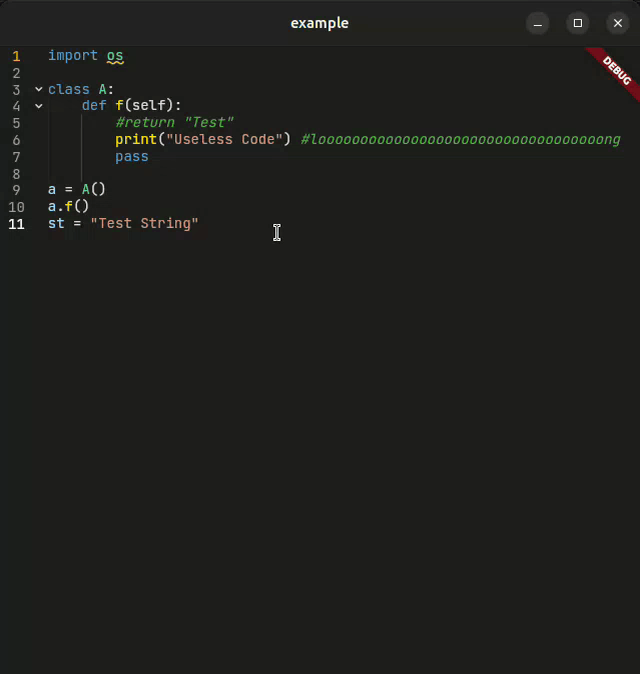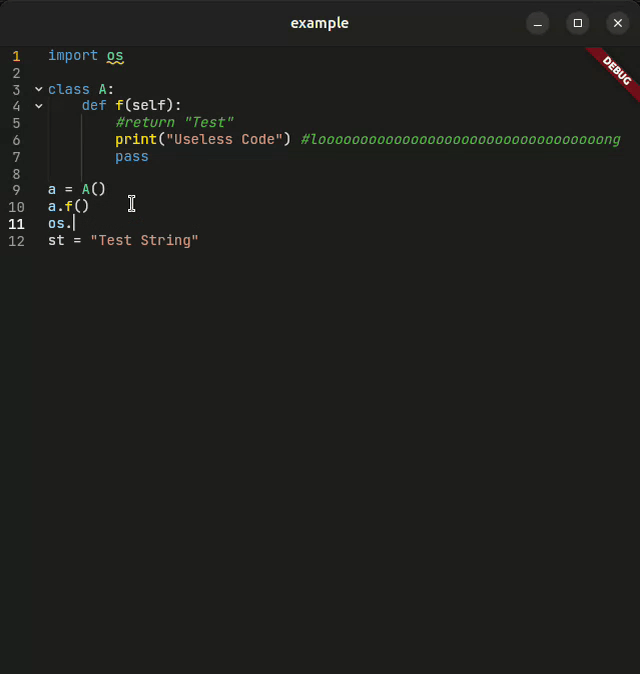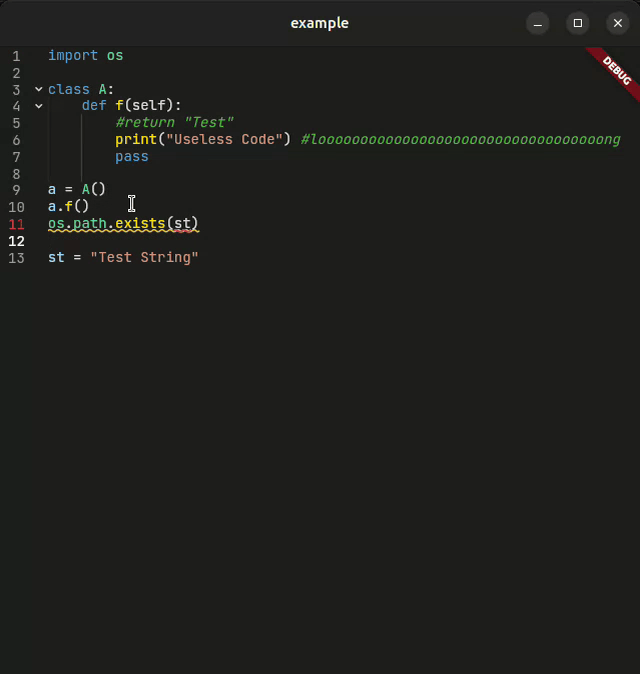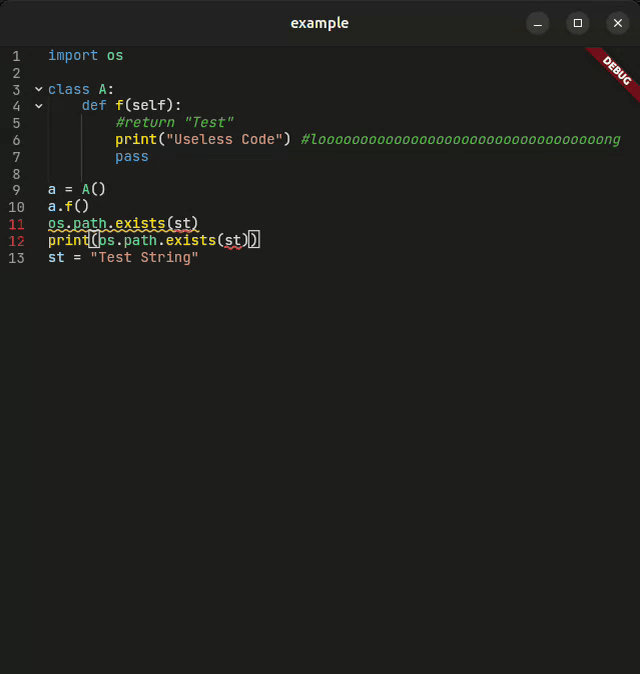
A powerful, feature-rich code editor created using Flutter
Bring VS Code-level editing experience to your Flutter apps
A complete and better alternative for re_editor, flutter_code_crafter, flutter_code_editor, code_text_field, etc
large code support (tested with 100k+ lines) and LSP based intelligent lazy highlighting
Note
