GitHub Action
Lighthouse CI Action
Audit URLs using Lighthouse and test performance with Lighthouse CI.
This action integrates Lighthouse CI with Github Actions environment. Making it simple to see failed tests, upload results, run jobs in parallel, store secrets, and interpolate env variables.
It is built in collaboration between Lighthouse Team, Treo (web performance monitoring company), and many excellent contributors.
Features:
- ✅ Audit URLs using Lighthouse v12
- 🎯 Test performance with Lighthouse CI assertions or performance budgets
- 😻 See failed results in the action interface
- 💾 Upload results to a private LHCI server, Temporary Public Storage, or as artifacts
- ⚙️ Full control over Lighthouse CI config
- 🚀 Fast action initialization (less than 1 second)
Run Lighthouse on each push to the repo, test performance budget, save results as action artifacts.
Create .github/workflows/main.yml with the list of URLs to audit using Lighthouse.
name: Lighthouse CI
on: push
jobs:
lighthouse:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Audit URLs using Lighthouse
uses: treosh/lighthouse-ci-action@v12
with:
urls: |
https://example.com/
https://example.com/blog
budgetPath: ./budget.json # test performance budgets
uploadArtifacts: true # save results as an action artifacts
temporaryPublicStorage: true # upload lighthouse report to the temporary storageDescribe your performance budget using a budget.json.
[
{
"path": "/*",
"resourceSizes": [
{
"resourceType": "document",
"budget": 18
},
{
