20A_Current_Sensor_SKU_SEN0214
[[/image:Name_DFRxxxx_sample1.png|thumb|300px|right|Product Name
Update/modify/delete Forbidden, 禁止更改本图,请更改图片名称新建图片
]]
This 20A current sensor uses a Hall effect-based linear current IC. It has many advantages like wide range, easy to use, small size, unnecessary to solder, also high accuracy. You can use this module to measure direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC). As to the PCB design, we added the high voltage isolation, which ensures the safety in use. The output of this module is a linear voltage to current input. And the Gravity 3P interface imporves the usability.
 WATCH OUT for SAFETY when measuring the high voltage! Long-firing Operation Over 20A (measured current) are not recommended.
WATCH OUT for SAFETY when measuring the high voltage! Long-firing Operation Over 20A (measured current) are not recommended.
- Supply Voltage: +5.0V
- Current Range: 0 ~ ±20A DC, 0 ~ 17A(RMS) AC
- Measurement Endure: 220V AC, 311V DC
- Relative Error: ±3%
- Size: 39mm * 22mm * 17mm
- Interface: Gravity PH2.0-3P
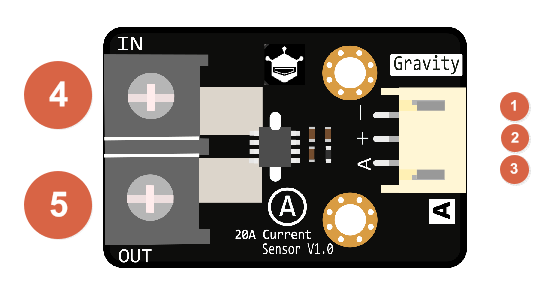 |
|
| --------- | ----------- |
| Num | Label |
| 1 | - |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | A |
| 4 | IN |
| 5 | OUT |
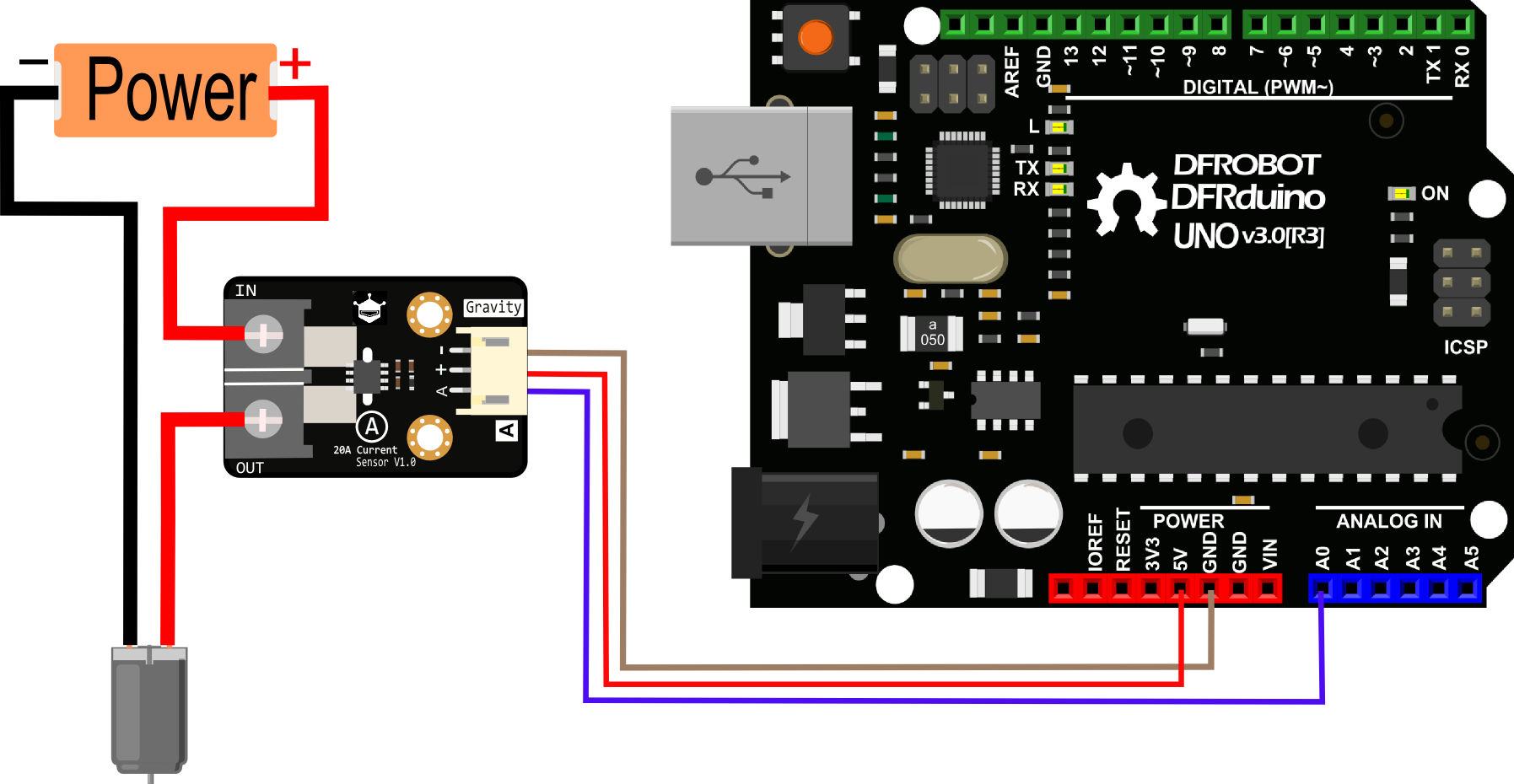
This tutorial will teach you to use the 20A current sensor.
