Prediction using Logistic Regression
1.Introduction Logistic regression is a supervised learning algorithm used to predict a dependent categorical target variable. In essence, if you have a large set of data that you want to categorize, logistic regression may be able to help. Logistic regression predicts the output of a categorical dependent variable. Therefore the outcome must be a categorical or discrete value. It can be either Yes or No, 0 or 1, true or False, etc. but instead of giving the exact value as 0 and 1, it gives the probabilistic values which lie between 0 and 1.
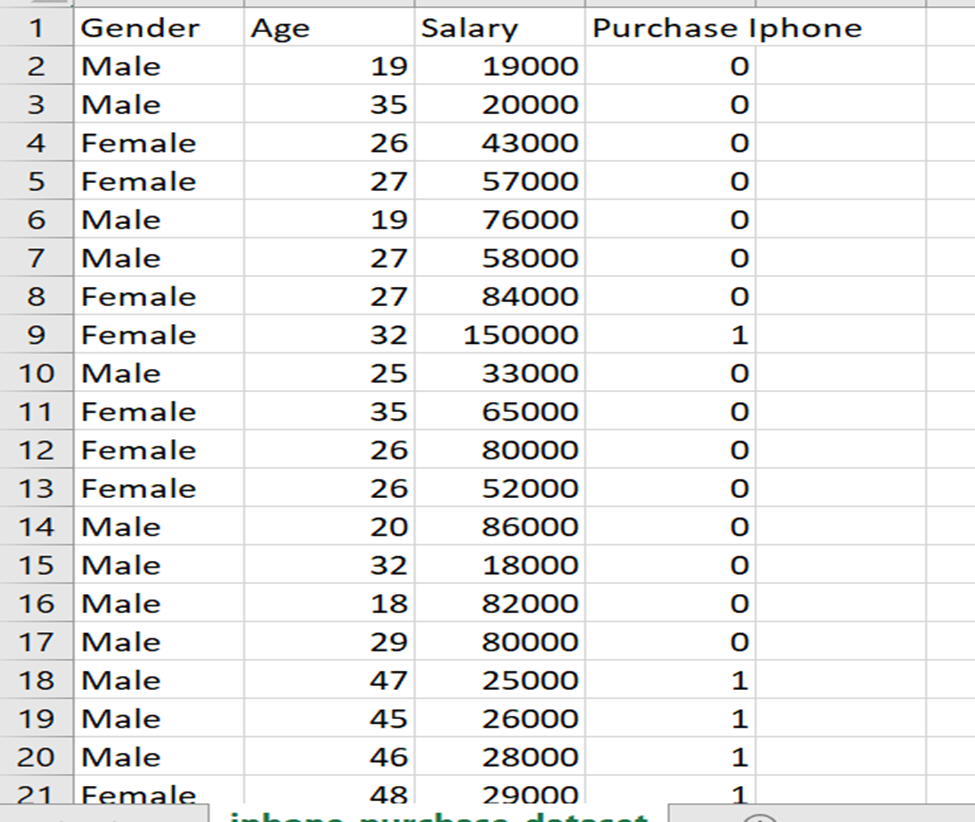
- Data Exploration: Let’s explore the dataset. It shows which users have purchased an Iphone. Our objective in this project is to predict if the customer will purchase an Iphone or not given their gender, age and salary. The sample rows are shown below. The column Gender is alphanumeric which is converted to numeric values. The columns “Gender”, “Age”, “Salary” are selected as features and the column “Purchase Iphone” is selected as a target.
-
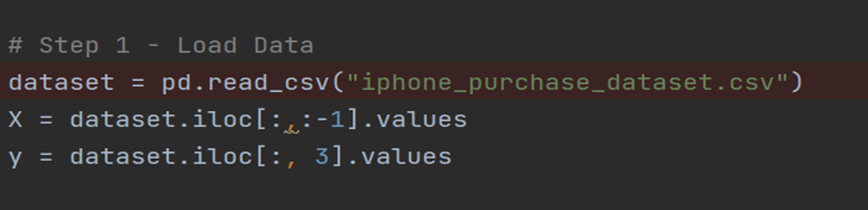
Load the dataset We will assign the three independent variables “Gender”, “Age”, “Salary” to X. The dependent variable that we need to predict – “Purchased iPhone” will be assigned to y.
