Week 13 Project Submission
The files in this repository were used to configure the network depicted below.
Cloud Security Network Diagram
These files have been tested and used to generate a live ELK deployment on Azure. They can be used to either recreate the entire deployment pictured above. Alternatively, select portions of the YAML and Config files may be used to install only certain pieces of it, such as filebeat.
This document contains the following details:
- Description of the Topology
- Access Policies
- ELK Configuration
- Beats in use
- Machines being monitored
- How to use the Ansible Build
The main purpose of this network is to expose a load-balanced and monitored instance of DVWA, the D#mn Vulnerable Web Application.
Load balancing ensures that the application will be highly functional, in addition to restricting traffic to the network.
-
What aspect of security do load balancers protect?
- Without a load balancer your network is more susceptible to be attacked via a DoS (Denial of Service). The purpose of a Load Balancer is to protect against DDoS attacks and it does so by analyzing the incoming traffic and determines which server to send the traffic. This prevents a server from getting bombarded with traffic since the Load Balancer is able to evenly distribute traffic among the servers that are in the Load Balancing Pool. Load Balancers are usually equipped with Health Probes which periodically examines and determines if a machine is functioning properly before puching traffic through. If there is an issue with a server the Load Balancer will redirect the traffic.
-
What is the advantage of a jump box?
