-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 514
Update Android push docs, and app setup for 1.17.0 #522
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
Changes from all commits
File filter
Filter by extension
Conversations
Jump to
Diff view
Diff view
There are no files selected for viewing
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
|
|
@@ -9,45 +9,12 @@ Add dependency to the application level `build.gradle` file. | |
|
|
||
| ```groovy | ||
| dependencies { | ||
| implementation 'com.parse:parse-android:1.16.7' | ||
| implementation 'com.parse:parse-android:latest.version.here' | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| **Step 2:** Setup Parse | ||
|
|
||
| - **Option 1:** Setup in the Manifest | ||
|
|
||
| You may define `com.parse.SERVER_URL` and `com.parse.APPLICATION_ID` meta-data in your `AndroidManifest.xml`: | ||
|
|
||
| ```xml | ||
| <application ...> | ||
| <meta-data | ||
| android:name="com.parse.SERVER_URL" | ||
| android:value="@string/parse_server_url" /> | ||
| <meta-data | ||
| android:name="com.parse.APPLICATION_ID" | ||
| android:value="@string/parse_app_id" /> | ||
| ... | ||
| </application> | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| Initializing Parse in the `Application` | ||
|
|
||
| ```java | ||
| import com.parse.Parse; | ||
| import android.app.Application; | ||
|
|
||
| public class App extends Application { | ||
| @Override | ||
| public void onCreate() { | ||
| super.onCreate(); | ||
| Parse.initialize(this); | ||
| } | ||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| - **Option 2:** Setup in the `Application` | ||
|
|
||
| Initialize Parse using your server configuration: | ||
| ```java | ||
| import com.parse.Parse; | ||
| import android.app.Application; | ||
|
|
@@ -58,33 +25,19 @@ public class App extends Application { | |
| super.onCreate(); | ||
| Parse.initialize(new Parse.Configuration.Builder(this) | ||
| .applicationId("YOUR_APP_ID") | ||
| .clientKey("YOUR_CLIENT_KEY") | ||
|
Contributor
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. Client key can be null, as it is by default |
||
| .server("http://localhost:1337/parse/") | ||
| .build() | ||
| ); | ||
| } | ||
|
Contributor
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. Don't we have to do (Or ParseGCM.register(this)) for an older version..)
Member
Author
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. Nope, it is not required for FCM. I think we will leave the GCM instructions out of here, only mentioning it at the bottom, so that people will move away from it.
Contributor
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. I was playing with it last night but couldnt get stuff to fire unless I did the register command with FCM...you sure it works without it?
Contributor
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. Never mind, I was putting a breakpoint on the wrong place. Works fine!
Contributor
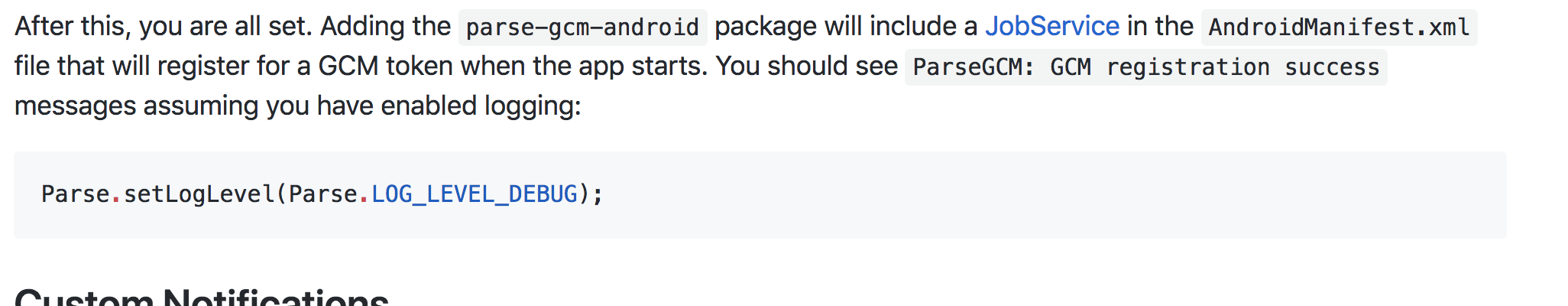
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. See my updates about how a JobService is scheduled to run when the app starts: https://github.com/parse-community/Parse-SDK-Android/pull/817/files |
||
| } | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| For either option, the custom `Application` class must be registered in `AndroidManifest.xml`: | ||