"resourceType": "total",
"budget": 200
}
]
}
]Run Lighthouse and validate against Lighthouse CI assertions.
Create .github/workflows/main.yml with the list of URLs to audit
and identify a lighthouserc file with configPath.
name: Lighthouse
on: push
jobs:
lighthouse:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Run Lighthouse on urls and validate with lighthouserc
uses: treosh/lighthouse-ci-action@v12
with:
urls: 'https://exterkamp.codes/'
configPath: './lighthouserc.json'Make a lighthouserc.json file with LHCI assertion syntax.
{
"ci": {
"assert": {
"assertions": {
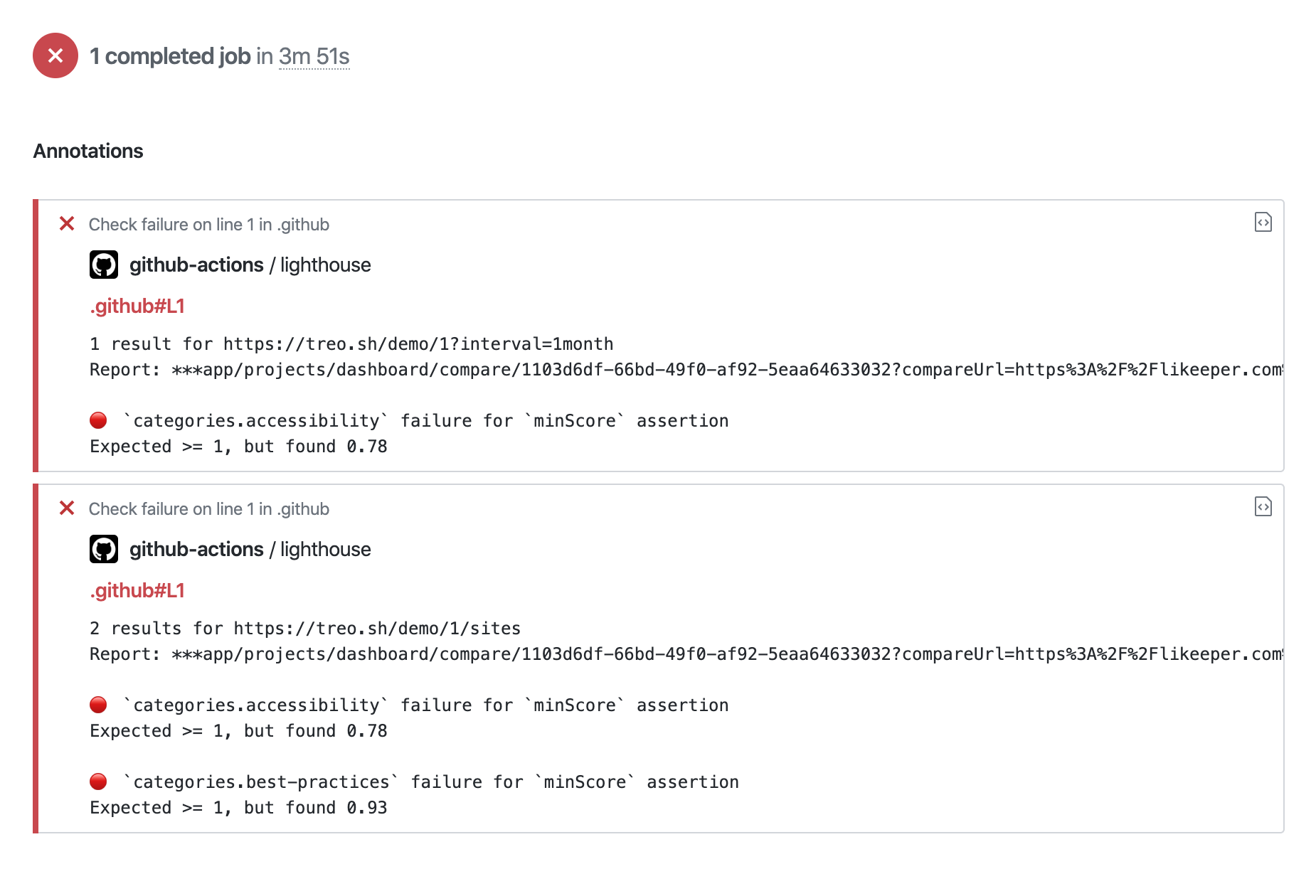
"first-contentful-paint": ["error", { "minScore": 0.6 }]
}
}
}
}
Upload results to a private LHCI server.
Create .github/workflows/main.yml with the list of URLs to audit using lighthouse,
and identify a serverBaseUrl to upload to and an token to use.
Note: use GitHub secrets to keep your server address hidden!
name: Lighthouse
on: push
jobs:
lighthouse:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Run Lighthouse on urls and upload data to private lhci server
uses: treosh/lighthouse-ci-action@v12
with:
urls: 'https://example.com/'
serverBaseUrl: ${{ secrets.LHCI_SERVER_URL }}
serverToken: ${{ secrets.LHCI_SERVER_TOKEN }}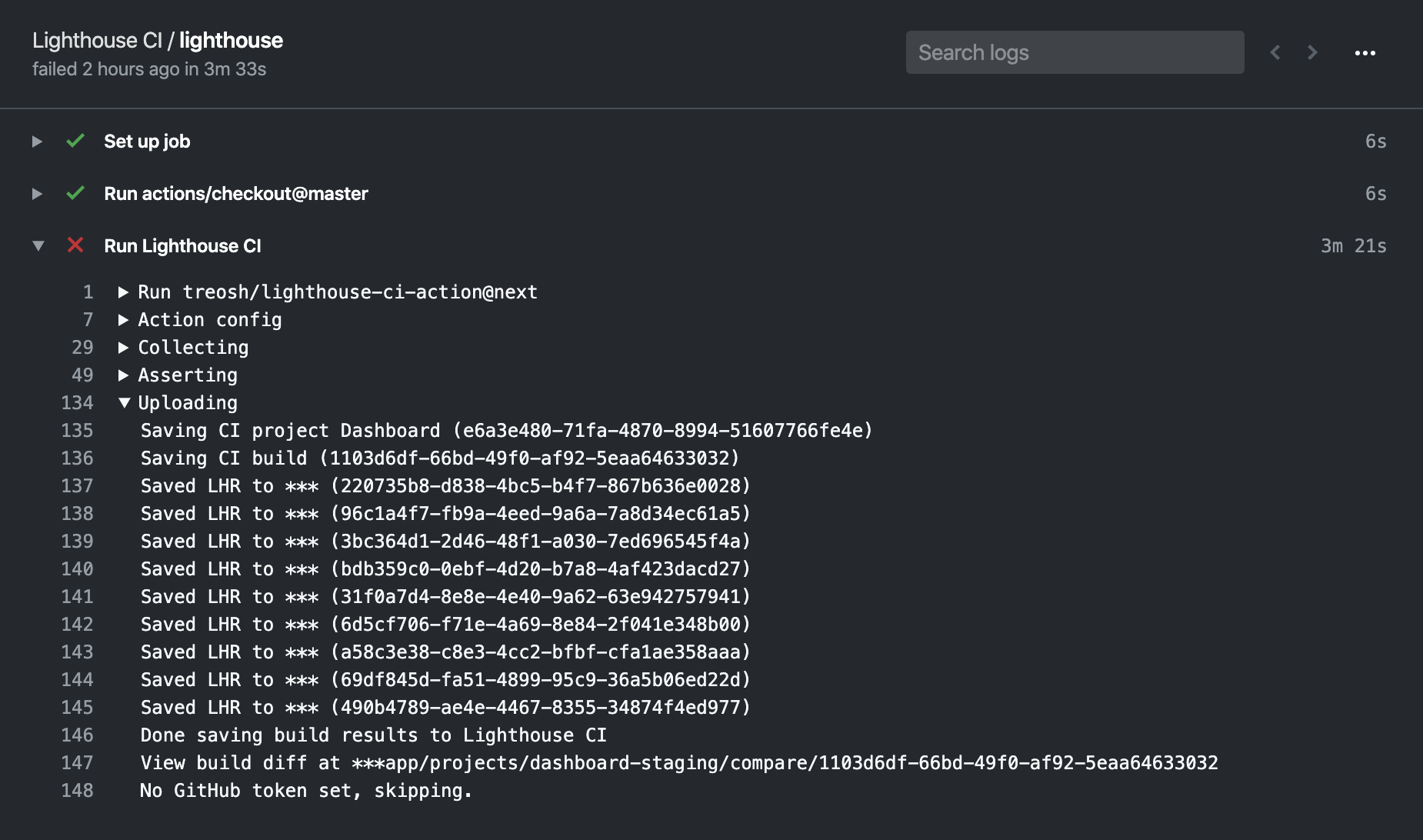
Audit with custom Chrome options and custom Lighthouse config.
Create .github/workflows/main.yml with the list of URLs to audit and
identify a lighthouserc file with configPath.
name: Lighthouse
on: push
jobs:
lighthouse:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Run Lighthouse on urls with lighthouserc
uses: treosh/lighthouse-ci-action@v12
with:
urls: 'https://example.com/'
configPath: './lighthouserc.json'Chrome flags can be set directly in the lighthouserc's collect section.
{
"ci": {
"collect": {
"numberOfRuns": 1,
"settings": {
"chromeFlags": "--disable-gpu --no-sandbox --no-zygote"
}
}
}
}Custom Lighthouse config can be defined in a seperate Lighthouse config using
the custom Lighthouse config syntax.
This is then referenced by the lighthouserc file in the configPath.
{
"ci": {
"collect": {
"numberOfRuns": 1,
"settings": {
"configPath": "./lighthouse-config.js"
}
}
}
}Then put all the custom Lighthouse config in the file referenced in the lighthouserc.
module.exports = {
extends: 'lighthouse:default',
settings: {
emulatedFormFactor: 'desktop',
audits: [{ path: 'metrics/first-contentful-paint', options: { scorePODR: 800, scoreMedian: 1600 } }],
},
}Test a static site without having to deploy it.
Create .github/workflows/main.yml and identify a lighthouserc file with a
staticDistDir config.
name: Lighthouse
on: push
jobs:
static-dist-dir:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Run Lighthouse against a static dist dir
uses: treosh/lighthouse-ci-action@v12
with:
# no urls needed, since it uses local folder to scan .html files
configPath: './lighthouserc.json'{
"ci": {
"collect": {
"staticDistDir": "./dist"
}
}
}Inside your staticDistDir there should be html files that make up your site.