CodeForge does not support Flutter web, as it relies on dart:io for core functionality. Web support may be considered in the future if dependencies allow.
CodeForge is a next-generation code editor widget designed for developers who demand more. Whether you're building an IDE, a code snippet viewer, or an educational coding platform, CodeForge delivers:
| Feature | CodeForge | Others |
|---|---|---|
| 🎨 Syntax Highlighting | ✅ 180+ languages Availabe languages |
✅ |
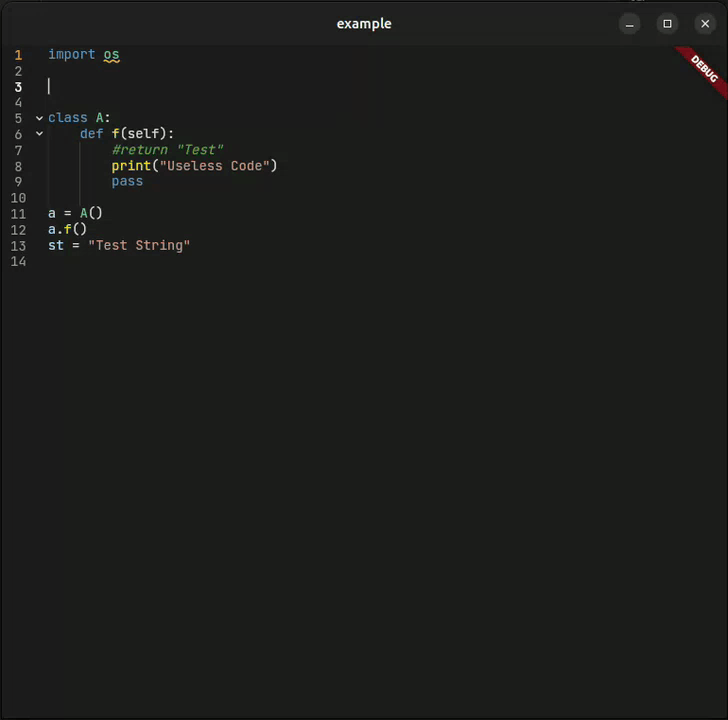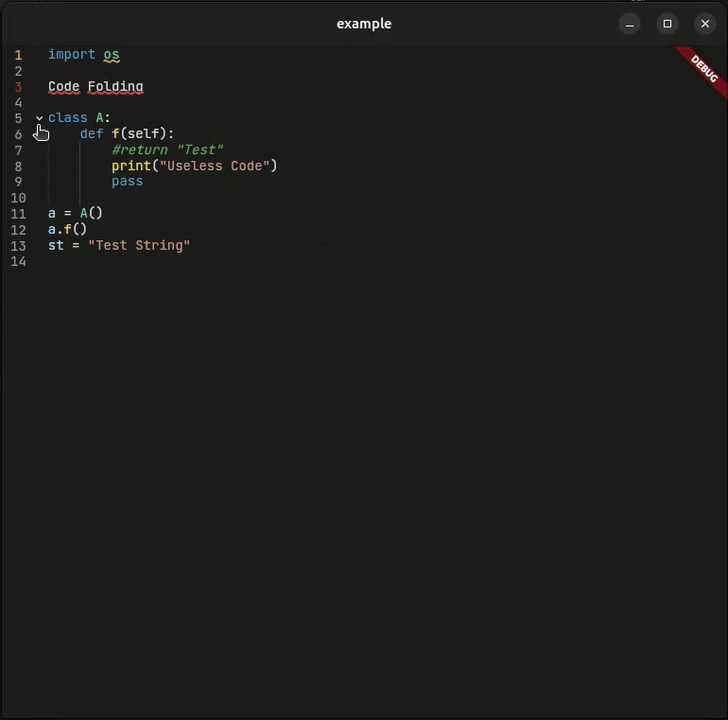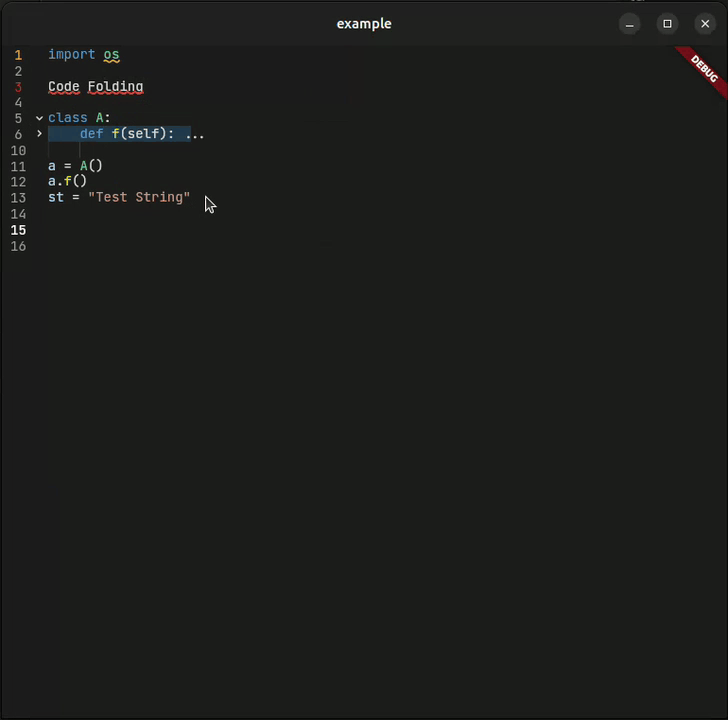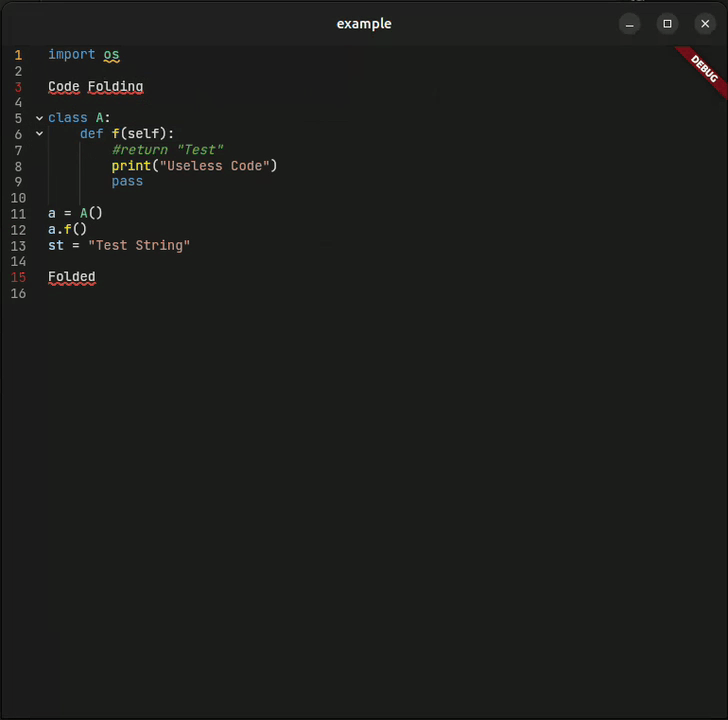
