-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 7
259. 3Sum Smaller #302
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
259. 3Sum Smaller #302
Conversation
|
I also try adding unit tests for this problem. |
|
|
||
| import java.util.Arrays; | ||
|
|
||
| public class ThreeSumSmallerIterative { |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
I just copy the explanation to track the code while reading it.
Resolves #55
Algorithm:
Points to notice:
- Adding 3 numbers being less than some value is equivalent to picking one of these numbers, subtracting it from the target value and the sum of the other 2 being less than target - subtracted value (
target_).- We can then sort the array, loop over it from from the lowest value to the largest, subtract the value from the target and look at the right rest of the array for pairs of suitable numbers.
- We can then start this comparison from the right next of the value. The other compared value should then be the largest value. If some largest value + the left value is smaller than
target_then all the values smaller then this right large value can be added with the left value to get a sum smaller thantarget_.- The right pointer must be always larger than the left pointer then.
- If the previous operation is successful, we can increment the left pointer to look for two sums with the number at this pointer. Remember, the array is sorted.
- We should then do this collect the possible two sum combinations each time until the loop condition is false.
- In the main loop, if we can't find any two sums at some index, that means that we won't be able to find two sums for numbers larger than it for further indices.
- We don't always need to initialize the right boundary with the size of the array. Since the numbers are always getting larger, our new first possible right pointer will either be smaller than or equal to the previous first possible. So, we can store that in a variable.
| int rightBoundary; | ||
|
|
||
| public int threeSumSmaller(int[] nums, int target) { | ||
|
|
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
| public int findTwoSumsSmaller(int start, int target) { | ||
|
|
||
| int p1 = start, p2 = rightBoundary; | ||
| int count = 0; | ||
| boolean foundBounds = false; | ||
| while (p1 < p2) { | ||
| if (nums[p1] + nums[p2] >= target) { | ||
| if (!foundBounds) { | ||
| rightBoundary--; | ||
| } | ||
| p2--; | ||
| } else { | ||
| foundBounds = true; | ||
| count += p2 - p1; | ||
| p1++; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return count; | ||
| } |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Similar simplification may be done here too.
| public int reduceTwoSumsSmaller(int start) { | ||
| int currTarget = target - nums[start]; | ||
| int p1 = start + 1, p2 = rightBoundary; | ||
| int count = 0; | ||
| boolean foundBounds = false; | ||
| while (p1 < p2) { | ||
| if (nums[p1] + nums[p2] >= currTarget) { | ||
| if (!foundBounds) { | ||
| rightBoundary--; | ||
| } | ||
| p2--; | ||
| } else { | ||
| foundBounds = true; | ||
| count += p2 - p1; | ||
| p1++; | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| return count == 0 ? 0 : count + reduceTwoSumsSmaller(start + 1); | ||
| } |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
How do we make use of the right boundary in this? I don't think itmis being used.
 altay9
left a comment
altay9
left a comment
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Thank you for your valuable contribution and collaboration Erdem.
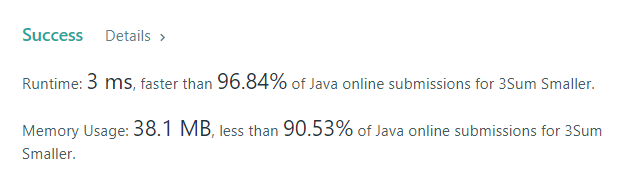

Resolves #55
Algorithm:
Points to notice:
target_).target_then all the values smaller then this right large value can be added with the left value to get a sum smaller thantarget_.