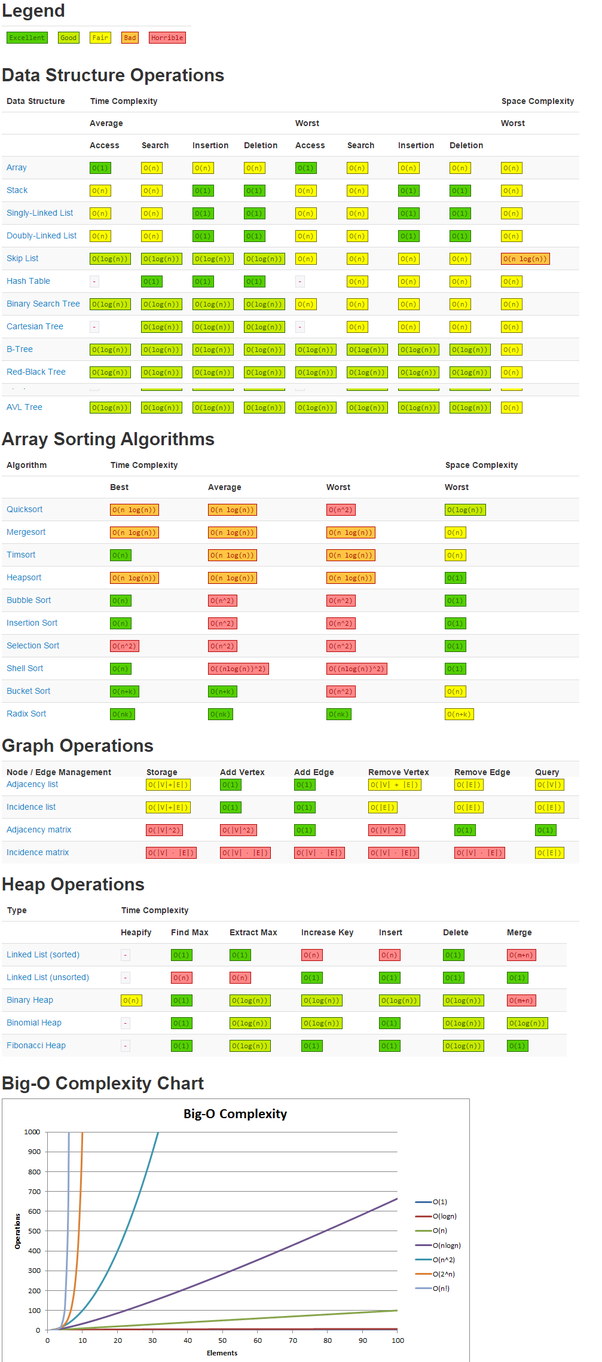
- Time complexity = speed, fast ,efficiency
- Space complexity = memory use (how much space is used) (extra variable and data structure to solve the algorithm)
In real world if you have large input for your functions both time and space starts to cause problems
we use these technique as an benchmark of the algorithm (to measure how good they are)
we dont compare it to the absolute ... we compare relative to the size of the input
Two time the input size ===>>> 2 times the time it takes
[1,2,3] = 1s(absolute) ,3(size)
[1,2,3,4,5,6] = 2s(absolute), 6(size)
we can also say that the relationship between time and input is 1 to 1 (1:1)
big O notation: o(n)
[1,2,3] = 0(extra space) 3(size) [1,2,3,4,5,6] = 0(extra space) 6(size)
if either space and the time has no realtionship with the input than we called it a constant space
big O notation: o(1)
order of efficiency
example =>
most efficient ==== > O(1) "constant"
O(log n) "logarithmic"
O(n) "linear"
O(n log n) "linear logarithmic"
O(n * n) "quadratic"
