Zero Field Magnetometer IOC
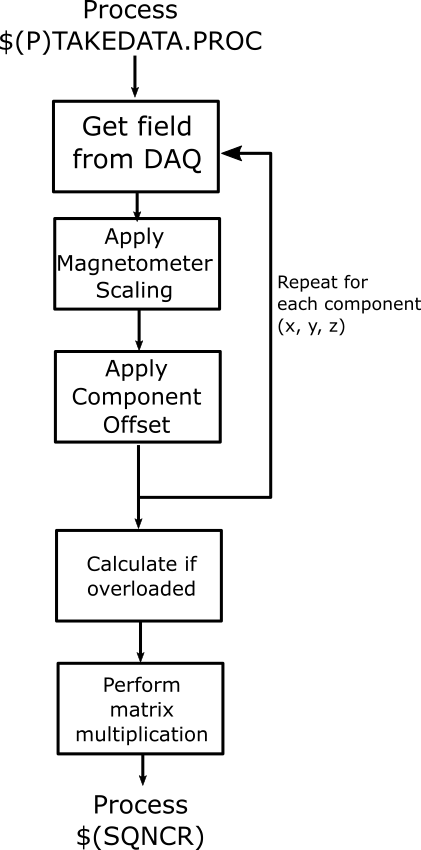
The magnetometer reads magnetic field strengths from the beamline. This IOC takes the magnetometer signal, applies corrections and performs a check to make sure that the magnetometer has not been overloaded.
This IOC is designed to be used in conjunction with a sequencer IOC, which uses the field values to calculate corrections needed to maintain a magnetic field strength. When a new field value is required, the sequencer will process the $(P)TAKEDATA PV of this IOC. When the new field values are available, this IOC processes $(PVPREFIX):ZFCNTRL_01:INPUTS_UPDATED.PROC, which it expects to allow the sequencer IOC to continue its calculations. This PV can be changed by setting the $(SQNCR) macro.
The maths which defines these operations is described in finer detail here.
-
Magnetometer range scaling
- The three field components are multiplied by a scaling factor to transform the input on to the range of the magnetometer. The scaling factor is set by the macro
$(RANGE), and is held in the PV$(P)RANGE.
- The three field components are multiplied by a scaling factor to transform the input on to the range of the magnetometer. The scaling factor is set by the macro
-
Applying offsets
- Each component has a unique offset which is subtracted from the scaled data. These offsets are set as the macros
$(OFFSETX), $(OFFSETY), $(OFFSETZ). These can also be set by the PVs$(P):X:OFFSETand from the OPI.
- Each component has a unique offset which is subtracted from the scaled data. These offsets are set as the macros
-
Multiply with sensor matrix
- To obtain the corrected field strengths, the scaled and offset values need to be multiplied by a 'field sensor' matrix.
- Macros define the sensor matrix:
$(MATRIX_X_Y), where X and Y are the row and column indices. - PVs hold the elements of the sensor matrix:
$(P)SENSORMATRIX:XY. These PVs can also be changed on the OPI. - The multiplication itself is done as an aSub record. This allows us to use the libraries available to us through GSL.
- Set up using GSL vector and matrix structures, performing the matrix multiplication is a relatively straightforward call to a vector/matrix multiplication BLAS routine in GSL.
- The documentation for GSL data structures used is here.
- The GSL documentation for BLAS routines is lacking (see documentation). To get more in-depth information about the arguments used I would look up the routine in the BLAS documentation.
-
Output
- The corrected field strengths are written directly to the PVs
$(P)X:CORRECTEDFIELDfrom the aSub record. - The aSub record also calculates the magnitude of the corrected field and places it in
$(P)FIELDSTRENGTH.
- The corrected field strengths are written directly to the PVs
High field values will overload the magnetometer, which is detected in this IOC. The overload condition for the EMU magnetometer is:
max(measured_field) > magnetometer_range * 4.5
Where:
- max(measured_field) is the largest component of the 3 scaled (but not offset or matrix multiplied) input field strengths.
- magnetometer_range is the scaling factor used in the magnetometer range scaling
- 4.5 is a constant taken from the EMU VI. This value may be different for other magnetometers.
A requirement of this IOC is to maintain as consistent a time as possible between measuring the data and performing calculations using it. To achieve this, no records in this IOC scan. Instead, each record forward links to the next record to be processed in order. This is outlined below:
TAKEDATA is processed at regular intervals by the sequencer which is running in the ZFCNTRL_01 ioc.