-
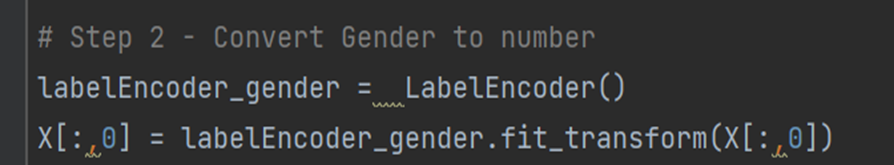
Convert Gender to Number The classification algorithm in sklearn library cannot handle the categorical (text) data. In our data, we have the Gender variable which we have to convert to numerical format. We will use the class LabelEncoder to convert text data of Gender variable to number.
-
Split the data into training and test set We will use the train_test split method to split our data into training and testing set. We will use 25% data for testing purpose.
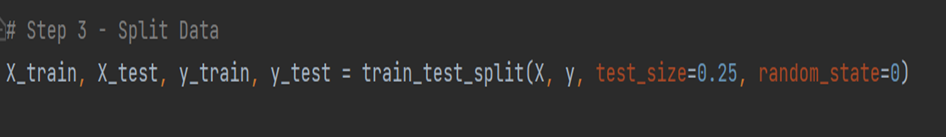
The train-test split is a technique for evaluating the performance of a machine learning algorithm. It can be used for classification or regression problems and can be used for any supervised learning algorithm. The procedure involves taking a dataset and dividing it into two subsets. The first subset is used to fit the model and is referred to as the training dataset. The second subset is not used to train the model; instead, the input element of the dataset is provided to the model, then predictions are made and compared to the expected values. This second dataset is referred to as the test dataset. Train Dataset: Used to fit the machine learning model. Test Dataset: Used to evaluate the fit machine learning model. The objective is to estimate the performance of the machine learning model on new data: data not used to train the model.
-
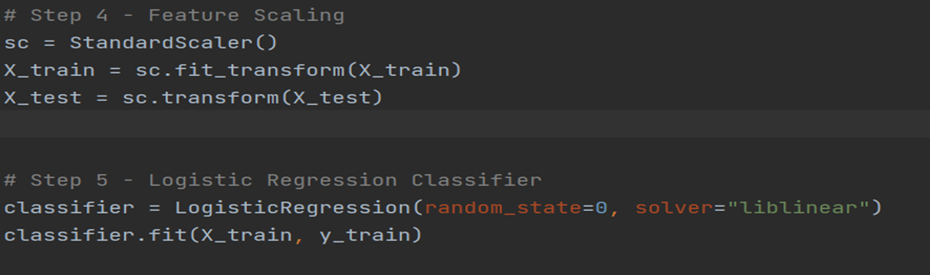
Feature Scaling and Fit the Classifier We will be using the DecisionTreeClassifier from the sklearn.tree library. When we create the object of DecisionTreeClassifier, we will set the criterion parameter as entropy.
-
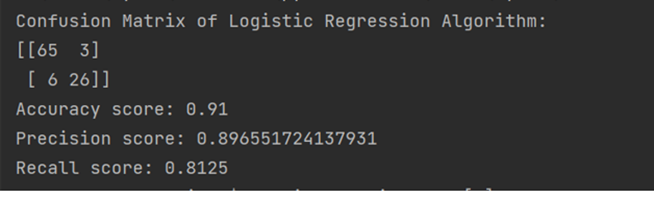
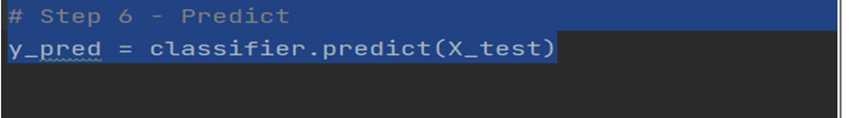
Make Predictions Now that we have trained the model, let’s make some predictions using the test dataset.
Precision Score: It is the percentage of predicted positive events that are actually positive.
Precision = TP / (TP + FP)