least efficient ==== > O(2 ^ n ) "exponential"
code example =
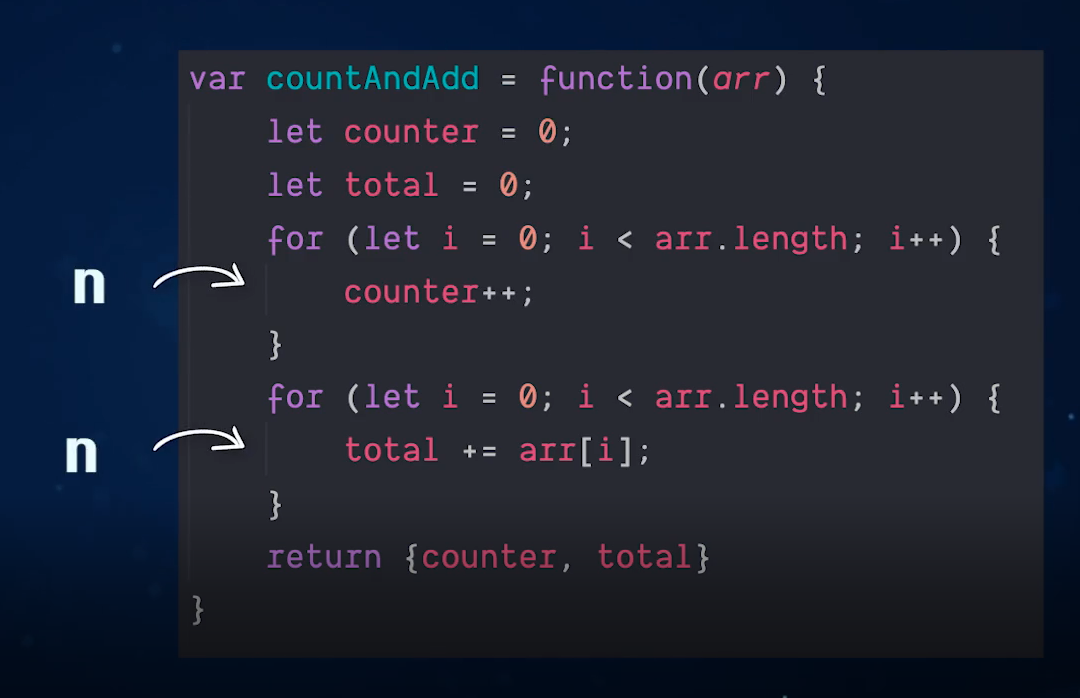
How does the input size effect the specific lines of the codes below
let length = (arr)=>{
// time and space will be constant here because int takes exactly the same space weather its 0 or 2,147,483,647
let counter = 0;
/* if we go from size [1] to [1,2]
size 1 2
iteration 1 2
so clearly there is 1 to 1 relationship which is linear */
for (let i = 0; i <arr.length; i++){ counter++; } return counter; }
so it is taking O(1) and 0(n) thats why we simplify and take the term which is in hghest order
simplifying BIG O
-- Drop the lower order term -- Drop constant term
n + n = 2n so we drop the 2 and remaining is the notation
1)best case 2) average case 3) worst case
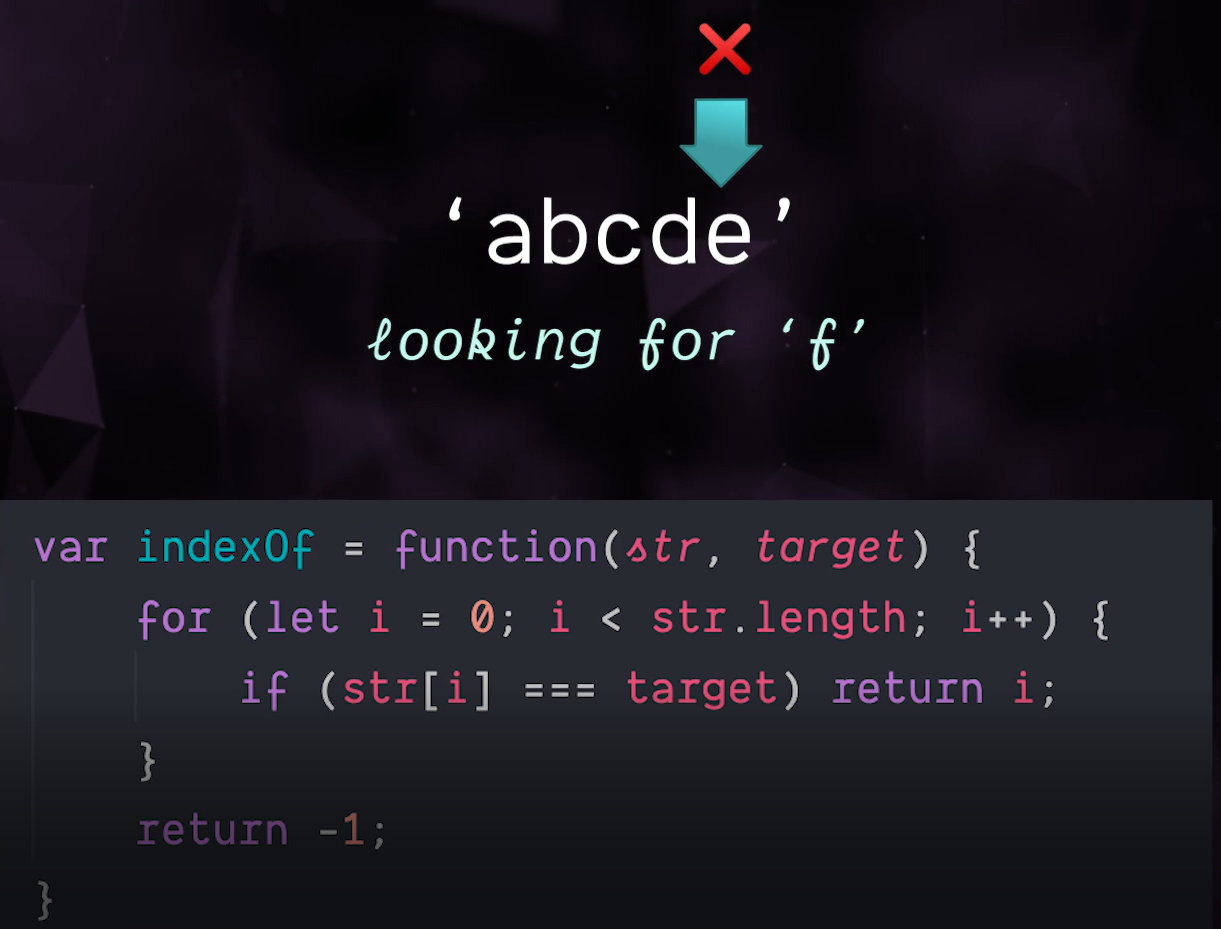
code example =
"abcde".indexof("b")
is "b" in "abcde"? if so return its index
- best case = less amount of effort
- average case = avg amount of effort
- worst case = most amount of effort
Hence, this "indexof" function is O(n) linear time