LHCI will run a simple static webserver to host the files, then run an audit
against each of them. More details on this process are in the Lighthouse CI docs.

Integrate Lighthouse CI with Netlify
It waits for Netlify to finish building a preview and then uses a built version to check performance. Hence, recipe is a composition of 2 actions: Wait for Netlify Action and Lighthouse CI Action.
name: Lighthouse CI for Netlify sites
on: pull_request
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Wait for the Netlify Preview
uses: jakepartusch/wait-for-netlify-action@v1.4
id: netlify
with:
site_name: 'gallant-panini-bc8593'
- name: Audit URLs using Lighthouse
uses: treosh/lighthouse-ci-action@v12
with:
urls: |
${{ steps.netlify.outputs.url }}
${{ steps.netlify.outputs.url }}/products/
budgetPath: ./budget.json
uploadArtifacts: trueUse URLs interpolation to pass secrets or environment variables
URLs support interpolation of process env variables so that you can write URLs like:
name: Lighthouse CI
on: push
jobs:
lighthouse:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Run Lighthouse and test budgets
uses: treosh/lighthouse-ci-action@v12
with:
urls: |
https://pr-$PR_NUMBER.staging-example.com/
https://pr-$PR_NUMBER.staging-example.com/blog
budgetPath: ./budgets.json
temporaryPublicStorage: true
env:
PR_NUMBER: ${{ github.event.pull_request.number }}Use with a Lighthouse plugin.
Combine the field performance plugin with Github Actions.
name: Lighthouse CI with a plugin
on: push
jobs:
lighthouse:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- run: npm install # install dependencies, that includes Lighthouse plugins
- name: Audit URLs with Field Performance Plugin
uses: treosh/lighthouse-ci-action@v12
with:
urls: |
https://www.example.com/
configPath: '.lighthouserc.json'
temporaryPublicStorage: true{
"ci": {
"collect": {
"settings": {
"plugins": ["lighthouse-plugin-field-performance"]
}
}
}
}Add a plugin as a dependency, so it's installed locally:
{
"devDependencies": {
"lighthouse-plugin-field-performance": "^2.0.1"
}
}Use `output` for a powerful composition with other actions
# Example of output usage
name: LHCI-output-webhook
on: push
jobs:
output-webhook:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Use output for sending data to API.
id: LHCIAction
uses: ./
with:
urls: |
https://treo.sh/
- name: Webhook
uses: denar90/webhook-action@0.1.1
with:
webhookUrl: ${{secrets.ACTION_WEBHOOK_URL}}
data: '{ "links": ${{steps.LHCIAction.outputs.links}}, "manifest": ${{steps.LHCIAction.outputs.manifest}} }'GitHub Action workflow on self-hosted GitHub runner (e.g. on-premise)
name: Lighthouse CI
on: push
jobs:
lighthouse:
runs-on: [self-hosted, your-custom-label]
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: install Node.js
- uses: browser-actions/setup-chrome@latest
- run: chrome --version
uses: actions/setup-node@v3
with:
node-version: ${{YOUR_REQUIRED_NODE_JS_VERSION}}
- name: Audit URLs using Lighthouse
uses: treosh/lighthouse-ci-action@v12
with:
urls: |
https://example.com/
https://example.com/blog
[...]
Dynamically generate URLs
Use github-script or any other means to dynamically generate a list of URLs to test
jobs:
lighthouse:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Generate URLs
id: urls
uses: actions/github-script@v6
with:
github-token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
script: |
const globber = await glob.create('elements/*/demo/*.html');
const files = await globber.glob();
const urls = files
.map(x => x.match(/([\w-]+)/)[1])
.map(x => `${${{ env.DOMAIN }}}/components/${x}/demo/`)
.join('\n');
core.setOutput('urls', urls);
- name: Lighthouse CI Action
id: lighthouse
uses: treosh/lighthouse-ci-action@v8
with:
urls: |
${{ steps.urls.outputs.urls }}
Explore more workflows in public examples. Submit a pull request with a new one if they don't cover your use case.
