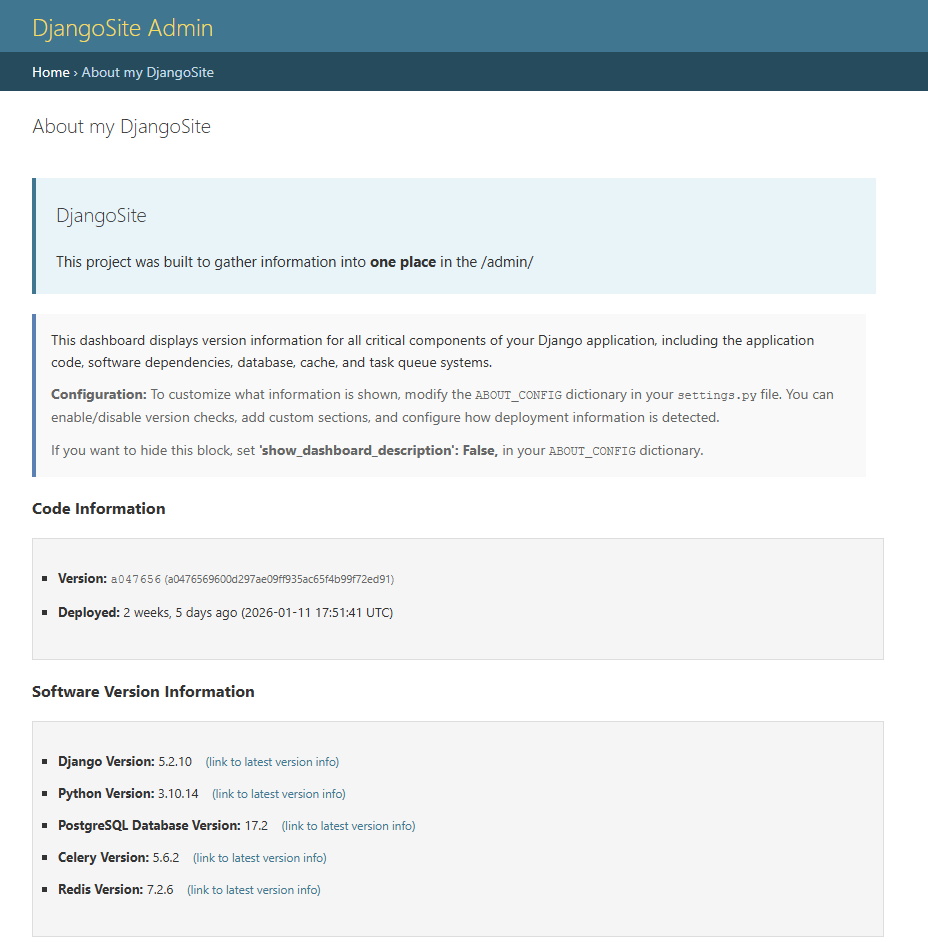
Django apps grouped by their distribution package:
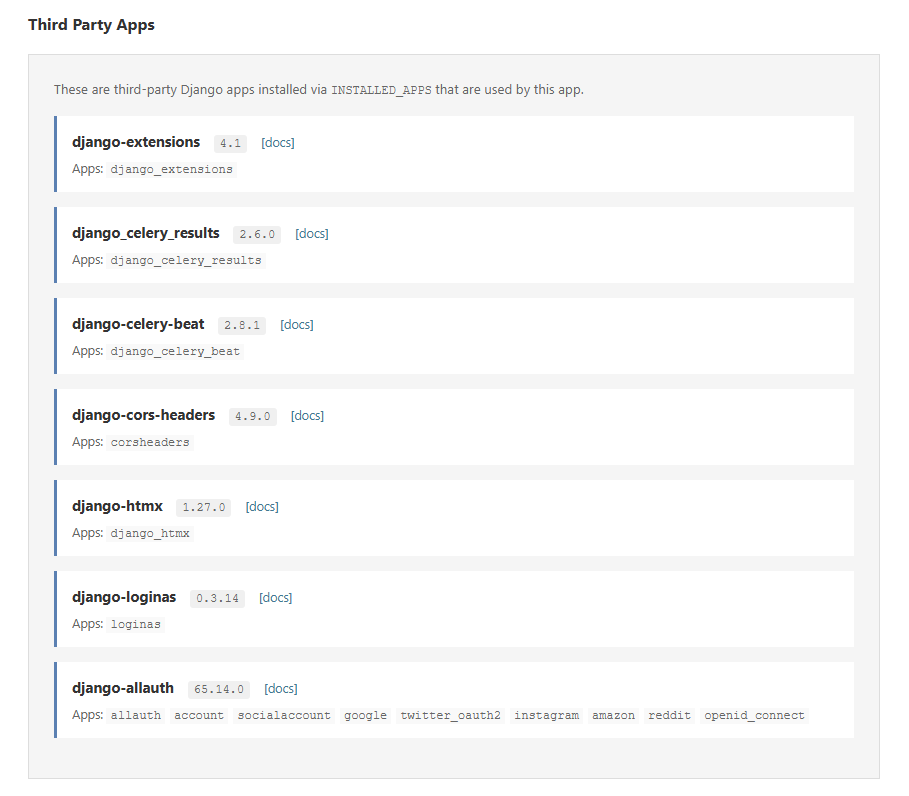
Important integrations highlighted, with others in a collapsible section:
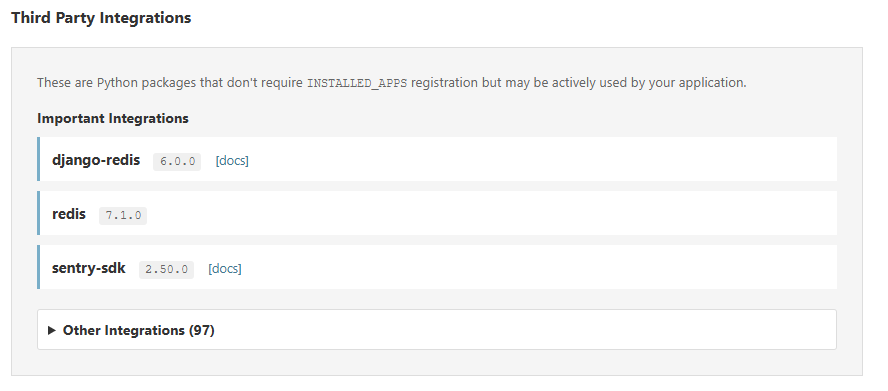
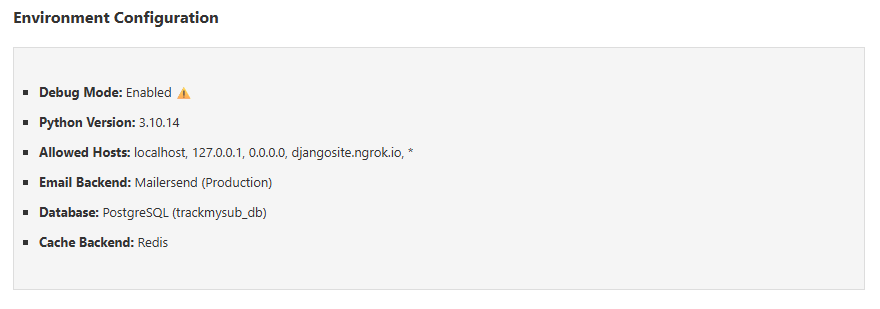
Example custom section showing environment configuration:
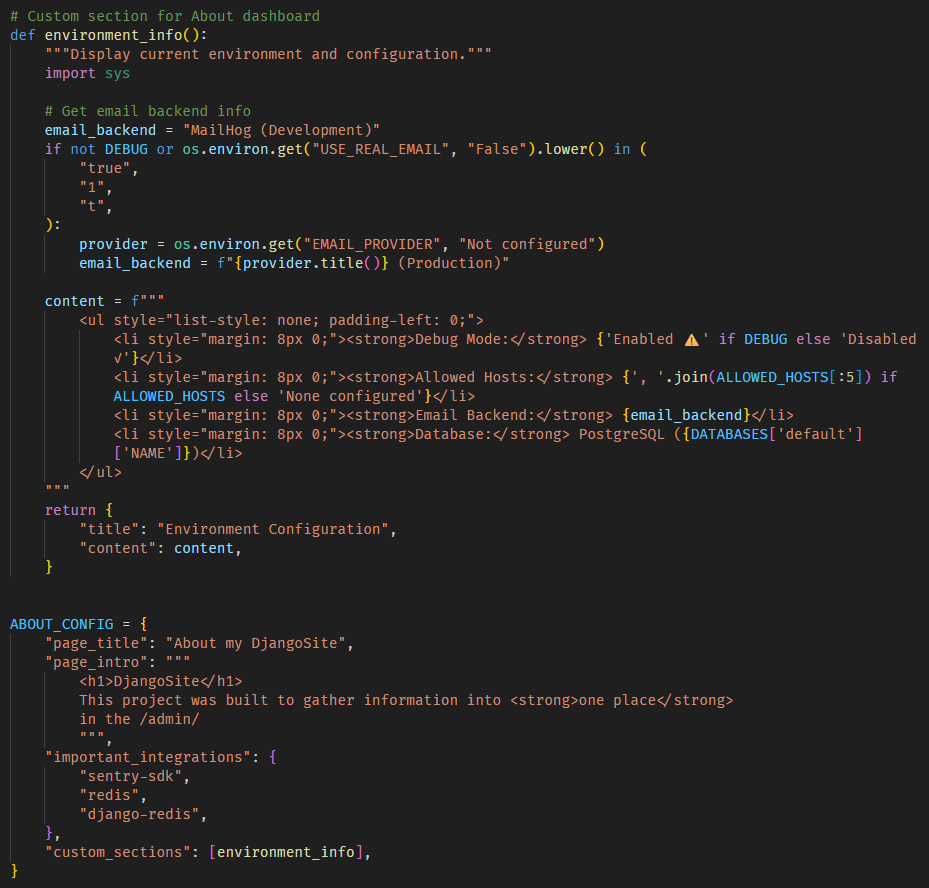
Example of how settings.py can be edited to show a custom section showing environment info:
The interface uses Django admin's native styling for a consistent, professional appearance.
Install using pip:
pip install django-aboutAdd about and django.contrib.humanize to your INSTALLED_APPS in settings.py:
INSTALLED_APPS = [
# ...
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.humanize', # Required for template filters
# ...
'about', # Add this
]Include the about URLs in your project's urls.py:
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/about/', include('about.urls')), # Add before admin
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
# ... other patterns
]- Start your Django development server
- Login to the Django admin at
/admin/ - Click on "About" in the admin index
- Or navigate directly to
