Arduino_I2C_to_GPIO_Module_(SKU_DFR0013)
Angelo edited this page Sep 21, 2016
·
3 revisions
 when arduino is used for robots or interactive media, digital io port is always found not enough? iic now turn i / o modules to help you solve the problem, arduino only two data lines (scl-analog pin5, sda-analog pin4) and iic can transfer i / o module communication, to convert the 16 digital io ports, read-write. 8 simultaneous parallel modules, each module can be set to address.
when arduino is used for robots or interactive media, digital io port is always found not enough? iic now turn i / o modules to help you solve the problem, arduino only two data lines (scl-analog pin5, sda-analog pin4) and iic can transfer i / o module communication, to convert the 16 digital io ports, read-write. 8 simultaneous parallel modules, each module can be set to address.
- Module power supply: +5 V
- 16 Digital IO port comes with internal pull-up
- Can be set to eight addresses (address range of 0x20 ~ 0x27)
- 8 modules simultaneously in parallel (IIC bus need to pull together)
- Module Size: 42x40mm
/******************************************************************************
Test Program for the 12C PCA9555 Board part number DFR0013 IIC TO GPIO module from dfrobot.com
16 outputs that I used to drive this relay board made in Bulgaria
http://www.denkovi.com/product/21/16-relay-board-for-your-pic-avr-project-12v.html
it's a great little expansion board that can be used to drive LEDs or anything you want.
made by peter@testelectronics.com
January 07th 2011
My biggest problem was figuring out the I2C address of the PCA9555.
If there are no jumpers the address is 1 0 0 '1 1 1'
Jumpers make the address 1 0 0 '0 0 0'. This is opposite of what I expected.
******************************************************************************/
#include <Wire.h>
// with no jumpers the full address is 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 A2 A1 A0 0x27 is the default address for the DFR0013 board with no jumpers.
#define PCA9555 0x27 // 0x27 is default address for the DFR0013 board with no jumpers.
// 0x20 is address for the DFR0013 board with all jumpers.
// COMMAND BYTE TO REGISTER RELATIONSHIP FROM PCA9555 DATA SHEET
// At reset, the device's ports are inputs with a high value resistor pull-ups to VDD
// If relays turning on during power up are a problem. Add a pull down resistor to each relay transistor base.
#define IN_P0 0x00 // Read Input port0
#define IN_P1 0x01 // Read Input port1
#define OUT_P0 0x02 // Write Output port0