| 📁 Code Folding | ✅ Smart detection | |
| 🔌 LSP Integration | ✅ Full support | ❌ |
| 🤖 AI Completion | ✅ Multi-model | ❌ |
| ⚡ Semantic Tokens | ✅ Real-time | ❌ |
| 🎯 Diagnostics | ✅ Inline errors | ❌ |
| ↩️ Undo/Redo | ✅ Smart grouping | |
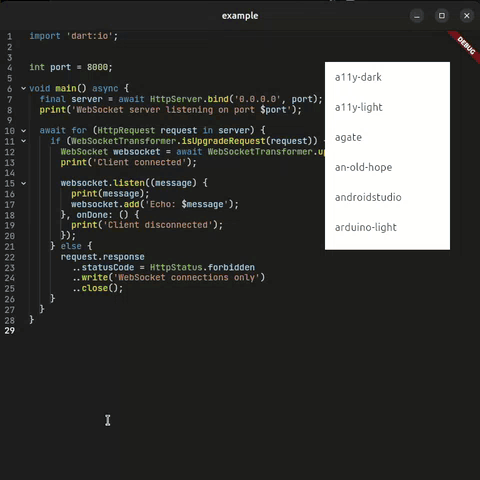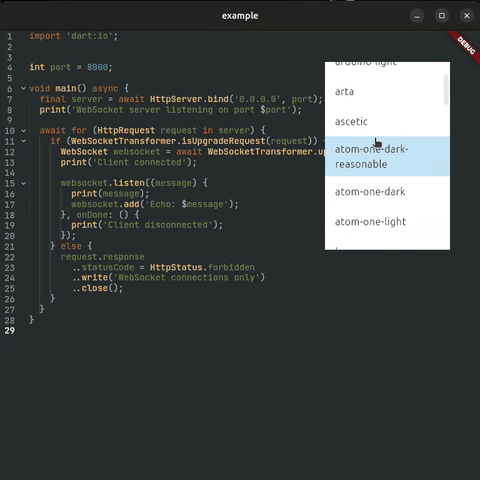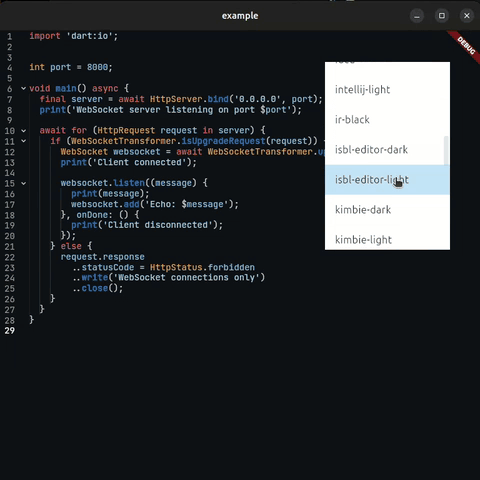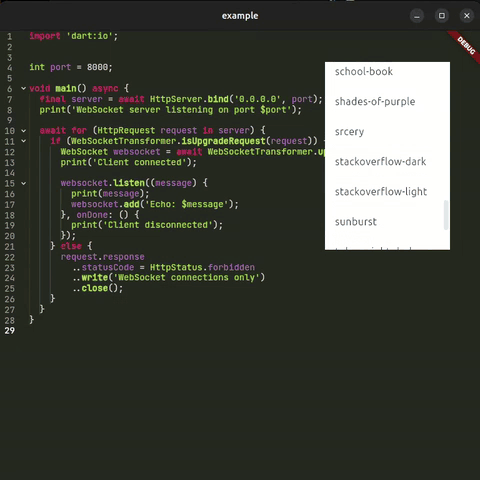
| 🎨 Full Theming | ✅ Everything Available themes |
- Uses the rope data structure instead of regular char array to to handle large text.
- Uses flutter's low level
RenderBoxandParagrahBuilderto render text insted ofTextFieldfor efficiency. - Built in Language Server Protocol client
- AI Code completion.
Intelligent code suggestions powered by AI models like Gemini. Auto, manual, or mixed completion modes with smart debouncing.
Full Language Server Protocol support with real-time diagnostics, hover documentation, and semantic highlighting.
Collapse and expand code blocks with visual indicators. Navigate large files with ease.