- A Jump Box is a great tool that allows you to have better control over who can gain access to a Virtual Network and everything inside. In order to access the other VM's on the network one will need the private IP's of those machines, which limits the outsiders from accessing information from your network.
Integrating an ELK server allows users to easily monitor the vulnerable VMs for the changes to the logs and system traffic.
- What does Filebeat watch for?
- The purpose of Filebeat is to watch out for any modifications in files and take note when those modifications were made by analyzing log files. Filebeat will also create and organize log files.
- What does Metricbeat record?
- The purpose of Metricbeat is to record data from the OS and services running on the server. With the help of tools such as Elastisearch, Logstash, and Kibana you are able to examine the data that is generated via Metricbeat.
The configuration details of each machine may be found below.
| Name | Function | IP Address | Operating System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jump Box | Gateway to run Docker w/Ansible | My Local IP | Linux |
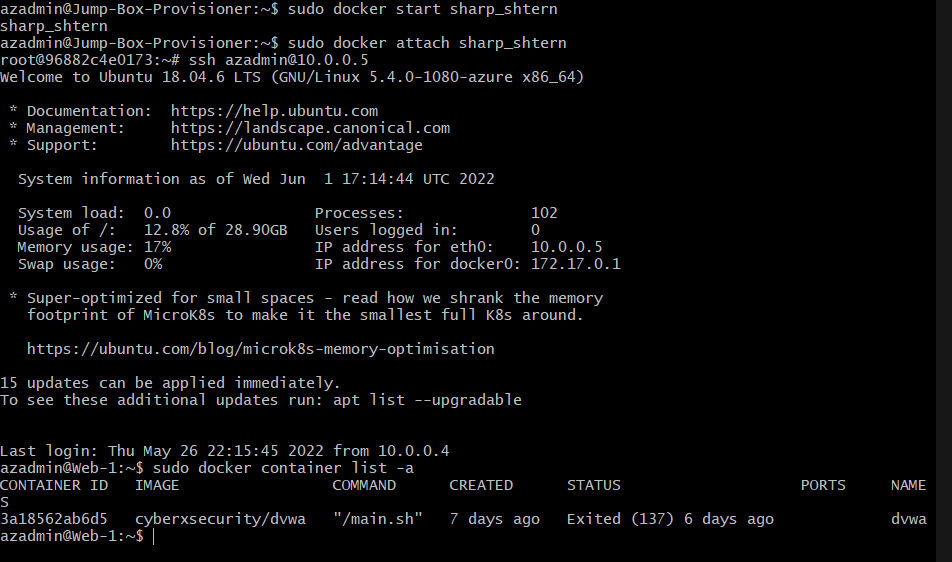
| Web-1 | Ubuntu Server to run DVWA | 10.0.0.5 | Linux |
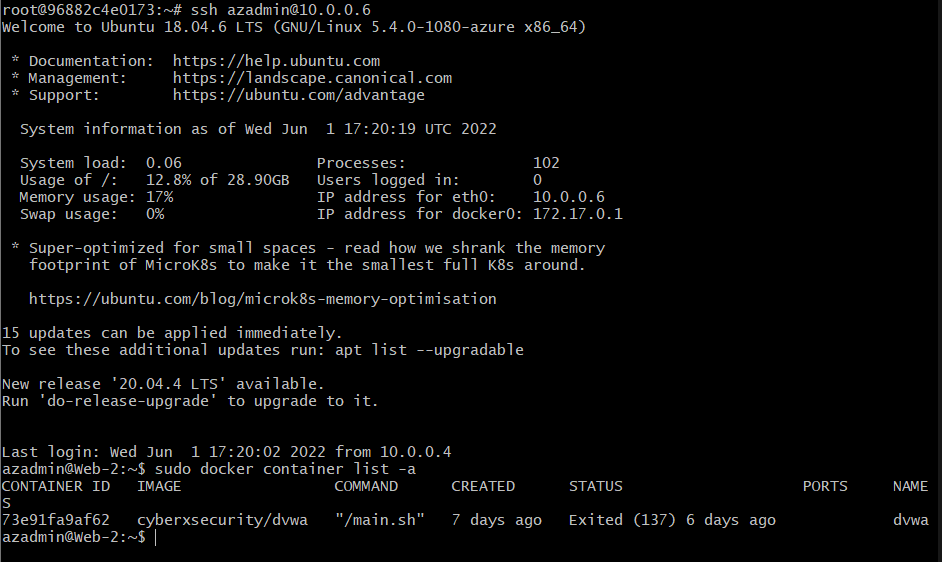
| Web-2 | Ubuntu Server to run DVWA | 10.0.0.6 | Linux |
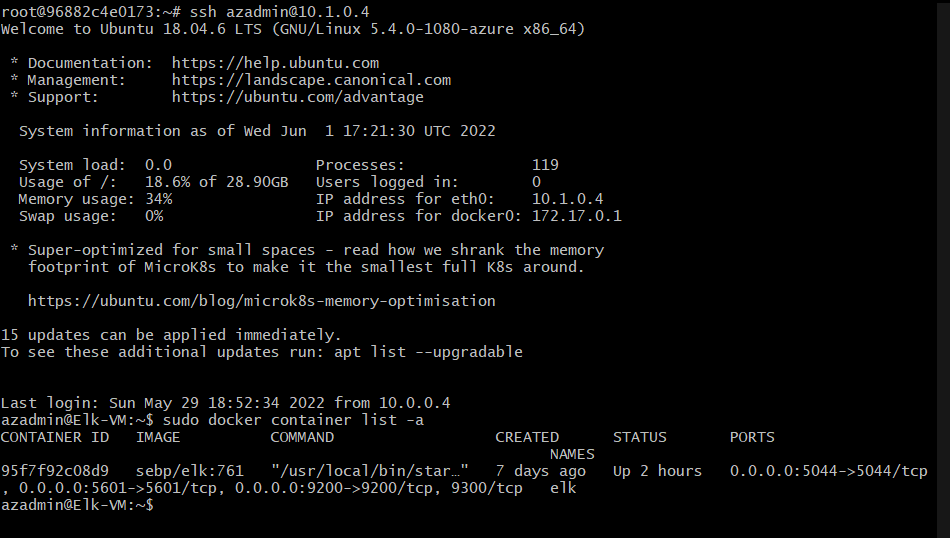
| Elk-VM | Elk Server | 10.1.0.4 | Linux |
The machines on the internal network are not exposed to the public Internet.
Only the Jump Box Provisioner can accept connections from the Internet. Access to this machine is only allowed from the following IP addresses:
- My Local IP Address via an SSH connection.
Machines within the network can only be accessed by Jump-Box-Provisioner.