#define OUT_P1 0x03 // Write Output port1
#define INV_P0 0x04 // Input Port Polarity Inversion port0 if B11111111 is written input polarity is inverted
#define INV_P1 0x05 // Input Port Polarity Inversion port1 if B11111111 is written input polarity is inverted
#define CONFIG_P0 0x06 // Configuration port0 configures the direction of the I/O pins 0 is output 1 is input
#define CONFIG_P1 0x07 // Configuration port1 configures the direction of the I/O pins 0 is output 1 is input
#define PAUSE 200
void setup()
{
Wire.begin(PCA9555); // join i2c bus (address optional for master) tried to get working
write_io (CONFIG_P0, B00000000); //defines all pins on Port0 are outputs
write_io (CONFIG_P1, B00000000); //defines all pins on Port1 are outputs
write_io (OUT_P0, B00000000); //clears all relays
write_io (OUT_P1, B00000000); //clears all relays
delay (PAUSE);
}
void loop()
{
write_io (OUT_P0, B00000001);
delay (PAUSE);
write_io (OUT_P0, B00000010);
delay (PAUSE);
write_io (OUT_P0, B00000100);
delay (PAUSE);
write_io (OUT_P0, B00001000);
delay (PAUSE);
write_io (OUT_P0, B00010000);
delay (PAUSE);
write_io (OUT_P0, B00100000);
delay (PAUSE);
write_io (OUT_P0, B01000000);
delay (PAUSE);
write_io (OUT_P0, B10000000);
delay (PAUSE);
write_io (OUT_P0, B00000000);
write_io (OUT_P1, B00000001);
delay (PAUSE);
write_io (OUT_P1, B00000010);
delay (PAUSE);
write_io (OUT_P1, B00000100);
delay (PAUSE);
write_io (OUT_P1, B00001000);
delay (PAUSE);
write_io (OUT_P1, B00010000);
delay (PAUSE);
write_io (OUT_P1, B00100000);
delay (PAUSE);
write_io (OUT_P1, B01000000);
delay (PAUSE);
write_io (OUT_P1, B10000000);
delay (PAUSE);
write_io (OUT_P1, B00000000);
}
void write_io(int command, int value)
{
Wire.beginTransmission(PCA9555);
Wire.send(command),Wire.send(value);
Wire.endTransmission();
}
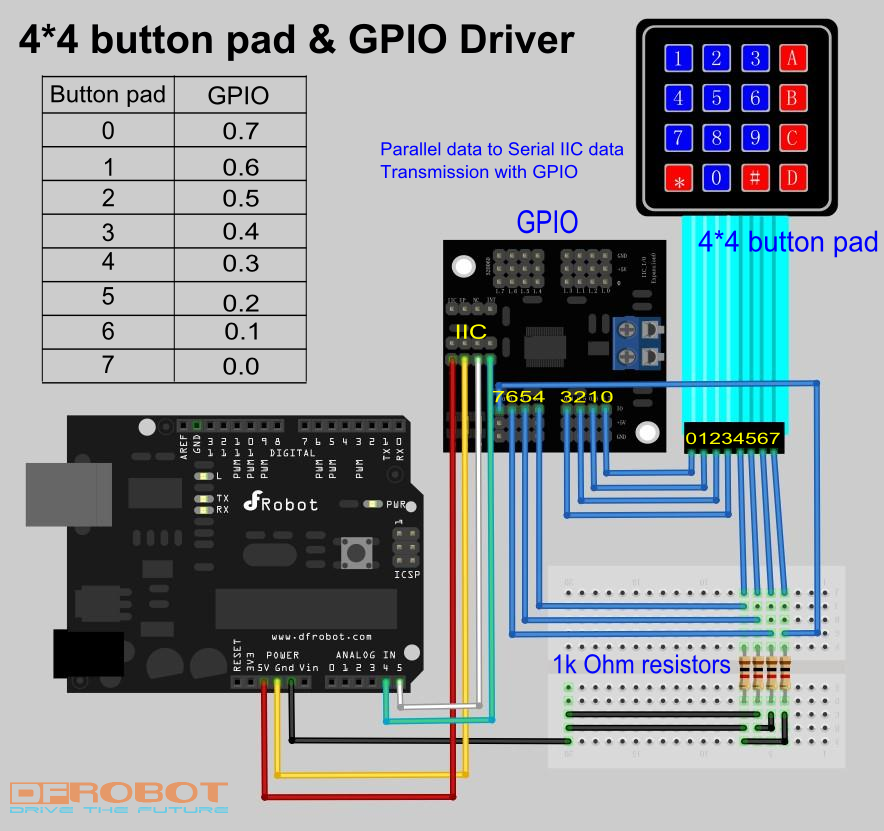
Let's see a practical example: Driving a 4*4 button pad with GPIO.
/*
Hardware preparation: a 4*4 button pad, a GPIO, 4 1k Ohm resistors.
sample code for Sealed membrane 4*4 button pad with sticker, it outputs the ASCII code for keys on the pad.
In this sample, to save the I/O port on Arduino board, we use a IIC-GPIO modulo (SKU:DFR0013). It transform the
IIC port on the Arduino board into GPIO I/O port.For more details, please turn to this page:
http://www.dfrobot.com/wiki/index.php?title=Arduino_I2C_to_GPIO_Module_(SKU:DFR0013)#Discussion
The general working principle of this key pad is a 4*4 matrix. The sample code scans the 4*4 matrix in a short time
and determines whether there is a signal input( pression on the keypad).