📋 Complete Feature List
- ⚡ Rope Data Structure — Optimized for large files
- 🎨 180+ Languages — Via
re_highlightpackage - 📁 Code Folding — Smart block detection
- 📏 Indentation Guides — Visual code structure
- 🔢 Line Numbers — With active line highlighting
- ↩️ Smart Undo/Redo — Timestamp-based grouping
- 🔍 Search Highlighting — Find and highlight matches
- ✂️ Line Operations — Move, duplicate, delete lines
- 💡 Intelligent Completions — Context-aware suggestions
- 📖 Hover Documentation — Rich markdown tooltips
- 🚨 Real-time Diagnostics — Errors and warnings
- 🎨 Semantic Highlighting — Token-based coloring
- 📡 Multiple Protocols — Stdio and WebSocket support
- 🤖 Multi-Model Support — Gemini and extensible
- ⚙️ Completion Modes — Auto, manual, or mixed
- 💾 Response Caching — Improved performance
- 🧹 Smart Parsing — Clean code extraction
- 🎨 Full Theming — Every element customizable
- 📐 Gutter Styling — Colors, icons, sizes
- ✨ Selection Styling — Cursor, selection, bubbles
- 💬 Popup Styling — Suggestions, hover details
Add CodeForge to your pubspec.yaml:
dependencies:
code_forge: ^1.0.2Then run:
flutter pub getImport a theme and a language from the re_highlight package and you are good to go. (Defaults to langDart and vs2015Theme):
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:code_forge/code_forge.dart';
import 'package:re_highlight/languages/python.dart';
import 'package:re_highlight/styles/atom-one-dark.dart';
void main() => runApp(const MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body: CodeForge(
language: langPython, // Defaults to langDart
editorTheme: atomOneDarkTheme, // Defaults to vs2015Theme
),
),
);
}
}For more control over the editor:
class _EditorState extends State<Editor> {
final _controller = CodeForgeController();
final _undoController = UndoRedoController();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return CodeForge(
controller: _controller, // Optional controller for more features.
undoController: _undoController, // Optional undo controller to control the undo-redo operations.
);
}
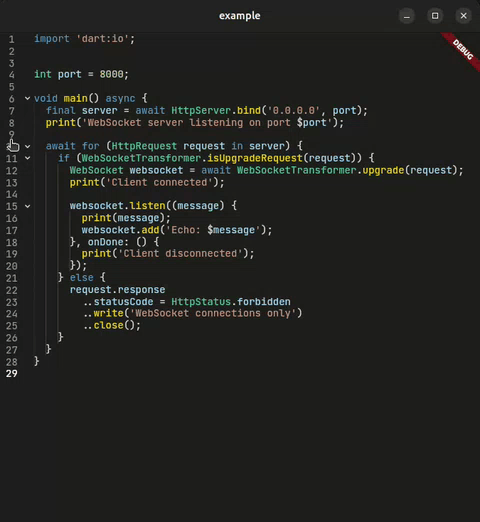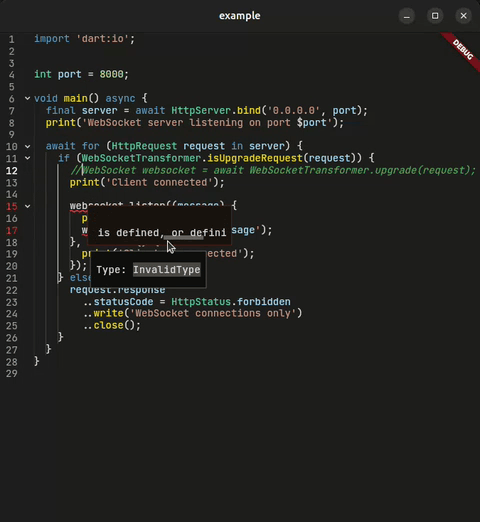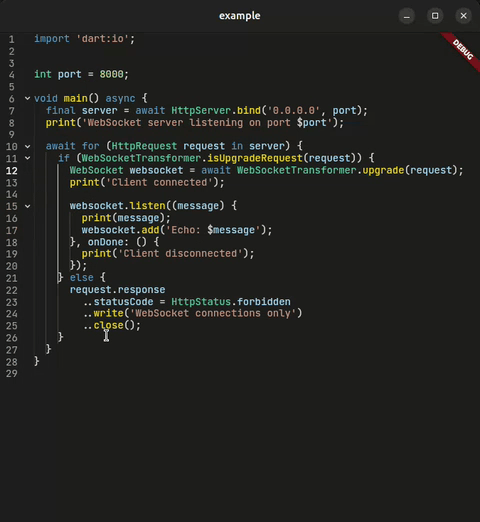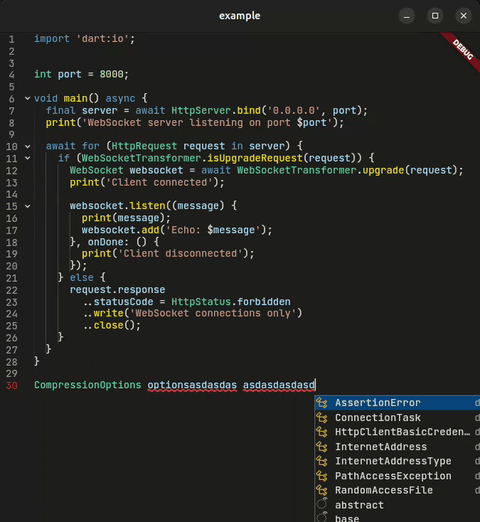
}Connect to any Language Server Protocol compatible server for intelligent code assistance.