|
|--> Arrays
|
|--> Graph
|
|--> Hash Tables
|
|--> Linked Lists
| |--> Singly Linked Lists
| |--> Doubly Linked Lists
|
|--> Sequential
| |--> Stacks
| |--> Queues |
|--> Trees
| |-->Binary Search Trees
| | |--> Avl Tree
| | |--> Red Black Tree
| |
| |--> Trie
| |--> Binary Heap
| |--> Priority Queue
|
|
|--> Graph
(n-1)*(n-1)
= n^2 - 2n + 1
==> O(n^2)Repeat n-1 times
for i from 0 to n-2
if ith and i + 1 element out of order
swap em'n+(n-1)+(n-2)+....+ 1
= (n+1)*n/2 = n^2/2 + n/2
==>O(n^2)for i from 0 to n-1
find smallest item between ith item and last item
swap smallest item with ith item(1+2+3+....(n-1))
=(n-1)*n/2
= n^2/2 - n/2
==>o(n^2)for i ← 1 to length(Array) do
currentIndex ← i
while currentIndex > 0 and Array[currentIndex - 1] > Array[currentIndex] do
temp ← Array[currentIndex]
Array[currentIndex] ← Array[currentIndex - 1]
Array[currentIndex - 1] ← temp
currentIndex ← currentIndex - 1
end while
i ← i + 1O(nlogn)if only one item
return
else
sort left half of items
sort right half of items
merge sorted halves