Provide the list of URLs separated by a new line. Each URL is audited using the latest version of Lighthouse and Chrome preinstalled on the environment.
urls: |
https://example.com/
https://example.com/blog
https://example.com/pricingUpload Lighthouse results as action artifacts to persist results. Equivalent to using actions/upload-artifact to save the artifacts with additional action steps.
uploadArtifacts: trueAdd extra args to the upload command.
uploadExtraArgs: "--extraHeaders.Authorization='Bearer X92sEo3n1J1F0k1E9' --extraHeaders.Foo='Bar'"Upload reports to the temporary public storage.
Note: As the name implies, this is temporary and public storage. If you're uncomfortable with the idea of your Lighthouse reports being stored on a public URL on Google Cloud, use a private LHCI server. Reports are automatically deleted 7 days after upload.
temporaryPublicStorage: trueUse a performance budget to keep your page size in check. Lighthouse CI Action will fail the build if one of the URLs exceeds the budget.
Learn more about the budget.json spec and practical use of performance budgets.
budgetPath: ./budget.jsonSpecify the number of runs to do on each URL.
Note: Asserting against a single run can lead to flaky performance assertions. Use
1only to ensure static audits like Lighthouse scores, page size, or performance budgets.
runs: 3Set a path to a custom lighthouserc file for full control of the Lighthouse environment and assertions.
Use lighthouserc to configure the collection of data (via Lighthouse config and Chrome Flags), and CI assertions (via LHCI assertions).
configPath: ./lighthouserc.jsonIf some configurations aren't set using action parameters, the settings are fetched from the config file provided here.
Upload Lighthouse results to a private LHCI server by specifying both serverBaseUrl and serverToken.
This will replace uploading to temporary-public-storage.
serverBaseUrl: ${{ secrets.LHCI_SERVER_BASE_URL }}
serverToken: ${{ secrets.LHCI_SERVER_TOKEN }}Note: Use Github secrets to keep your token hidden!
Lighthouse servers can be protected with basic authentication LHCI server basic authentication by specifying both basicAuthUsername and basicAuthPassword will authenticate the upload.
basicAuthUsername: ${{ secrets.LHCI_SERVER_BASIC_AUTH_USERNAME }}
basicAuthPassword: ${{ secrets.LHCI_SERVER_BASIC_AUTH_PASSWORD }}Note: Use Github secrets to keep your username and password hidden!
Use outputs to compose results of the LHCI Action with other Github Actions, like webhooks, notifications, or custom assertions.
A path to .lighthouseci results folder:
/Users/lighthouse-ci-action/.lighthouseci
A JSON string with a links to uploaded results:
{
'https://treo.sh/': 'https://storage.googleapis.com/lighthouse-infrastructure.appspot.com/reports/1593981455963-59854.report.html'
...
}A JSON string with assertion results:
[
{
name: 'maxNumericValue',
expected: 61440,
actual: 508455,
values: [508455],
operator: '<=',
passed: false,
auditProperty: 'total.size',
auditId: 'resource-summary',
level: 'error',
url: 'https://treo.sh/',
auditTitle: 'Keep request counts low and transfer sizes small',
auditDocumentationLink: 'https://developers.google.com/web/tools/lighthouse/audits/budgets',
},
...
]A JSON string with report results (LHCI docs reference):
[
{
"url": "https://treo.sh/",
"isRepresentativeRun": true,
"htmlPath": "/Users/lighthouse-ci-action/.lighthouseci/treo_sh-_-2020_07_05_20_37_18.report.html",
"jsonPath": "/Users/lighthouse-ci-action/.lighthouseci/treo_sh-_-2020_07_05_20_37_18.report.json",
"summary": { "performance": 0.99, "accessibility": 0.98, "best-practices": 1, "seo": 0.96, "pwa": 0.71 }
}
]