| The custom `Application` class must be registered in `AndroidManifest.xml`: | ||
| ```xml | ||
| <application | ||
| android:name=".App" | ||
| ...> | ||
| ... | ||
| </application> | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| **Step 3:** Setup permissions in the Manifest | ||
|
|
||
| You have to define `INTERNET`permissions in your `AndroidManifest.xml`: | ||
|
|
||
| ```xml | ||
| <manifest ...> | ||
|
|
||
| <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" /> | ||
|
|
||
| <application ...> | ||
| ... | ||
| </application> | ||
| </manifest> | ||
| ``` | ||
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
|
|
@@ -8,29 +8,7 @@ If you haven't installed the SDK yet, [head over to the Push QuickStart]({{ site | |
|
|
||
| If you want to start using push, start by completing the [Android Push Notifications QuickStart Guide]({{ site.baseUrl }}/parse-server/guide/#push-notifications-quick-start) to learn how to configure your app and send your first push notification. Come back to this guide afterwards to learn more about the push features offered by Parse. | ||
|
|
||
| The Parse library provides push notifications using Google Cloud Messaging (GCM) if Google Play Services are available. Learn more about Google Play Services [here](https://developers.google.com/android/guides/overview). | ||
|
|
||
| When sending pushes to Android devices with GCM, there are several pieces of information that Parse keeps track of automatically: | ||
|
|
||
| * **Registration ID**: The GCM registration ID uniquely identifies an app/device pairing for push purposes. | ||
| * **Sender ID**: The GCM sender ID is a public number that identifies the sender of a push notification. | ||
| * **API key**: The GCM API key is a server secret that allows a server to send pushes to a registration ID on behalf of a particular sender ID. | ||
|
|
||
| The Parse Android SDK now requires you to specify the GCM sender ID with the following `<meta-data>` tag as a child of the `<application>` element in your app's `AndroidManifest.xml`: | ||
|
|
||
| ```java | ||
| <meta-data android:name="com.parse.push.gcm_sender_id" | ||
| android:value="id:YOUR_SENDER_ID" />; | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| In the sample snippet above, `YOUR_SENDER_ID` should be replaced by a numeric GCM sender ID. Note that the Parse SDK expects you to prefix your sender ID with an `id:` prefix, as shown in the sample snippet. | ||
|
|
||
| If you want to register your app with multiple additional sender IDs, then the `android:value` in the `<meta-data>` element above should hold a comma-delimited list of sender IDs, as in the following snippet: | ||
|
|
||
| ```java | ||
| <meta-data android:name="com.parse.push.gcm_sender_id" | ||
| android:value="id:YOUR_SENDER_ID_1,YOUR_SENDER_ID_2,YOUR_SENDER_ID_3" />; | ||
| ``` | ||
| The Parse library provides push notifications using Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) if Google Play Services are available. Learn more about Google Play Services [here](https://firebase.google.com/docs/cloud-messaging/). | ||
|
Contributor
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. I think this section should include the fact that calling ParseFCM.register(this) automatically passes the Installation object to the Parse server as a GCM token type.