CodeForge provides a built-in LSP client that allows you to connect to any LSP server for intelligent highlighting, completions, hover details, diagnostics, and more.
- Using WebSocket (easy and recommended)
- Using stdio
The class LspSocketConfig is used to connect to an LSP server using WebSocket. It takes the following parameters:
serverUrl: The WebSocket URL of the LSP server.filePath: A filePath is required by the LSP server to provide completions and diagnostics.workspacePath: The workspace path is the current directory or the parent directory which holds thefilePathfile.languageId: This is a server specific parameter. eg:'python'is the language ID used in basedpyright/pyright language server.
You can easily start any language server using websocket using the lsp-ws-proxy package. For example, to start the basedpyright language server, you can use the following command:
(On Android, you can use Termux)
cd /Downloads/lsp-ws-proxy_linux # Navigate to the directory where lsp-ws-proxy is located
./lsp-ws-proxy --listen 5656 -- basedpyright-langserver --stdio # Start the pyright language server on port 5656create a LspSocketConfig object and pass it to the CodeForge widget.
final lspConfig = LspSocketConfig(
filePath: '/home/athul/Projects/lsp/example.py',
workspacePath: "/home/athul/Projects/lsp",
languageId: "python",
serverUrl: "ws://localhost:5656"
),Then pass the lspConfig instance to the CodeForge widget:
CodeForge(
controller: controller,
theme: anOldHopeTheme,
filePath: "/home/athul/Projects/lsp/example.py" // Pass the same filePath used in LspConfig
lspConfig: lspConfig, // Pass the LSP config here
),This method is easy to start—no terminal setup or extra packages are needed—but it does require a bit more setup in your code. The LspStdioConfig.start() method connects to an LSP server using stdio and is asynchronous, so you'll typically use a FutureBuilder to handle initialization. It accepts the following parameters:
executable: Location of the LSP server executable file.args: Arguments to pass to the LSP server executable.filePath: A filePath is required by the LSP server to provide completions and diagnostics.workspacePath: The workspace path is the current directory or parent directory which holds thefilePathfile.languageId: This is a server specific parameter. eg:'python'is the language ID used in pyright language server.
To get the executable path, you can use the which command in the terminal. For example, to get the path of the basedpyright-langserver, you can use the following command:
which basedpyright-langserverCreate an async method to initialize the LSP configuration.
Future<LspConfig?> _initLsp() async {
try {
final config = await LspStdioConfig.start(
executable: '/home/athul/.nvm/versions/node/v20.19.2/bin/basedpyright-langserver',
args: ['--stdio'],
filePath: '/home/athul/Projects/lsp/example.py',
workspacePath: '/home/athul/Projects/lsp',
languageId: 'python',
);
return config;
} catch (e) {
debugPrint('LSP Initialization failed: $e');
return null;
}
}Then use a FutureBuilder to initialize the LSP configuration and pass it to the CodeForge widget:
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body: SafeArea(
child: FutureBuilder(
future: _initLsp(), // Call the async method to get the LSP config
builder: (context, snapshot) {
if(snapshot.connectionState == ConnectionState.waiting) {
return Center(child: CircularProgressIndicator());
}
return CodeForge(
editorTheme: anOldHopeTheme,
controller: controller,
filePath: '/home/athul/Projects/lsp/example.py',
textStyle: TextStyle(fontSize: 15, fontFamily: 'monospace'),
lspConfig: snapshot.data, // Pass the LSP config here
);
}
),
)
),
);
}Future<LspConfig> setupDartLsp() async {
return await LspStdioConfig.start(
executable: 'dart',
args: ['language-server', '--protocol=lsp'],
filePath: '/path/to/your/file.dart',
workspacePath: '/path/to/your/project',
languageId: 'dart',
);
}
// In your widget
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body: SafeArea(
child: FutureBuilder<LspConfig>(
future: setupDartLsp(),
builder: (context, snapshot) {
if (snapshot.connectionState == ConnectionState.waiting) {
return CircularProgressIndicator();
}
return CodeForge(
language: langDart,
textStyle: GoogleFonts.jetBrainsMono(),
lspConfig: snapshot.data,
filePath: '/path/to/your/file.dart', // Mandatory field and should be same as the [filePath] given in the [LspConfig]
);
},
),
),
),
);
}Supercharge your editor with AI-powered code completion.
model: An instance of theModelsclass, which can be one of the built-in AI models or a custom model.
enableCompletion: A boolean value to enable or disable AI code completion. Defaults totrue.completionType: The type of AI code completion. Defaults toCompletionType.auto.debounceTime: The debounce time in milliseconds for AI code completion. Defaults to1000.
create an instance of the AiCompletion class with any of the built-in AI models or custom model and pass it to the CodeForge widget.