/admin/about/
That's it! The about dashboard should now be accessible.
All configuration is optional. Add a ABOUT_CONFIG dictionary to your settings.py to customize:
ABOUT_CONFIG = {
# What to display (all default to True)
'show_django_version': True,
'show_python_version': True,
'show_database_version': True,
'show_celery_version': True,
'show_redis_version': True,
'show_git_info': True,
'show_cache_stats': True,
'show_third_party_apps': True,
'show_dashboard_description': True, # Show default description text
# Page customization
'page_title': 'About',
'page_intro': 'This project does this and that really well.',
# Where to get release version (checked in order)
'release_env_vars': [
'HEROKU_SLUG_COMMIT',
'GIT_COMMIT',
'COMMIT_SHA',
'CI_COMMIT_SHA',
],
# Where to get release date (checked in order)
'release_date_env_vars': [
'HEROKU_RELEASE_CREATED_AT',
'DEPLOY_DATE',
'RELEASE_DATE',
],
# Highlight important integrations at the top
'important_integrations': {
'sentry-sdk',
'rollbar',
'scout-apm',
'redis',
'django-redis',
'whitenoise',
},
# Custom sections (list of callables)
'custom_sections': [],
}Add a custom introduction at the top of the dashboard to describe your project:
ABOUT_CONFIG = {
'page_intro': """
This project does this and that really well.
<strong>Use this dashboard to check in on the software that runs your site/project.</strong>
""",
}The intro text appears in a highlighted box at the top of the page, before the standard dashboard description. HTML is supported, so you can use tags like <strong>, <em>, <a>, <ul>, etc. for formatting.
Tip: If you provide a custom page_intro, you can hide the default dashboard description by setting show_dashboard_description: False in your config.
You can add custom information sections to the dashboard to display application-specific data. Each section function should return a dict with title and content keys:
from django.conf import settings
def environment_info():
"""Display current environment and feature flags."""
env = settings.ENVIRONMENT_NAME
debug = settings.DEBUG
content = f"""
<ul>
<li><strong>Environment:</strong> {env}</li>
<li><strong>Debug Mode:</strong> {'Enabled' if debug else 'Disabled'}</li>
<li><strong>Allowed Hosts:</strong> {', '.join(settings.ALLOWED_HOSTS)}</li>
</ul>
"""
return {
'title': 'Environment Configuration',
'content': content,
}
def external_services():
"""Show configured external services."""
