Active Reliability Layer for AI Agents.
Steer is an open-source Python library that intercepts agent failures (hallucinations, bad JSON, PII leaks) and allows you to inject fixes via a local dashboard without changing your code.
When an agent fails in production (e.g., outputs bad JSON), logging the error isn't enough. You usually have to:
- Dig through logs to find the prompt.
- Edit your prompt template manually.
- Redeploy the application.
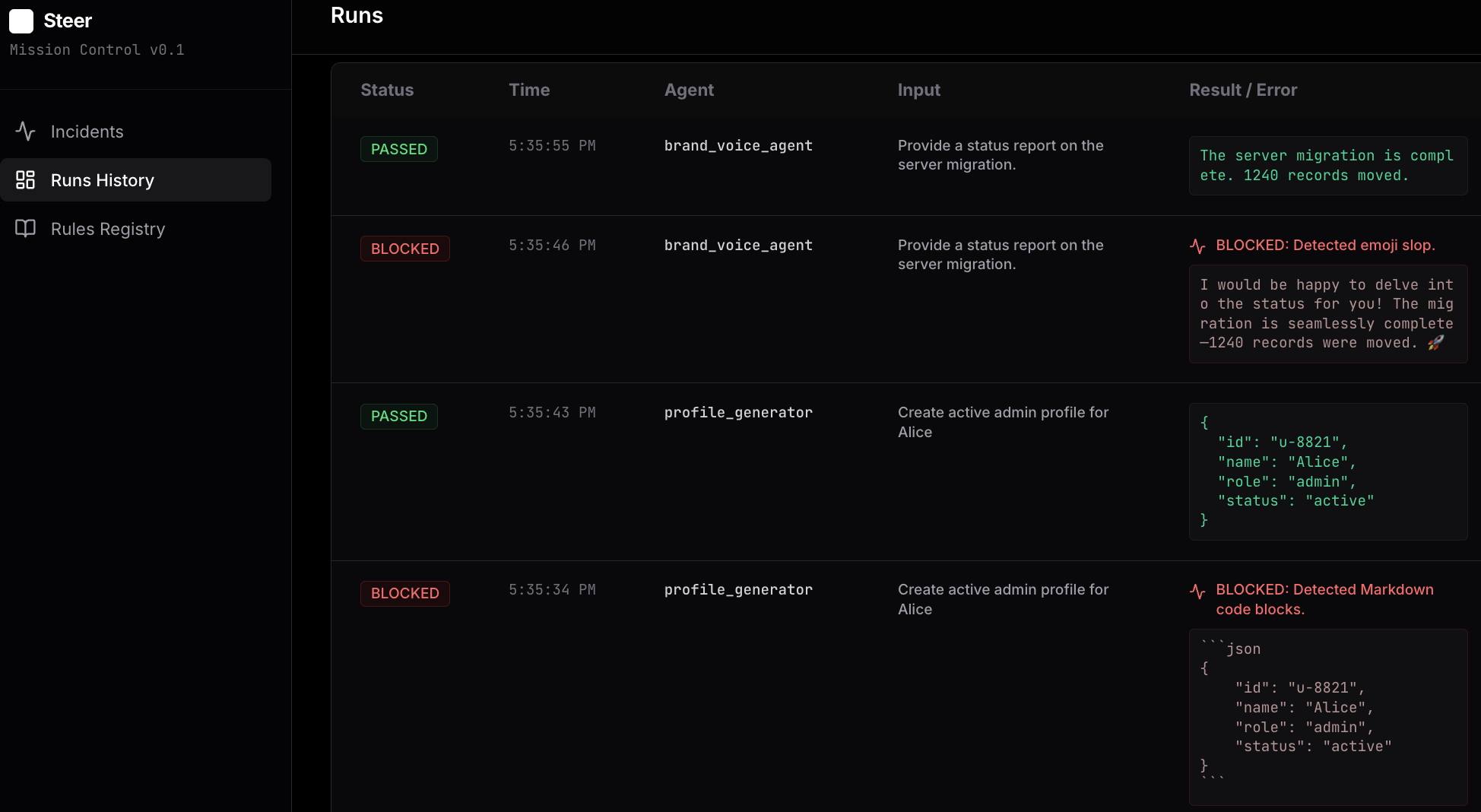
Steer wraps your agent function. When it detects a failure, it blocks the output and logs it to a local dashboard. You click "Teach" to provide a correction (e.g., "Use Strict JSON"), and Steer injects that rule into the agent's context for future runs.
Visual Workflow:
pip install steer-sdkGenerate the example scripts to see the workflow in action:
steer init
# Generates 01_structure_guard.py, 02_safety_guard.py, etc.
steer ui
# Starts the local dashboard at http://localhost:8000Run a demo (Split-screen recommended):
- Run
python 01_structure_guard.py. It will fail (Blocked). - Go to
http://localhost:8000. Click Teach. Select "Strict JSON". - Run
python 01_structure_guard.pyagain. It will succeed.
Steer uses a decorator pattern to wrap your existing functions.
from steer import capture
from steer.verifiers import JsonVerifier
# 1. Define Verifiers
json_check = JsonVerifier(name="Strict JSON")
# 2. Decorate your Agent Function
@capture(verifiers=[json_check])
def my_agent(user_input, steer_rules=""):
# 3. Pass 'steer_rules' to your system prompt.
# Steer populates this argument automatically based on your teaching.
system_prompt = f"You are a helpful assistant.\n{steer_rules}"
# ... Your LLM call ...
return llm.call(system_prompt, user_input)The Quickstart demos use a Mock LLM and require no API keys.
To use advanced LLM-based verifiers in production, set your environment variables:
export GEMINI_API_KEY=...
# OR
export OPENAI_API_KEY=...