Example of using Gemini AI completion:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:code_crafter/code_crafter.dart';
final aiCompletion = AiCompletion(
model: Gemini(
apiKey: "Your API Key",
)
)Then pass the aiCompletion instance to the CodeForge widget:
CodeForge(
controller: controller,
theme: anOldHopeTheme,
aiCompletion: aiCompletion, // Pass the AI completion instance here
),pass the aiCompletionTextStyle parameter to the CodeForge widget to style the AI completion text. This is a TextStyle object that will be applied to the AI completion text. Recommended to leave it null as default style, which is similar to VSCode completion style.
CodeForge(
controller: controller,
theme: anOldHopeTheme,
aiCompletion: aiCompletion,
aiCompletionTextStyle: TextStyle(
color: Colors.grey, // Change the color of the AI completion text
fontStyle: FontStyle.italic, // Make the AI completion text italic
),
),If you want to trigger AI code completion manually, you can use the getManualAiCompletion() callback in the CodeForgeController. This callback will be called when the AI code completion is triggered.
In this example, a FloatingActionButton is used to trigger the AI code completion manually:
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(onPressed: ()=> controller.getManualAiSuggestion()),
body: SafeArea(
child: CodeForge(
editorTheme: anOldHopeTheme,
controller: controller,
textStyle: GoogleFonts.notoSansMono(
fontSize: 15,
),
aiCompletion: AiCompletion(
completionType: CompletionType.manual,
model: Gemini(
apiKey: apiKey,
)
),
),
)
),
);
}apiKey: Your Gemini API key.
model: The model to use for completion. Defaults togemini-2.0-flash.temperature: The temperature to use for completion. Defaults tonull.maxOutPutTokens: The maximum number of tokens to generate. Defaults tonull.TopP: The top P value to use for completion. Defaults tonull.TopK: The top K value to use for completion. Defaults tonull.stopSequences: The stop sequences to use for completion. Defaults tonull.
apiKey: Your OpenAI API key.model: The model to use for completion.
apiKey: Your Claude API key.model: The model to use for completion.
apiKey: Your OpenAI API key.model: The model to use for completion.
apiKey: Your OpenAI API key.model: The model to use for completion.
apiKey: Your OpenAI API key.model: The model to use for completion.
apiKey: Your OpenAI API key.model: The model to use for completion.
apiKey: Your OpenAI API key.model: The model to use for completion.
apiKey: Your OpenAI API key.model: The model to use for completion.
apiKey: Your OpenAI API key.model: The model to use for completion.
If want to use a custom AI model that running on your own server or a third party service not listed above, you can create an instance of the CustomModel class and pass it to the AiCompletion class.
url: The URL of the AI model endpoint.customHeaders: The custom headers to use for the request.Stringcontent.requestBuilder: The request builds the request and return the response. This is a function that takes twoStringparameters code and instruction as input and returns aMap<String, dynamic>.customParser: A function that parse the json response and returnsStringcontent.
late final Models model;
@override
void initState() {
model = CustomModel(
url: "https://api.together.xyz/v1/chat/completions",
customHeaders: {
"Authorization": "Bearer ${your_api_key}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
requestBuilder: (code, instruction){
return {
"model": "deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3",
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": instruction
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": code
}
]
};
},
customParser: (response) => response['choices'][0]['message']['content']
);
controller = CodeCrafterController();
controller.language = python;
super.initState();
}Then pass the model instance to the AiCompletion class:
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body: CodeForge(
editorTheme: anOldHopeTheme,
controller: controller,
aiCompletion: AiCompletion(
model: model // Pass the custom model here
),
)
),
);
}CodeForge offers extensive customization options for every aspect of the editor.