Before reading this sample code, you'd better have a look at the sample connection pic. You may wonder why there are
four resistors. This is because that if there are no such resistors, the data analogRead() gets will be a stochastic value
between 0-1023. It will be impossible to determine whether the connection is made by pressing the button on the key pad.
*/
/*
Support: Arduino 1.0 or lower version
Author: Sheng Kaiyu
Editor: Michael
from DFrobot, Shanghai, China
Date: 2012/3/13
*/
#include <Wire.h>
#define PCA9555 0x20 // address for PCA9555
#define OUT_P0 0x02 // Write Output port0
#define CONFIG_P0 0x06 // Configuration port0 configures the direction of the I/O pins, 0 is output, 1 is input
#define IN_P0 0x00 //Read Input port0
#if defined(ARDUINO) && ARDUINO >= 100
#define printIIC(args) Wire.write((uint8_t)args)
#define readIIC() Wire.read()
#else
#define printIIC(args) Wire.send(args)
#define readIIC() Wire.receive()
#endif
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Wire.begin(PCA9555); // join i2c bus (address optional for master) tried to get working
write_io (CONFIG_P0, B00001111); //define port 0.7-0.4 as output, 0.3-0.0 as input
}
void loop()
{
unsigned char key; // read and output once until the next pression
key=readdata();
if (key!='E')
{Serial.println(key);}
delay(100); // to avoid interruption
while (readdata()==key)
{}
}
unsigned char readdata(void) //main read function
{
int input=128; //binary 10000000, set pin 0.7 HIGH
for (int i=0;i<4;i++) //for loop
{
write_io (OUT_P0, input);
unsigned int temp=0x8; //temporary integer, binary 1000, to compare with gpio_read() function and determine pression
for (int j=0;j<4;j++)
{
if (gpio_read(PCA9555)==temp)
{ return outputchar(i,j);} // output the char
temp=temp>>1 ; // shift right
}
input=input>>1; //shift right, set the next pin HIGH, set previous one LOW
}
return 'E'; // if no button is pressed, return E
}
void write_io(int command, int value) //write into register
{
Wire.beginTransmission(PCA9555); //begin transmission
printIIC(command); //which register
printIIC(value); //write value
Wire.endTransmission(); //end transmission
}
unsigned int gpio_read(int address) //read from pin 0.3 ~ 0.0
{
int data = 0;
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
printIIC(IN_P0); // warning: this may be a bug in Arduino 1.0. transform 0x00 (input register) into byte 0, otherwise this compiler will return error
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
Wire.requestFrom(address, 1);
if (Wire.available())
{
data = readIIC( )&0x0F ; // read lower 4 bit 0.3 ~ 0.0
}
Wire.endTransmission();
return data;
}
unsigned char outputchar(int i, int j) // output chars on the pad
{
if (i==0)
{ switch (j)
{case 0:
return '1'; break;
case 1:
return '2'; break;
case 2:
return '3'; break;
case 3:
return 'A'; break;
}
}
if (i==1)
{ switch (j)
{case 0:
return '4'; break;
case 1:
return '5'; break;
case 2:
return '6'; break;
case 3:
return 'B'; break;
}
}
if (i==2)
{ switch (j)
{case 0:
return '7'; break;
case 1:
return '8'; break;
case 2:
return '9'; break;
case 3:
return 'C'; break;
}
}
if (i==3)
{ switch (j)
{case 0:
return '*'; break;
case 1:
return '0'; break;
case 2:
return '#'; break;
case 3:
return 'D'; break;
}
}
} shopping arduino i2c to gpio module (sku:dfr0013)
category: Product Manual category: DFR Series category: Modules category: Source category: Diagram
shopping arduino i2c to gpio module (sku:dfr0013)
category: Product Manual category: DFR Series category: Modules category: Source category: Diagram