-
Hardware
- UNO x1
- 20A Current Sensor module x1
- Gravity 3P Analog Wire x1
- Dupont Line Several
-
Software
- Arduino IDE V1.6.8 Click to Download Arduino IDE from Arduino®
/***********************************************************
This sample code shows how to use 20A current sensor module.
Created 2016-4-26
By Bernie Chen <bernie.chen@dfrobot.com>
GNU Lesser General Public License.
See <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/> for details.
All above must be included in any redistribution
****************************************************/
/***********Notice and Trouble shooting***************
1.Connection and Diagram can be found here, http://www.dfrobot.com/wiki/index.php?title=20A_Current_Sensor_SKU:SEN0214
2.This code is tested on Arduino Uno.
****************************************************/
const int currentSensorPin = A0; //define sensor pin
const int mVperAmp = 100; // use 185 for 5A Module, and 66 for 30A Module
float Vref = 0; //read your Vcc voltage,typical voltage should be 5000mV(5.0V)
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
Vref = readVref(); //read the reference votage(default:VCC)
}
void loop()
{
/*If you are reading DC current, use this function to read DC current. Then uncomment the AC function.*/
float CurrentValue = readDCCurrent(currentSensorPin);
/*If you are reading AC current, use this function to read AC current, it returns the RMS. Then uncomment the DC function.*/
//float CurrentValue = readACCurrent(currentSensorPin);
Serial.println(CurrentValue);
delay(500);
}
/*read DC Current Value*/
float readDCCurrent(int Pin)
{
int analogValueArray[31];
for(int index=0;index<31;index++)
{
analogValueArray[index]=analogRead(Pin);
}
int i,j,tempValue;
for (j = 0; j < 31 - 1; j ++)
{
for (i = 0; i < 31 - 1 - j; i ++)
{
if (analogValueArray[i] > analogValueArray[i + 1])
{
tempValue = analogValueArray[i];
analogValueArray[i] = analogValueArray[i + 1];
analogValueArray[i + 1] = tempValue;
}
}
}
float medianValue = analogValueArray[(31 - 1) / 2];
float DCCurrentValue = (medianValue / 1024.0 * Vref - Vref / 2.0) / mVperAmp; //Sensitivity:100mV/A, 0A @ Vcc/2
return DCCurrentValue;
}
/*read AC Current Value and ruturn the RMS*/
float readACCurrent(int Pin)
{
int analogValue; //analog value read from the sensor output pin
int maxValue = 0; // store max value
int minValue = 1024; // store min value
unsigned long start_time = millis();
while((millis()-start_time) < 200) //sample for 0.2s
{
analogValue = analogRead(Pin);
if (analogValue > maxValue)
{
maxValue = analogValue;
}
if (analogValue < minValue)
{
minValue = analogValue;
}
}
float Vpp = (maxValue - minValue) * Vref / 1024.0;
float Vrms = Vpp / 2.0 * 0.707 / mVperAmp; //Vpp -> Vrms
return Vrms;
}
/*read reference voltage*/
long readVref()
{
long result;
#if defined(__AVR_ATmega168__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega328__) || defined (__AVR_ATmega328P__)
ADMUX = _BV(REFS0) | _BV(MUX3) | _BV(MUX2) | _BV(MUX1);
#elif defined(__AVR_ATmega32U4__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega1280__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega2560__) || defined(__AVR_AT90USB1286__)
ADMUX = _BV(REFS0) | _BV(MUX4) | _BV(MUX3) | _BV(MUX2) | _BV(MUX1);
ADCSRB &= ~_BV(MUX5); // Without this the function always returns -1 on the ATmega2560 http://openenergymonitor.org/emon/node/2253#comment-11432
#elif defined (__AVR_ATtiny24__) || defined(__AVR_ATtiny44__) || defined(__AVR_ATtiny84__)
ADMUX = _BV(MUX5) | _BV(MUX0);
#elif defined (__AVR_ATtiny25__) || defined(__AVR_ATtiny45__) || defined(__AVR_ATtiny85__)
ADMUX = _BV(MUX3) | _BV(MUX2);
#endif
#if defined(__AVR__)
delay(2); // Wait for Vref to settle
ADCSRA |= _BV(ADSC); // Convert
while (bit_is_set(ADCSRA, ADSC));
result = ADCL;
result |= ADCH << 8;
result = 1126400L / result; //1100mV*1024 ADC steps http://openenergymonitor.org/emon/node/1186
return result;
#elif defined(__arm__)
return (3300); //Arduino Due
#else
return (3300); //Guess that other un-supported architectures will be running a 3.3V!
#endif
}Function Introduction: float readDCCurrent(int Pin) ,this function is used to measure the DC current. float readACCurrent(int Pin) , this function is used to measure the AC current, and it returns the RMS of AC current. You should use one of them according to the measured current. Do not use both of them at the same time.
 For any questions/advice/cool ideas to share, please visit DFRobot Forum.
For any questions/advice/cool ideas to share, please visit DFRobot Forum.
- Documents
 shopping from dfrobot store or dfrobot distributor.
shopping from dfrobot store or dfrobot distributor.