- Jump-Box-Provisioner IP address: 20.211.93.7
A summary of the access policies in place can be found in the table below.
| Name | Publicly Accessible | Allowed IP Addresses |
|---|---|---|
| Jump Box | No | My Local IP |
| Web-1 | No | 10.0.0.4 |
| Web-2 | No | 10.0.0.4 |
| Elk-VM | No | 10.0.0/6 |
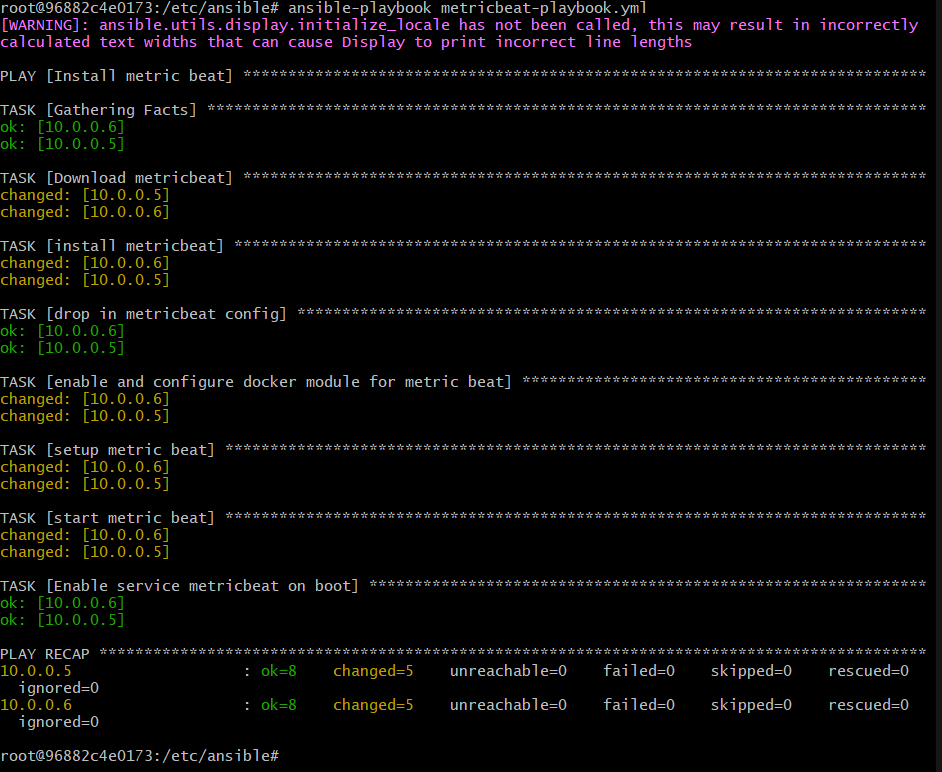
Ansible was used to automate configuration of the ELK machine. No configuration was performed manually, which is advantageous because...
- What is the main advantage of automating configuration with Ansible?
- Trying to set up an environment without Ansible would be very difficult and time consuming. The best part about ansible is it's flexibility: allowing you to manage the entire environment no matter the location. No major coding skills are required to create Ansible's playbooks making it simple to set up and utilize.
The playbook implements the following tasks:
- Installs docker.io on the Elk-VM.
- Installs Python3 on the Elk-VM.
- Downloads, installs and executes the Docker Elk Container on the Elk-VM on reboot so container doesn't need a manual boot.
- Enables docker on boot.
The following screenshot displays the result of running 'docker ps' after sucessfully configuring the ELK instance.
This ELK server is configured to monitor the following machines:
- 10.0.0.5
- 10.0.0.6
We have installed the following Beats on these machines:
These Beats allow us to collect the following information from each machine:
- The Filebeat collects information from the file system logs and determines what files have been altered and when this alteration occured. By connecting to Kibana one is able to examine the collected data from the Filebeat. From here one can then adjust for their desired time intervals and check for any modifications.
In order to use the playbook, you will need to have an Ansible control node already configured. Assuming you have such a control node provisioned:
SSH into the control node and follow the steps below:
- Copy the YAML file to the ansible directory.
- Update the config file to include the internal IP along with specified ports.
- In order to check that the ELK server is running navigate to: http://[ELK.VM.IP]:5601/app/kibana