this repo is based on introduction course to cryptography in my college so i decided to share my work and add more algorithms with some documentations.
- this algorithm is the simplest and is easy to be attacked by brute force just trying all 26 possibilities.
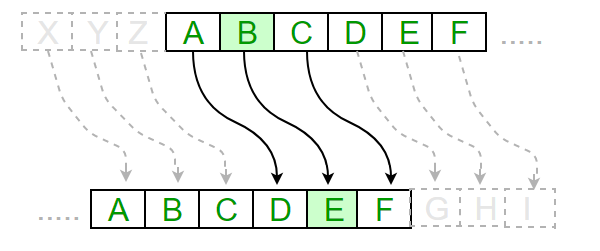
- the main idea is to shift the ascii value of the characters by the key.
- instead of just shifting characters we can substitute them.
- the key works as an index of every character substitution so it should have all the characters.
- things become a bit complex so focus.
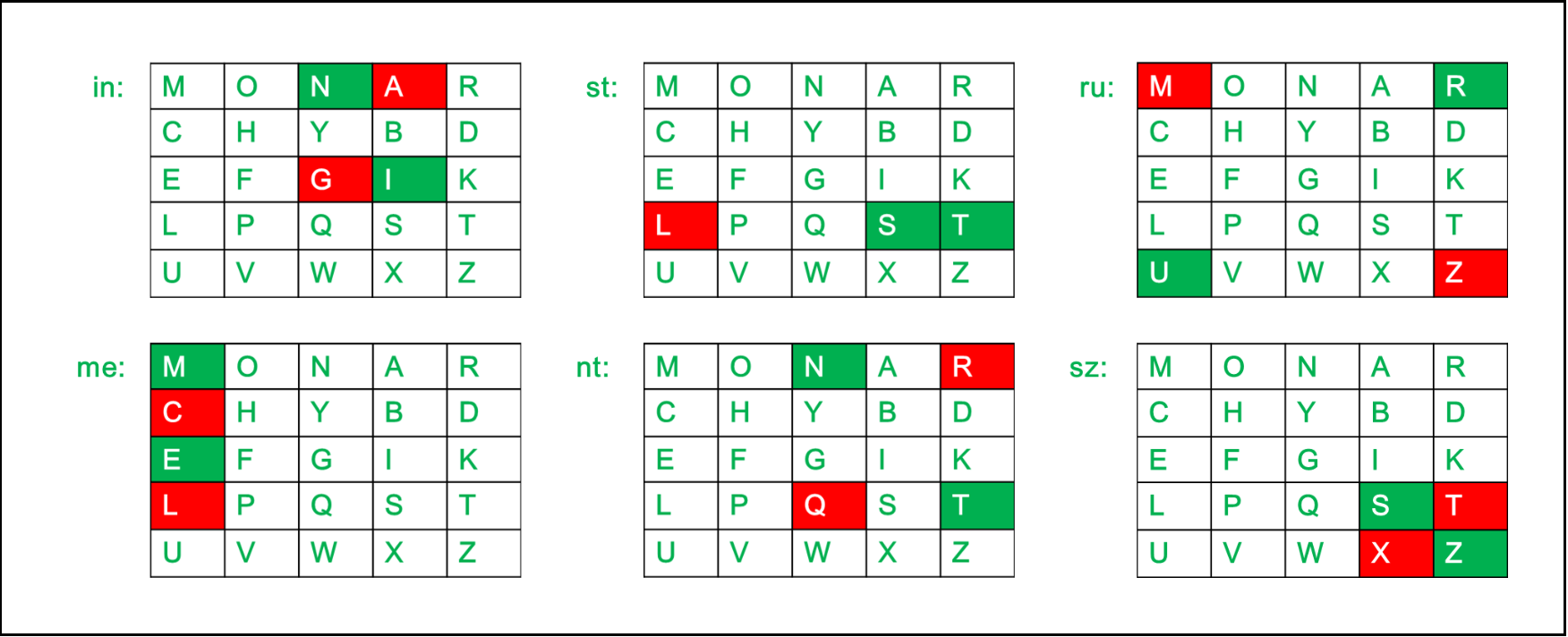
- the main idea is having a 5x5 matrix and substitute every character with another character in the matrix but in special way!
- the key should be a string.
- first step is initializing the matrix we will encrypt with.
- we put every character in the key so that we don't make any repetition (eg. bool -> b|o|l|...).
- then we but all the remaining characters in the matrix considering i and j as the same character.
- the way we encrypt is if the characters in the same row then we encrypt them to the characters beside them and if the character at the end of the row we substitute it with the first character.
- if they were in the same column we substitute them with the characters under them.
- if they were in different row and column then we substitute them with the inverse square(eg. ch1[0][1] , ch2[1][2] -> cipher1[0][2], cipher2[1][1]).
- simplest polyalphabetic substitution cipher
- the key is a string
- main idea : the key is shifter depending on the place of the character in the alphabet.
- we build the key by adding the input key multiple times until it reaches the length of the text (eg. poly-> polypolypo...etc).
- then we shift every character in the plain text by the place of the character in alphabet in the key(eg. home, key = abcd -> cipher = (h+0)(o + 1)(m + 2)(e + 3) = HPOH)
- autokey is mostly the same as vigenère with one difference that the key is filled with the plaintext rather that the key itself multiple times.
- (eg. plain = "helloworld", key = "keyhellowo")
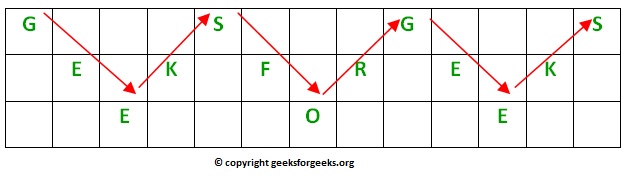
- the main idea : we have number of rows equal to the key
- every sequence of characters equal to the key is in separate row until we form a matrix with all characters in the plain text.
- then we encrypt by just putting every row of characters to the cipher text.
- the key in this image is 3 see how we put the 'G' in the first row then the 'E' and finally the 'E' the 3 sequence of characters then we moved up to put the other two characters in separate rows too.
- the encrypted text here is "GSGSEKFREKEOE"
- another example with key 4.
- the key: the key is a string containing numbers indicates the index of the column.
- in this cipher we put our plain text in a matrix such that every row has the length of the key and then fill the row with characters to z if the row's length is lower than the key length.
- then we read the matrix column by column instead of row by row.
- the idea here is to read the column with the first number in the key then 2nd one and so on to make the transposition in rows.
- so the cipher is generated by just reading every column but in the order given in the key.
- as you see here we first read the 3rd column as indexed in the key then the 4th one and we continue till we generate the cipher text.