services = [
('Stripe API', settings.STRIPE_PUBLISHABLE_KEY[:20] + '...'),
('SendGrid API', 'Configured' if settings.SENDGRID_API_KEY else 'Not configured'),
('S3 Bucket', settings.AWS_STORAGE_BUCKET_NAME),
]
rows = ''.join([
f'<tr><td><strong>{name}</strong></td><td>{value}</td></tr>'
for name, value in services
])
content = f'<table style="width: 100%;"><tbody>{rows}</tbody></table>'
return {
'title': 'External Services',
'content': content,
}
ABOUT_CONFIG = {
'custom_sections': [environment_info, external_services],
}Use cases for custom sections:
- Display environment-specific configuration
- Show feature flags and their current state
- List configured external services (APIs, S3, email providers)
- Display application-specific metrics
- Show active background jobs or scheduled tasks
- List custom middleware or installed plugins
Django About can display git commit information in several ways:
Set environment variables before deploying:
export GIT_COMMIT=$(git rev-parse HEAD)
export DEPLOY_DATE=$(date -u +"%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ")Enable dyno metadata:
heroku labs:enable runtime-dyno-metadata -a your-app-nameDjango About will automatically detect HEROKU_SLUG_COMMIT and HEROKU_RELEASE_CREATED_AT.
If no environment variables are set, Django About will try to run git commands to detect the current commit. This works in development but won't work in production (git is typically not installed in production containers).
-
Required:
- Python 3.8+
- Django 3.2+
-
Optional (auto-detected):
- Celery (for Celery version display)
- Redis / django-redis (for cache statistics)
- Git (for automatic commit detection in development)
Django About detects versions for:
- Django: Via
django.get_version() - Python: Via
sys.version - PostgreSQL: Via
SELECT version()SQL query - MySQL/MariaDB: Via
SELECT version()SQL query - SQLite: Via
SELECT version()SQL query - Celery: Via
celery.__version__(graceful fallback if not installed) - Redis: Via Redis INFO command (graceful fallback if not available)
All version detection includes graceful error handling - if a component can't be detected, it simply won't be displayed.
The about view is restricted to staff users only (users with is_staff=True). This is enforced via Django's @staff_member_required decorator.
When Redis is configured as your cache backend, Django About displays:
- Cache backend type
- Total number of cache keys
- Used memory / Max memory
- Redis server version
- Connected clients
- Redis uptime
Note: Cache statistics are read-only. This package does NOT provide cache clearing functionality for safety reasons.
Django About automatically detects and displays information about third-party packages in your project:
Shows third-party Django apps (from INSTALLED_APPS) grouped by their distribution package, including:
- Package name and version
- Homepage/documentation links
- All Django app labels provided by that package
Example: django-allauth would show with all its apps: allauth, account, socialaccount, etc.
Shows Python packages that don't require INSTALLED_APPS registration but may be actively used by your application (like sentry-sdk, redis, requests, etc.), separated into:
- Important Integrations: Packages you specify in
important_integrationsconfig (e.g., Sentry, monitoring tools) - Other Integrations: All other installed packages, collapsed by default in an accordion
ABOUT_CONFIG = {
'important_integrations': {
'sentry-sdk', # Error tracking
'rollbar', # Alternative error tracking
'scout-apm', # Performance monitoring
'redis', # Redis client
'django-redis', # Django Redis integration
'whitenoise', # Static file serving
},
}This helps you quickly identify critical integrations while keeping the interface clean.
| Django Version | Python Version | Status |
|---|---|---|
| 5.2 | 3.10 - 3.12 | ✅ Tested |
| 5.1 | 3.10 - 3.12 | ✅ Tested |
| 5.0 | 3.10 - 3.12 | ✅ Supported |
| 4.2 (LTS) | 3.8 - 3.12 | ✅ Supported |
| 4.1 | 3.8 - 3.11 | ✅ Supported |
| 4.0 | 3.8 - 3.10 | ✅ Supported |
| 3.2 (LTS) | 3.6 - 3.10 | ✅ Supported |
To set up for development:
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/markcerv/django-about.git
cd django-about
# Create virtual environment
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # or `venv\Scripts\activate` on Windows
# Install in development mode
pip install -e ".[dev]"
# Run tests
pytestContributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request.
- Fork the repository
- Create your feature branch (
git checkout -b feature/amazing-feature) - Commit your changes (
git commit -m 'Add some amazing feature') - Push to the branch (
git push origin feature/amazing-feature) - Open a Pull Request
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
Created for use in Django projects that need to display system version information.
See CHANGELOG.md for version history.