CodeForge(
controller: controller,
language: langDart,
// Editor theme (syntax colors)
editorTheme: vs2015Theme,
// Text styling
textStyle: GoogleFonts.jetBrainsMono(fontSize: 14),
// AI Completion styling
aiCompletionTextStyle: TextStyle(
color: Colors.grey, // Change the color of the AI completion text
fontStyle: FontStyle.italic, // Make the AI completion text italic
),
// Selection & cursor
selectionStyle: CodeSelectionStyle(
cursorColor: Colors.white,
selectionColor: Colors.blue.withOpacity(0.3),
cursorBubbleColor: Colors.blue,
),
// Gutter (line numbers & fold icons)
gutterStyle: GutterStyle(
lineNumberStyle: TextStyle(color: Colors.grey),
backgroundColor: Color(0xFF1E1E1E),
activeLineNumberColor: Colors.white,
foldedIconColor: Colors.grey,
unfoldedIconColor: Colors.grey,
errorLineNumberColor: Colors.red,
warningLineNumberColor: Colors.orange,
),
// Suggestion popup
suggestionStyle: SuggestionStyle(
backgroundColor: Color(0xFF252526),
textStyle: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
elevation: 8,
),
// Hover documentation
hoverDetailsStyle: HoverDetailsStyle(
backgroundColor: Color(0xFF252526),
textStyle: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),
),
)CodeForge(
// Enable/disable features
enableFolding: true, // Code folding
enableGutter: true, // Line numbers
enableGuideLines: true, // Indentation guides
enableGutterDivider: false, // Gutter separator line
enableSuggestions: true, // Autocomplete
// Behavior
readOnly: false, // Read-only mode
autoFocus: true, // Auto-focus on mount
lineWrap: false, // Line wrapping
)| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
controller |
CodeForgeController? |
Text and selection controller |
undoController |
UndoRedoController? |
Undo/redo history controller |
language |
Mode? |
Syntax highlighting language |
editorTheme |
Map<String, TextStyle>? |
Syntax color theme |
textStyle |
TextStyle? |
Base text style |
lspConfig |
LspConfig? |
LSP server configuration |
aiCompletion |
AiCompletion? |
AI completion settings |
filePath |
String? |
File path for LSP |
initialText |
String? |
Initial editor content |
readOnly |
bool |
Read-only mode |
enableFolding |
bool |
Enable code folding |
enableGutter |
bool |
Show line numbers |
enableGuideLines |
bool |
Show indentation guides |
selectionStyle |
CodeSelectionStyle? |
Selection styling |
gutterStyle |
GutterStyle? |
Gutter styling |
suggestionStyle |
SuggestionStyle? |
Suggestion popup styling |
hoverDetailsStyle |
HoverDetailsStyle? |
Hover popup styling |
final controller = CodeForgeController();
// Text operations
controller.text = 'Hello, World!';
String content = controller.text;
// Selection
controller.selection = TextSelection(baseOffset: 0, extentOffset: 5);
// Line operations
int lineCount = controller.lineCount;
String line = controller.getLineText(0);
int lineStart = controller.getLineStartOffset(0);
// Folding
controller.foldAll();
controller.unfoldAll();
controller.toggleFold(lineNumber);
// Search
controller.searchHighlights = [
SearchHighlight(start: 0, end: 5, color: Colors.yellow),
];GutterStyle({
TextStyle? lineNumberStyle,
Color? backgroundColor,
double? gutterWidth,
IconData foldedIcon,
IconData unfoldedIcon,
double? foldingIconSize,
Color? foldedIconColor,
Color? unfoldedIconColor,
Color? activeLineNumberColor,
Color? inactiveLineNumberColor,
Color errorLineNumberColor,
Color warningLineNumberColor,
Color? foldedLineHighlightColor,
})CodeSelectionStyle({
Color? cursorColor,
Color selectionColor,
Color cursorBubbleColor,
})CodeForge supports a variety of keyboard shortcuts for efficient editing:
- Ctrl+C — Copy selected text
- Ctrl+X — Cut selected text
- Ctrl+V — Paste text
- Ctrl+A — Select all text
- Ctrl+D — Duplicate current line
- Ctrl+Z — Undo last action
- Ctrl+Y — Redo last action
- Ctrl+Backspace — Delete word backward
- Ctrl+Delete — Delete word forward
- Ctrl+Arrow Left — Move cursor to previous word
- Ctrl+Arrow Right — Move cursor to next word
- Ctrl+Shift+Arrow Left — Select to previous word
- Ctrl+Shift+Arrow Right — Select to next word
- Ctrl+Shift+Arrow Up — Move current line up
- Ctrl+Shift+Arrow Down — Move current line down
- Tab — Indent current line or accept AI completion/suggestion
- Shift+Tab — Unindent current line
- Arrow Up/Down — Navigate through suggestions
- Enter/Tab — Accept current suggestion
- Escape — Close suggestions or hover details
- Shift+Arrow Keys — Extend selection
- Shift+Home — Select to line start
- Shift+End — Select to line end
Contributions are welcome! Whether it's bug fixes, new features, or documentation improvements.
- Fork the repository
- Create your feature branch (
git checkout -b feature/amazing-feature) - Commit your changes (
git commit -m 'Add amazing feature') - Push to the branch (
git push origin feature/amazing-feature) - Open a Pull Request
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
- re_highlight — Syntax highlighting
- markdown_widget — Markdown rendering
- web_socket_channel — WebSocket support
Built with ❤️ for the Flutter community