Member
Author
There was a problem hiding this comment. Choose a reason for hiding this commentThe reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more. The user should never have to call this manually given our setup. Do you think we should still mention that it is happening? |
||
|
|
||
| ## Installations | ||
|
|
||
|
|
@@ -48,9 +26,8 @@ While it is possible to modify a `ParseInstallation` just like you would a `Pars | |
| * **`channels`**: An array of the channels to which a device is currently subscribed. | ||
| * **`installationId`**: Unique Id for the device used by Parse _(readonly)_. | ||
| * **`deviceType`**: The type of device, "ios", "osx", "android", "winrt", "winphone", "dotnet", or "embedded". On Android devices, this field will be set to "android" _(readonly)_. | ||
| * **`pushType`**: This field is reserved for directing Parse to the push delivery network to be used. If the device is registered to receive pushes via GCM, this field will be marked "gcm". If Google Play Services is not available, it will be blank _(readonly)_. | ||
| * **`GCMSenderId`**: This field only has meaning for Android `ParseInstallation`s that use the GCM push type. It is reserved for directing Parse to send pushes to this installation with an alternate GCM sender ID. This field should generally not be set unless you are uploading installation data from another push provider. If you set this field, then you must set the GCM API key corresponding to this GCM sender ID in your Parse application's push settings. | ||
| * **`deviceToken`**: The token used by GCM to keep track of registration ID. On iOS devices, this is the Apple generated token _(readonly)_. | ||
| * **`pushType`**: This field is reserved for directing Parse to the push delivery network to be used. If the device is registered to receive pushes via FCM, this field will be marked "gcm". If Google Play Services is not available, it will be blank _(readonly)_. | ||
| * **`deviceToken`**: The token used by FCM to keep track of registration ID. On iOS devices, this is a generated token _(readonly)_. | ||
| * **`appName`**: The display name of the client application to which this installation belongs. This value is synchronized every time a `ParseInstallation` object is saved from the device _(readonly)_. | ||
| * **`appVersion`**: The version string of the client application to which this installation belongs. This value is synchronized every time a `ParseInstallation` object is saved from the device _(readonly)_. | ||
| * **`parseVersion`**: The version of the Parse SDK which this installation uses. This value is synchronized every time a `ParseInstallation` object is saved from the device _(readonly)_. | ||
|
|
@@ -341,7 +318,7 @@ Make sure you've gone through the [Android Push QuickStart]({{ site.baseUrl }}/p | |
|
|
||
| When a push notification is received, the “title” is displayed in the status bar and the “alert” is displayed alongside the “title” when the user expands the notification drawer. If you choose to subclass `com.parse.ParsePushBroadcastReceiver`, be sure to replace that name with your class' name in the registration. | ||
|
|
||
| Note that some Android emulators (the ones without Google API support) don't support GCM, so if you test your app in an emulator make sure to select an emulator image that has Google APIs installed. | ||
| Note that some Android emulators (the ones without Google API support) don't support FCM, so if you test your app in an emulator make sure to select an emulator image that has Google APIs installed. | ||
|
|
||
| ### Customizing Notifications | ||
|
|
||
|
|
@@ -520,11 +497,9 @@ You can check the Push Delivery Report for the cause of failed deliveries: Misma | |
|
|
||
| If everything looks great so far, but push notifications are not showing up on your phone, there are a few more things you can check. | ||
|
|
||
| * [Upgrade to the latest SDK](https://github.com/parse-community/Parse-SDK-Android). This documentation covers the push API introduced in the 1.7.0 version of the Android Parse SDK. Please upgrade if you are getting compiler errors following these instructions. | ||
| * Make sure you are using the correct `packageName` in your `AndroidManifest.xml`. | ||
| * Make sure you have the correct permissions listed in your `AndroidManifest.xml` file, as outlined in the [Android Push Quickstart]({{ site.baseUrl }}/parse-server/guide/#push-notifications-quick-start). If you are using a a custom receiver, be sure you have registered it in the Manifest file with the correct `android:name` property and the proper intent filters. | ||
| * [Upgrade to the latest SDK](https://github.com/parse-community/Parse-SDK-Android). This documentation covers the push API introduced in the 1.17.0 version of the Android Parse SDK. Please upgrade if you are getting compiler errors following these instructions. | ||
| * Make sure you've used the correct App ID and client key, and that `Parse.initialize()` is being called. `Parse.initialize()` lets the service know which application it is listening for; this code must be in your `Application.onCreate` rather than `Activity.onCreate` for a particular `Activity`, so that any activation technique will know how to use Parse. | ||
| * Check that the push registration call is being called successfully. Your device must successfully register a ParseInstallation object with a valid GCM Registration id in the "deviceToken" field, if using GCM. | ||
| * Check that the push registration call is being called successfully. Your device must successfully register a ParseInstallation object with a valid FCM Registration id in the "deviceToken" field | ||
| * Check that the device is set to accept push notifications from your app. | ||
| * Note that, by design, force-killed apps will not be able to receive push notifications. Launch the app again to reenable push notifications. | ||
| * Check the number of subscribers in your Parse Push Console. Does it match the expected number of subscribers? Your push might be targeted incorrectly. | ||
|
|
||
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
we should put a comment about adding the FCM package here as optional
implementation 'com.parse:parse-fcm-android:latest.version.here'There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
I think maybe we should have a note about push somewhere in the README, but there are plenty of people/apps that use Parse Android without using any form of push, so I think it might be confusing here.