A simple project that uses pytest and GitHub Actions to automatically run a short series of tests on push or pull request.
Implement a simple continuous integration with:
- Python 3.9
- pytest
- GitHub Actions
Two simple function which will be tested later:
def say_hi(name):
greeting = "Hello world! says " + name
return greetingSimple set of tests implemented with pytest.
Install pytest by running pip -U pytest in your command line. Afterwards you can check that you installed the correct version by pytest --version.
Write your tests and save them to a file with a name beginning with test_ or ending with _test.py. After running pytest in your command line the framework will search for the files following the naming structure and will automatically run the tests.
Within the test file define the tests you'd like to run. Pytest will assert whether the returned values match the expected results.
def test_greeting():
assert greetings.say_hi("Greta") == "Hello world! says Greta"Now we are getting to the main purpose of this project - setting up a simple continuous integration. For this we will use GitHub Actions.
To add a GitHub actions workflow to your project you'll need to click on "Actions" button in the repository you'd like to setup the action for.
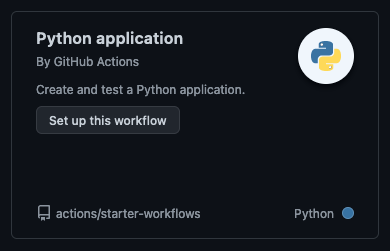
This project uses "Python Application" workflow template.
By choosing the workflow, GitHub will create a folder structure and autofill the template for you to edit/commit. The structure of the yaml code is following:
name: Running the tests- choose a name that will be displayed in your "Workflows"
on:
push:
branches: [ main ]
pull_request:
branches: [ main ]- what events will trigger the workflow, in this case this would be both push and pull_request in the main branch
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Set up Python 3.9
uses: actions/setup-python@v2
with:
python-version: 3.9
- name: Install dependencies
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install flake8 pytest
if [ -f requirements.txt ]; then pip install -r requirements.txt; fi
- name: Lint with flake8
run: |
# stop the build if there are Python syntax errors or undefined names
flake8 . --count --select=E9,F63,F7,F82 --show-source --statistics
# exit-zero treats all errors as warnings. The GitHub editor is 127 chars wide
flake8 . --count --exit-zero --max-complexity=10 --max-line-length=127 --statistics
- name: Test with pytest
run: |
pytest- the workflow step by step:
- sets up an environment, in this case Python 3.9
- installs flake8 for linting and pytest for testing along with dependencies required by the project
- lints with flake8
- runs the
test_and_test.pyfiles in the repository
When ready, commit the workflow file.
You have set up an easy CI that si triggered by events mentioned in the yaml file. Run a push or pull request on main branch to test it out. You can find the results of your tests under "Actions" in your repository.
- Installation and Getting Started for pytest (https://docs.pytest.org/en/6.2.x/getting-started.html)
- Quickstart for GitHub Actions (https://docs.github.com/en/actions/quickstart)