Smart computation management - Only recalculate what's necessary
Loman tracks the state of your computations and their dependencies, enabling intelligent partial recalculations that save time and computational resources. Perfect for data pipelines, real-time systems, and complex analytical workflows.
- ✨ Features
- 📥 Installation
- 🛠️ Development
- 🚀 Quick Start
- 📖 Documentation
- ☁️ Codespaces
- 👥 Contributing
Build smarter computation graphs with automatic dependency tracking
- 🔄 Smart Recalculation: Only compute what's changed - save time and resources
- 📊 Dependency Tracking: Automatic graph-based dependency management
- 🎯 Selective Updates: Control which outputs to compute and when
- 💾 State Persistence: Serialize computation graphs for inspection and recovery
- 🔍 Visual Debugging: Built-in GraphViz integration for computation visualization
- ⚡ Real-time Ready: Perfect for systems with inputs that tick at different rates
- 🧪 Research Friendly: Iterate quickly by updating methods and re-running only necessary computations
- 🔗 Framework Agnostic: Works with NumPy, Pandas, and your favorite Python libraries
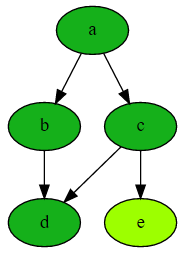
The above computation graph was generated with this simple Loman code:
from loman import Computation
# Create a computation graph
comp = Computation()
comp.add_node('a', value=1) # Input node
comp.add_node('b', lambda a: a + 1) # b depends on a
comp.add_node('c', lambda a, b: 2 * a) # c depends on a and b
comp.add_node('d', lambda b, c: b + c) # d depends on b and c
comp.add_node('e', lambda c: c + 1) # e depends on c
# Smart computation - only calculates what's needed
comp.compute('d') # Will not compute 'e' unnecessarily!
# Inspect intermediate values
comp.to_dict()
# {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 2, 'd': 4, 'e': None}
# Visualize the computation graph
comp.draw() # Creates the graph shown above
📚 Explore More: Check out our Interactive Examples including:
- 💰 Interest Rate Swap Pricing
- 📈 Portfolio Valuation
- 🏦 CDO Modeling
Loman transforms how you build and maintain complex data processing pipelines by making computational dependencies explicit and manageable. Instead of manually tracking what needs to be recalculated when data changes, Loman handles this automatically.
-
🔴 Real-time Systems: Handle inputs that tick at different rates efficiently
- Only recalculate affected downstream computations
- Control which outputs are computed and when
- Monitor status of all components in your pipeline
-
📦 Batch Processing: Build robust daily/periodic processes
- Serialize computation state for easy inspection and debugging
- Replace inputs or override intermediate values without full recomputation
- Recover from failures efficiently by resuming from last good state
-
🔬 Research & Analytics: Accelerate iterative development
- Modify calculation methods and re-run only what's needed
- Track complex dependencies in evolving analysis pipelines
- Reuse expensive intermediate computations across experiments
📖 Learn More: The Introduction explains in detail how Loman can transform your workflow.
pip install lomangit clone https://github.com/janusassetallocation/loman.git
cd loman
pip install -e .Note: Use -e flag for editable installation during development
For contributors and advanced users
Loman uses modern Python development tools for a smooth developer experience:
# 📦 Install development dependencies
make install
# 🧪 Run tests with coverage
make test
# ✨ Format and lint code
make check- Testing: pytest with coverage reporting
- Formatting: ruff for code formatting and linting
- Task Management: Taskfile for build automation
- Quality: Pre-commit hooks for code quality
- 📚 Complete Documentation: Comprehensive guides and API reference
- 🚀 Quickstart Guide: Get up and running in minutes
- 💡 User Guide: In-depth concepts and strategies
- 📊 Interactive Examples: Real-world financial modeling examples
- 🔧 API Reference: Complete function and class documentation
Instant development environment in your browser Click the button to launch a fully configured development environment in your browser.
- 🐍 Python 3.13 - Latest Python with all dependencies pre-installed
- 🛠️ Development Tools - pytest, ruff, mypy, pre-commit hooks ready to go
- 📓 Interactive Notebooks - Marimo notebooks for exploring examples
- ⚡ Zero Setup - Everything configured ready to go
- 🎯 VS Code Extensions - Python, testing, and productivity extensions pre-installed
We welcome contributions! 🎉
Whether you're fixing bugs, adding features, or improving documentation, your help makes Loman better for everyone.
- 🍴 Fork the repository
- 🌿 Create your feature branch:
git checkout -b feature/amazing-feature - ✨ Make your changes and add tests
- 🧪 Test your changes:
make test - 📝 Commit your changes:
git commit -m 'Add amazing feature' - 🚀 Push to your branch:
git push origin feature/amazing-feature - 🎯 Open a Pull Request
- Jebel-Quant/rhiza for standardised CI/CD templates and project tooling
⭐ If you find Loman useful, please consider giving it a star! ⭐